Opportunity enters Marathon Valley
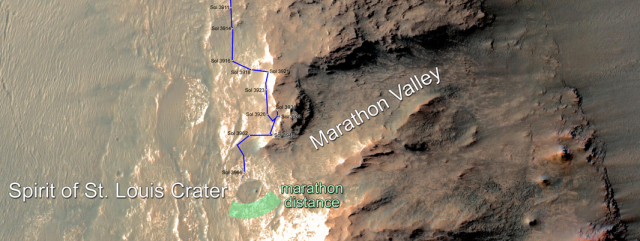
For the John Batchelor Show tonight John and I taped this afternoon a two-segment interview with geologist Bill Farrand, who is part of the science team for Opportunity. The image above shows Opportunity’s recent travels as well as its next target. (Click on the image for the full resolution image.) Assuming the rover’s memory problems don’t get worse and Congress decides to reverse the decision of the Obama administration to end all funding for Opportunity, the scientists hope to take the rover east into Marathon Valley, a very distinct break in the rim of Endeavour Crater.
Whether they will continue east into the crater itself Bill could not say. Some scientists have been pushing for that eventual goal, while others would prefer to do more research along the rim.
What is interesting about Marathon Valley is that it takes the rover deep into the crater’s rim. Previously Opportunity has been limited to exploring the rim’s outer edges, since the rim itself is generally too rugged for the rover to traverse.
For the John Batchelor Show tonight John and I taped this afternoon a two-segment interview with geologist Bill Farrand, who is part of the science team for Opportunity. The image above shows Opportunity’s recent travels as well as its next target. (Click on the image for the full resolution image.) Assuming the rover’s memory problems don’t get worse and Congress decides to reverse the decision of the Obama administration to end all funding for Opportunity, the scientists hope to take the rover east into Marathon Valley, a very distinct break in the rim of Endeavour Crater.
Whether they will continue east into the crater itself Bill could not say. Some scientists have been pushing for that eventual goal, while others would prefer to do more research along the rim.
What is interesting about Marathon Valley is that it takes the rover deep into the crater’s rim. Previously Opportunity has been limited to exploring the rim’s outer edges, since the rim itself is generally too rugged for the rover to traverse.