The monthly update by NOAA of the solar cycle is out, showing the sunspot activity for the Sun in October, As I do every month, I am posting it here, with annotations to give it context.
Despite the appearance last month of the largest sunspot in almost a quarter century, the number of sunspots in October dropped significantly, bringing overall activity back to levels seen in 2012, prior to the second peak in the solar maximum. If things go as expected (not something I would bet much money on), the overall ramp down of sunspot activity should now continue over the next few years. There will obviously be jumps periodically, but the general output of sunspots should steadily decline.
I also want to reiterate what I noted last month, that the 2009 prediction of the solar scientist community is looking better and better with time. Other than over-estimating the total activity somewhat while missing the dip between the two peaks, their overall curve, indicated by the red line, is reasonably close to what has actually happened.
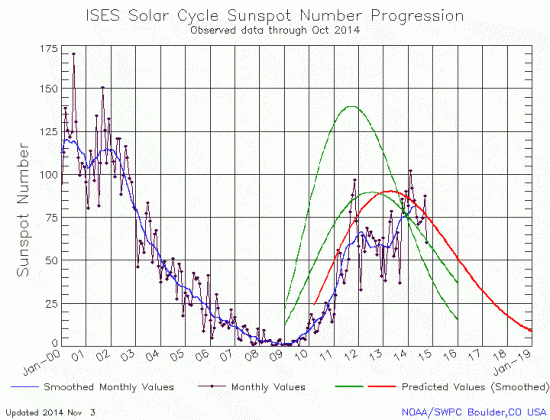
The graph above has been modified to show the predictions of the solar science community. The green curves show the community’s two original predictions from April 2007, with half the scientists predicting a very strong maximum and half predicting a weak one. The red curve is their revised May 2009 prediction.






