Capitalsm in space: SpaceX’s first BFR passenger will be Yusaku Maezawa, the owner of Japanese fashion company, shown on the right.
Maezawa began his statement by echoing John Kennedy with these words, “I choose to go to the Moon.” He purchased the entire first flight, and will invite six to eight artists to join him on the flight and ask them to create art afterward inspired by the flight. They are aiming for a launch in 2023.
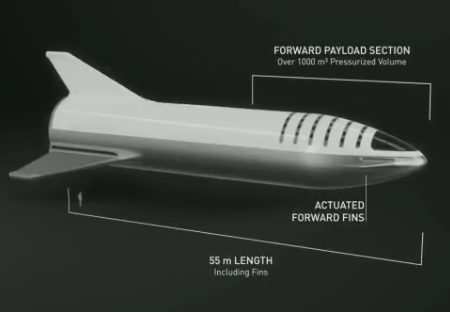
Musk began the presentation tonight with an overview of the status of BFR, noting that they plan unmanned test launches before putting humans on the rocket. The image an the right shows the habitable upper stage.
During the question and answer session after the announcement Musk was asked questions about the present stage of BFR design, and whether it has been finalized. He said they plan “a lot of test flights” and are aiming for first orbital flights in 2 to 3 years, “if things go really well.”
Musk made it clear that Maezawa chose SpaceX for the flight, rather than the other way around. Musk also said that Maezawa was paying them a lot of money for the flight, though they were not going to reveal the amount. Musk did note that the price was not trivial, and that Maezawa has already made a significant deposit. Maezawa had first approached them for a Dragon/Falcon Heavy flight, but because of the limitations of of those spacecraft, they decided it better to go with the bigger rocket.
Musk noted that the first test hops of the upper stage to test its landing capabilities will take place at Boca Chica in Texas. The launch site for the orbital missions is not yet decided.
Musk estimated that the cost for developing BFR is going to probably be around $5 billion, which he also noted rightly is quite small for this kind of project. He also said that right now they are only devoting 5% of SpaceX’s resources to this mission. As they complete the crew Dragon project, they will then begin to shift resources to BFR. He estimated that will happen sometime late next year.
Overall, it strikes me that they really do not have all the details yet worked out, with the rocket or their flight schedule. As Musk openly admitted when asked if they are sure about the schedule, “We are definitely not sure.” This is not necessarily a bad thing, since it is often better to keep an open-mind in planning something this ambitious. At the same time it tells us not to expect any of this to happen, as described.
One final point: Musk at one point said he wants a base on the Moon. “It’s 2018, why don’t we have a base on the Moon?” To me, this was an almost direct dig at NASA’s Gateway/FLOP-G project, which isn’t a base but locks us in lunar orbit. Musk was being very careful to avoid criticizing NASA, his biggest customer, but anyone who knows what is going on will quickly recognize that BFR is in direct competition with SLS/Orion/Gateway.
Based on SpaceX’s history, going from first orbit flight to flying the world’s largest rocket in only ten years, I am very confident that this company could get that first base on the Moon, long before NASA even gets Gateway launched.