Planning Hayabusa-2’s next sample grab on Ryugu
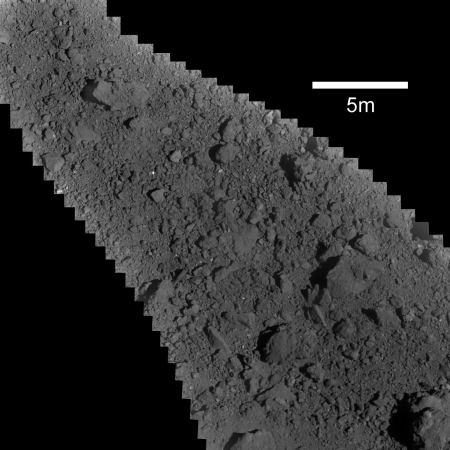
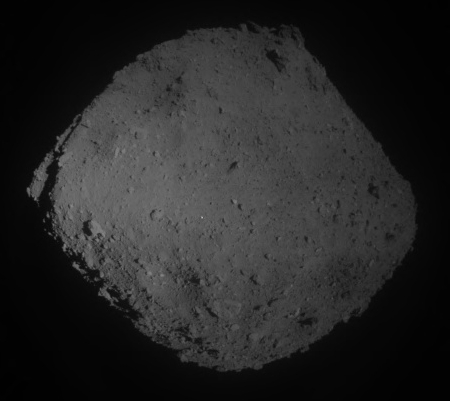
The Hayabusa-2 science team today released a mosaic image created using the images taken during the four close approaches to the site of the man made crater put there by a projectile fired from the spacecraft. The image on the right, reduced and cropped to post here, shows this area, with the white spot being the target they dropped onto the site during the most recent close approach. As they note in their release:
In order to collect this material, we need a second touchdown for which the project has been steadily preparing. At this point, it has not yet been decided whether or not to go ahead with a second touchdown, but here we will introduce our preparations in the “Approach to the second touchdown”.
After the operation to form the artificial crater, the spacecraft descended a total of four times above or near the crater site. These descent operations allowed us to obtain detailed data of the region near the artificial crater. In addition, we succeeded in dropping a target marker in the area close to the artificial crater on May 30. Combined, these operations mean that the situation around the artificial crater is now well understood.
Figure 1 [the image to the right] shows an image taken during the low altitude descent observation operation (PPTD-TM1B) conducted from June 11 – 13. The target marker was captured in the image and you can get a handle on the state of the surface. [emphasis mine]
Unfortunately they do not show us exactly where the man made crater is located in this mosaic. Nor was I able to locate it by comparing today’s image to a previous image that did indicate the location.
The only place that seems acceptable for their touch-and-go sample grab seems to be just above or to the left of the target. Whether this will get them any interior material thrown up during the impact however is unclear.
The Hayabusa-2 science team today released a mosaic image created using the images taken during the four close approaches to the site of the man made crater put there by a projectile fired from the spacecraft. The image on the right, reduced and cropped to post here, shows this area, with the white spot being the target they dropped onto the site during the most recent close approach. As they note in their release:
In order to collect this material, we need a second touchdown for which the project has been steadily preparing. At this point, it has not yet been decided whether or not to go ahead with a second touchdown, but here we will introduce our preparations in the “Approach to the second touchdown”.
After the operation to form the artificial crater, the spacecraft descended a total of four times above or near the crater site. These descent operations allowed us to obtain detailed data of the region near the artificial crater. In addition, we succeeded in dropping a target marker in the area close to the artificial crater on May 30. Combined, these operations mean that the situation around the artificial crater is now well understood.
Figure 1 [the image to the right] shows an image taken during the low altitude descent observation operation (PPTD-TM1B) conducted from June 11 – 13. The target marker was captured in the image and you can get a handle on the state of the surface. [emphasis mine]
Unfortunately they do not show us exactly where the man made crater is located in this mosaic. Nor was I able to locate it by comparing today’s image to a previous image that did indicate the location.
The only place that seems acceptable for their touch-and-go sample grab seems to be just above or to the left of the target. Whether this will get them any interior material thrown up during the impact however is unclear.