Tag: science
The universe’s oldest water
The next Mars rover will land at Gale Crater
The next Mars rover will land at Gale Crater.
The car-sized Mars Science Laboratory, or Curiosity, is scheduled to launch late this year and land in August 2012. The target crater spans 96 miles (154 kilometers) in diameter and holds a mountain rising higher from the crater floor than Mount Rainier rises above Seattle. Gale is about the combined area of Connecticut and Rhode Island. Layering in the mound suggests it is the surviving remnant of an extensive sequence of deposits. The crater is named for Australian astronomer Walter F. Gale. . . . The portion of the crater where Curiosity will land has an alluvial fan likely formed by water-carried sediments. The layers at the base of the mountain contain clays and sulfates, both known to form in water.
More here, including images of landing site.
The next Mars rover will land at Gale Crater.
The car-sized Mars Science Laboratory, or Curiosity, is scheduled to launch late this year and land in August 2012. The target crater spans 96 miles (154 kilometers) in diameter and holds a mountain rising higher from the crater floor than Mount Rainier rises above Seattle. Gale is about the combined area of Connecticut and Rhode Island. Layering in the mound suggests it is the surviving remnant of an extensive sequence of deposits. The crater is named for Australian astronomer Walter F. Gale. . . . The portion of the crater where Curiosity will land has an alluvial fan likely formed by water-carried sediments. The layers at the base of the mountain contain clays and sulfates, both known to form in water.
More here, including images of landing site.
The budget battle over resuming production of nuclear fuel for unmanned space missions heats up
The budget battle over resuming production of nuclear fuel for unmanned space missions heats up.
The budget battle over resuming production of nuclear fuel for unmanned space missions heats up.
The journal Science finally admits things have not gotten warmer in the past decade
The journal Science finally admits things have not gotten warmer in the past decade.
The explanation provided, that recent volcanic eruptions cooled a warming earth, might be true, though the conclusions are based not so much on data but on climate computer models, a fact that leaves me somewhat skeptical. Nonetheless, what is significant to me about this article is that Science — which has been decidedly in the global warming political camp for years and has frequently lambasted scientists who suggested the climate’s warming has slowed or even stopped in the past decade — has now been forced to admit that the warming has stopped. That they feel compelled to push the global warming threat in the same sentence only reveals their continuing scientific bias.
The journal Science finally admits things have not gotten warmer in the past decade.
The explanation provided, that recent volcanic eruptions cooled a warming earth, might be true, though the conclusions are based not so much on data but on climate computer models, a fact that leaves me somewhat skeptical. Nonetheless, what is significant to me about this article is that Science — which has been decidedly in the global warming political camp for years and has frequently lambasted scientists who suggested the climate’s warming has slowed or even stopped in the past decade — has now been forced to admit that the warming has stopped. That they feel compelled to push the global warming threat in the same sentence only reveals their continuing scientific bias.
A new image from Dawn
A new image of Vesta from Dawn.
A new image of Vesta from Dawn.
The shuttle Atlantis has landed, ending the shuttle program
The shuttle Atlantis has landed, ending the shuttle program.
The shuttle Atlantis has landed, ending the shuttle program.
The sun, climate change, and censorship
The chief of CERN has prohibited its scientists from drawing any conclusions from a major experiment that appears to prove that solar activity and the resulting ebb and flow of cosmic rays has a direct effect on the climate.
Two points:
First, the results described provide strong evidence that the sun is a much more important component in climate change than any climate model has previously predicted. These results could help explain the Little Ice Age, which took place around 1700 at exactly the same time the sun became very quiet and stopped producing sunspots for decades. They could explain the Medieval Warm Period around 1000 AD, when cosmic ray activity declined (which also suggests the sun become more active) and the earth apparently warmed. And they might very well even explain the recent cooling during the past decade, which also took place during a period of solar inactivity and a comparable increase in cosmic ray activity.
» Read more
A new study finds that just looking at the American flag makes one more prone to support the Republican Party
A new study finds that just looking at the American flag makes one more prone to support the Republican party.
I have doubts about these results. Nonetheless, the research does sort of confirm the earlier study from Harvard that suggested that patriotism and celebrating the Fourth of July tended to make people favor the Republican party over the Democratic party. In both cases, these results really tell us a great deal about the perception people have of both parties. It is not hard for people to imagine modern Democrats as almost being hostile to America and its founding principles.
A new study finds that just looking at the American flag makes one more prone to support the Republican party.
I have doubts about these results. Nonetheless, the research does sort of confirm the earlier study from Harvard that suggested that patriotism and celebrating the Fourth of July tended to make people favor the Republican party over the Democratic party. In both cases, these results really tell us a great deal about the perception people have of both parties. It is not hard for people to imagine modern Democrats as almost being hostile to America and its founding principles.
A flag in the dust
Bumped: I posted this essay last July 20th on the anniversary of the Apollo 11 landing on the moon. I think it is worth rereading again, even as the shuttle is about to return to Earth for the last time.
Today, July 20th, is the anniversary of the Apollo 11 landing on the Moon, the first time ever that a human being arrived on another planet. Americans love to celebrate this event, as it symbolizes one of the finest moments in our history, when we set out to achieve something truly great and noble and succeeded far better than we could have imagined. Not only did we get to the Moon as promised, over the next three and a half years we sent another five missions, each with increasingly sophisticated equipment, each sent to explore some increasingly alien terrain. Forty-plus years later, no one has come close to matching this achievement, a fact that emphasizes how difficult it was for the United States to accomplish it.
There is one small but very important detail about the Apollo 11 mission, however, that most Americans are unaware of. In mounting the American flag, the astronauts found the lunar surface much harder than expected. They had a great deal of trouble getting the flagpole into the ground. As Andrew Chaikin wrote in his book, A Man on the Moon, “For a moment it seemed the flag would fall over in front of a worldwide audience, but at last the men managed to steady it.” Then Armstrong took what has become one of the world’s iconic images, that of Buzz Aldrin standing on the lunar surface saluting the flag of the United States of America.

What people don’t know, however, is that when Armstrong and Aldrin blasted off from the lunar surface, the blast wave from the Lunar Module’s rocket knocked the flag over. As Chaikin also wrote, “Outside, a spray of gold foil and debris from the descent stage flew away in all directions. The flag toppled to the dust.”
Thus, for the last four decades this American flag, shown so proudly unfurled on the surface of the Moon, has actually been lying unceremoniously on the ground, in the lunar dust.
It might actually be possible to see this, though the photos at this time remain unclear and quite blurry.
» Read more
Hubble has discovered a fourth moon orbiting Pluto
Hubble has discovered a fourth moon orbiting Pluto.
Hubble has discovered a fourth moon orbiting Pluto.
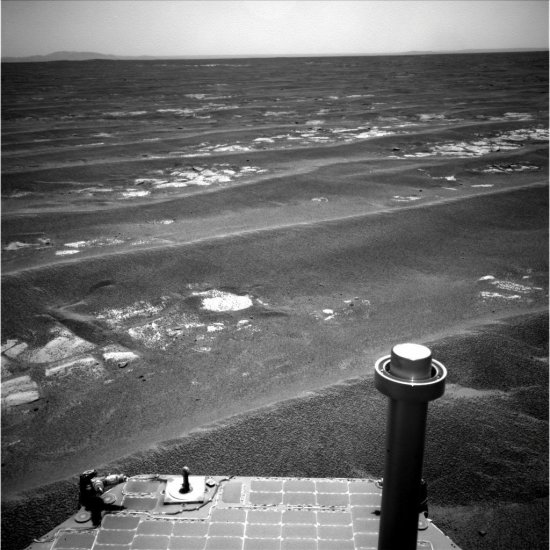
Opportunity’s journey on Mars tops 20 miles
On July 17 the Mars rover Opportunity passed the twenty mile mark on its now seven year journey on Mars. The image below was taken on that day. In the distance, now only about 4,000 feet away, can be seen the rim of Endeavour Crater, fourteen miles wide. Opportunity has been traveling toward that crater now since 2008.
With the rover able to travel about 300 to 500 feet each sol, it should be reaching the crater’s rim sometime in the next few weeks.

The dying NASA astrophysics program
The dying NASA astrophysics program.
With support from President Barack Obama, the agency’s Earth science budget is at an all-time high. Over the next four months, the planetary science division is due to launch three major missions: to the Moon, to Mars and to Jupiter. And the heliophysics division plans to send a probe plunging into the blistering atmosphere of the Sun, closer than ever before. But because the overall NASA science budget is relatively flat, something had to give. Since 2008, astrophysics funding has plunged relative to other NASA science and relative to physics and astronomy funding at other agencies.
The dying NASA astrophysics program.
With support from President Barack Obama, the agency’s Earth science budget is at an all-time high. Over the next four months, the planetary science division is due to launch three major missions: to the Moon, to Mars and to Jupiter. And the heliophysics division plans to send a probe plunging into the blistering atmosphere of the Sun, closer than ever before. But because the overall NASA science budget is relatively flat, something had to give. Since 2008, astrophysics funding has plunged relative to other NASA science and relative to physics and astronomy funding at other agencies.
Japanese tsunami set record at 132.5 feet high
The March 11th Japanese tsunami was the highest on record, 132.5 feet high.
The March 11th Japanese tsunami was the highest on record, 132.5 feet high.
Vesta, sharp and clear
Some good news: Dawn has returned its first sharp close-up image of Vesta.
The image to below the fold is to me a relief, as it shows that the spacecraft’s camera is fine and that my engineering friends were correct in telling me so. Forgive me for being a skeptical and nervous reporter.
» Read more
NASA to announce on Friday the landing site of Curiousity, the next Mars rover
NASA to announce on Friday the landing site of Curiousity, the next Mars rover.
NASA to announce on Friday the landing site of Curiousity, the next Mars rover.
The U.S. and the rising Russian space program
The Russians yesterday successfully launched their first space telescope since the fall of the Soviet Union. Here is a Google translation of a Russian article describing Spektr-R’s research goals:
[Spektr-R is] designed to study galaxies and quasars in the radio, the study of black holes and neutron stars in the Milky Way, as well as the regions immediately adjacent to the massive black holes. In addition, using the observatory, scientists expect to receive information about pulsars and the interstellar plasma. It is planned that the “Spektr-R” will work in orbit for at least 5 years.
Though this particular space telescope is probably not going to rewrite the science of astrophysics, its launch is historically significant. It indicates that Russia has just about recovered from the seventy-plus years of bankrupt communist rule that ended in 1990.
» Read more
Nearly one-fourth of the people polled asserted that they would give up sex if it meant that they could avoid a PowerPoint presentation.
Now here’s a useful data point: A new poll finds that nearly one-fourth of those polled would give up sex if it meant that they could avoid a PowerPoint presentation.
Now here’s a useful data point: A new poll finds that nearly one-fourth of those polled would give up sex if it meant that they could avoid a PowerPoint presentation.
Dawn enters orbit around Vesta
Dawn enters orbit around Vesta.
Dawn enters orbit around Vesta.
Wither the Arctic Icecap?
In a paper published today in Geophysical Research Letters, climate scientists have estimated the distribution and trends for the Arctic icecap from 1980 through March 2011. What they have found is a significant decline in older ice on top of an overall declining trend that showed a strong but partial recovery since 2008. The graph below, from the paper, illustrates clearly these trends.
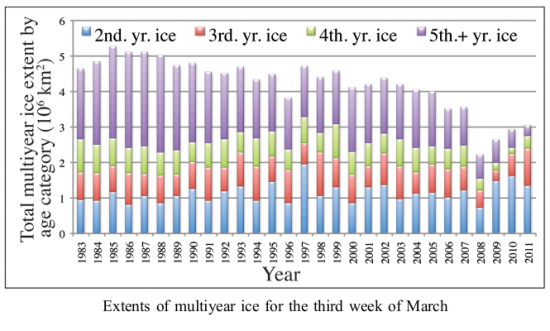
What this means for the icecap itself remains unclear. As the scientists themselves note in their conclusion:
» Read more
Bill Nye the Science Guy explains caves
Environmental terrorists destroy genetically modified test plots of wheat and potatoes
Leftwing civility: Environmental terrorists destroy genetically modified test plots of wheat and potatoes.
On the night of 9 July, half a dozen masked attackers overpowered the security guard watching over test fields in Gross Lüsewitz, near Rostock. They then destroyed a field of wheat resistant to fungal diseases and a field of potatoes engineered to produce cyanophycin, an amino acid polymer that could potentially be used to make plastics. . . . Two nights later, a dozen attackers threatened guards with pepper spray and bats at a demonstration garden in Üplingen, in the state of Saxony-Anhalt. They destroyed a field of potatoes and trampled wheat and maize.
Leftwing civility: Environmental terrorists destroy genetically modified test plots of wheat and potatoes.
On the night of 9 July, half a dozen masked attackers overpowered the security guard watching over test fields in Gross Lüsewitz, near Rostock. They then destroyed a field of wheat resistant to fungal diseases and a field of potatoes engineered to produce cyanophycin, an amino acid polymer that could potentially be used to make plastics. . . . Two nights later, a dozen attackers threatened guards with pepper spray and bats at a demonstration garden in Üplingen, in the state of Saxony-Anhalt. They destroyed a field of potatoes and trampled wheat and maize.
Cats cause global warming
How did Al Gore miss this important fact? Cats cause global warming!
How did Al Gore miss this important fact? Cats cause global warming!
Bad news for climate modelers
A new analysis of the orbits of Ceres and Vesta says that in a surprisingly short time those orbits become chaotic and therefore unpredictable. More significantly, those orbits interact with the Earth’s and also make its long term orbit chaotic and unpredictable. From the abstract:
Although small, Ceres and Vesta gravitationally interact together and with the other planets of the Solar System. Because of these interactions, they are continuously pulled or pushed slightly out of their initial orbit. Calculations show that, after some time, these effects do not average out. Consequently, the bodies leave their initial orbits and, more importantly, their orbits are chaotic, meaning that we cannot predict their positions. The two bodies also have a significant probability of impacting each other, estimated at 0.2% per billion year. Last but not least, Ceres and Vesta gravitationally interact with the Earth, whose orbit also becomes unpredictable after only 60 million years. This means that the Earth’s eccentricity, which affects the large climatic variations on its surface, cannot be traced back more than 60 million years ago. This is indeed bad news for Paleoclimate studies. [emphasis mine]
The scientists found that it became impossible to calculate the orbits of the two largest asteroids after only several ten thousand years. They also found that “numerous asteroids in the main belt will behave in the same way with . . . much more chaotic behavior than previously thought.” Worse, the possibility of collisions was far higher than ever thought. Ceres and Vesta have a 1 in 500 chance of colliding with each other every billion years, while other asteroids have chances as low as 1 in 1000.
The importance of this discovery, which still needs to be confirmed by other researchers, cannot be understated.
» Read more
Another fuzzy Dawn image?
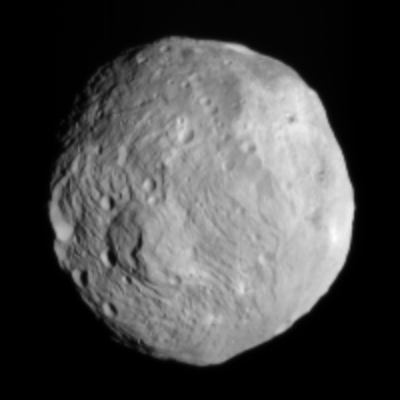

Another image of Vesta from Dawn has been released. This image was taken on July 9 from a distance of 26,000 miles away. It is definitely an improvement over the previous image, with more small details becoming visible. However, I once again wonder about the softness of the image. Look at the limb of the planet. It is soft against the black sky. This is not what one would expect from perfectly focused camera.
Dawn goes into orbit around Vesta next week. We sure learn then for sure if there is a problem with its camera, or whether I am merely being a bit too nervous.
Astronomers have found two new brown dwarf stars only 15 and 18 light years away
Astronomers have found two new brown dwarf stars only 15 and 18 light years away.
Most brown dwarfs have reached surface temperatures below the “oven temperature” of about 500 Kelvin (about 230 degrees Celsius), may be even as cool as the temperature at the surface of the Earth. The search for these elusive neighbours of the Sun is currently in full swing. It cannot be excluded that ultracool brown dwarfs surround us in similar high numbers as stars and that our nearest known neighbour will soon be a brown dwarf rather than Proxima Centauri.
Astronomers have found two new brown dwarf stars only 15 and 18 light years away.
Most brown dwarfs have reached surface temperatures below the “oven temperature” of about 500 Kelvin (about 230 degrees Celsius), may be even as cool as the temperature at the surface of the Earth. The search for these elusive neighbours of the Sun is currently in full swing. It cannot be excluded that ultracool brown dwarfs surround us in similar high numbers as stars and that our nearest known neighbour will soon be a brown dwarf rather than Proxima Centauri.
Second ARTEMIS space probe about to enter lunar orbit
The second ARTEMIS space probe will enter lunar orbit on Sunday.
“With two spacecraft orbiting in opposite directions, we can acquire a full 3-D view of the structure of the magnetic fields near the moon and on the lunar surface,” said Vassilis Angelopoulos, principal investigator for the THEMIS and ARTEMIS missions and a professor of space physics at UCLA. “ARTEMIS will be doing totally new science, as well as reusing existing spacecraft to save a lot of taxpayer money.”
The second ARTEMIS space probe will enter lunar orbit on Sunday.
“With two spacecraft orbiting in opposite directions, we can acquire a full 3-D view of the structure of the magnetic fields near the moon and on the lunar surface,” said Vassilis Angelopoulos, principal investigator for the THEMIS and ARTEMIS missions and a professor of space physics at UCLA. “ARTEMIS will be doing totally new science, as well as reusing existing spacecraft to save a lot of taxpayer money.”
White dwarf stars in a dance of death
White dwarf stars in a dance of death.
[The binary pair of] white dwarfs are so near they make a complete orbit in just 13 minutes, but they are gradually slipping closer together. About 900,000 years from now – a blink of an eye in astronomical time – they will merge and possibly explode as a supernova. By watching the stars converge, scientists will test both Einstein’s general theory of relativity and the origin of some peculiar supernovae.
The two white dwarfs are circling at a bracing speed of 370 miles per second (600 km/s), or 180 times faster than the fastest jet on Earth. “I nearly fell out of my chair at the telescope when I saw one star change its speed by a staggering 750 miles per second in just a few minutes,” said Smithsonian astronomer Warren Brown, lead author of the paper reporting the find.
The brighter white dwarf contains about a quarter of the Sun’s mass compacted into a Neptune-sized ball, while its companion has more than half the mass of the Sun and is Earth-sized. A penny made of this white dwarf’s material would weigh about 1,000 pounds on Earth. Their mutual gravitational pull is so strong that it deforms the lower-mass star by three percent. If the Earth bulged by the same amount, we would have tides 120 miles high. [emphasis mine]
White dwarf stars in a dance of death.
[The binary pair of] white dwarfs are so near they make a complete orbit in just 13 minutes, but they are gradually slipping closer together. About 900,000 years from now – a blink of an eye in astronomical time – they will merge and possibly explode as a supernova. By watching the stars converge, scientists will test both Einstein’s general theory of relativity and the origin of some peculiar supernovae.
The two white dwarfs are circling at a bracing speed of 370 miles per second (600 km/s), or 180 times faster than the fastest jet on Earth. “I nearly fell out of my chair at the telescope when I saw one star change its speed by a staggering 750 miles per second in just a few minutes,” said Smithsonian astronomer Warren Brown, lead author of the paper reporting the find.
The brighter white dwarf contains about a quarter of the Sun’s mass compacted into a Neptune-sized ball, while its companion has more than half the mass of the Sun and is Earth-sized. A penny made of this white dwarf’s material would weigh about 1,000 pounds on Earth. Their mutual gravitational pull is so strong that it deforms the lower-mass star by three percent. If the Earth bulged by the same amount, we would have tides 120 miles high. [emphasis mine]
Dawn nears Vesta
I’ve posted earlier about Dawn’s approach to Vesta. However, in looking at the images from Dawn, it dawned on me recently that they seems more fuzzy for what you’d normally expect from a space probe. I am now wondering if there is something fundamentally wrong with Dawn’s camera, causing its images to be slightly out of focus.
I’ve posted earlier about Dawn’s approach to Vesta. However, in looking at the images from Dawn, it dawned on me recently that they seems more fuzzy for what you’d normally expect from a space probe. I am now wondering if there is something fundamentally wrong with Dawn’s camera, causing its images to be slightly out of focus.
The competing extinction theories battle it out
New evidence bolsters the asteroid impact theory of dinosaur extinction 65 million years ago.
I am sure you all thought the cause of the dinosaurs’ extinction — an asteroid impact on the Yucatan peninsula — was settled science. Wrong!
» Read more
Skeleton May Help Solve Mystery of Doomed Franklin Expedition
Starvation, scurvy, or lead poisoning? A skeleton from the 1848 Franklin Expedition to the Arctic may tell scientists what caused the expedition’s destruction.
Starvation, scurvy, or lead poisoning? A skeleton from the 1848 Franklin Expedition to the Arctic may tell scientists what caused the expedition’s destruction.
