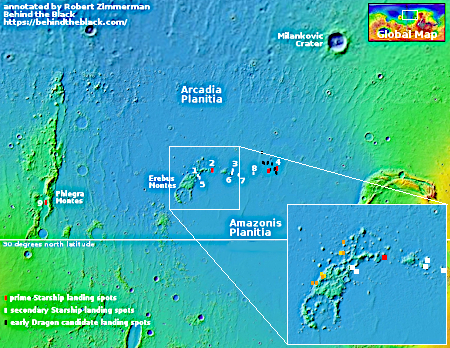
FAA moves forward on its environmental assessment of SpaceX’s proposal to launch Starship/Superheavy from Kennedy Space Center
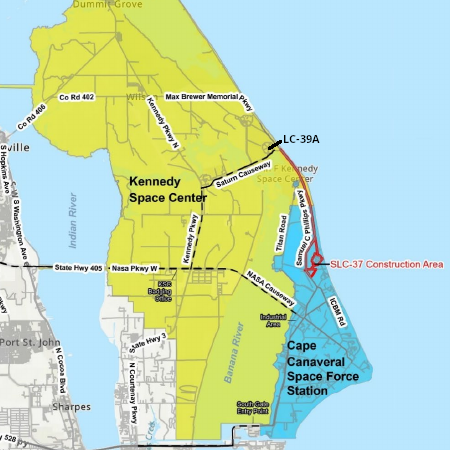
Proposed Starship/Superheavy launchsites at
Kennedy (LC-39A) and Cape Canaveral (SLC-37)
While NASA has already determined that Starship/Superheavy launches from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida will have no significant impact on the environment, the FAA has not yet completed its own environmental impact statement.
Last week it released a preliminary summary [pdf] of its impact statement, revealing that it has reduced its final options to either approving SpaceX’s request to do as many as 44 launches per year, or to reject any changes — the “no action alternative” — which would block all Starship/Superheavy launches at Kennedy.
The overall tone of this summary suggests strongly that the FAA is almost certainly going to approve SpaceX’s request, allowing as many as 44 launches per year from launchpad LC-39A, as shown on the map to the right. As it notes in describing the “no action alternative”:
SpaceX would not launch Starship-Super Heavy from LC-39A. NASA would not develop, implement, or approve agreements with SpaceX associated with Starship-Super Heavy operations at LC-39A. The No Action Alternative would not meet the purpose and need. [emphasis mine]
In other words, rejecting SpaceX’s request would not fulfill the FAA’s obligation to serve the public. It would also not fulfill the FAA’s obligation to serve a fellow government agency, NASA, which has already approved this SpaceX request in a 2019 environmental assessment.
It appears a final decision by the FAA is imminent. A nice summary of this FAA document can be found here, which notes that if approved, it will give SpaceX license approval to launch Starship/Superheavy as much as 146 times per year, from its launchpads at Boca Chica, Kennedy, and Cape Canaveral. Note too that this FAA assessment is independent of the Air Force’s environment assessment, which has already approved 76 launches per year at the SLC-37 launchpad.

Proposed Starship/Superheavy launchsites at
Kennedy (LC-39A) and Cape Canaveral (SLC-37)
While NASA has already determined that Starship/Superheavy launches from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida will have no significant impact on the environment, the FAA has not yet completed its own environmental impact statement.
Last week it released a preliminary summary [pdf] of its impact statement, revealing that it has reduced its final options to either approving SpaceX’s request to do as many as 44 launches per year, or to reject any changes — the “no action alternative” — which would block all Starship/Superheavy launches at Kennedy.
The overall tone of this summary suggests strongly that the FAA is almost certainly going to approve SpaceX’s request, allowing as many as 44 launches per year from launchpad LC-39A, as shown on the map to the right. As it notes in describing the “no action alternative”:
SpaceX would not launch Starship-Super Heavy from LC-39A. NASA would not develop, implement, or approve agreements with SpaceX associated with Starship-Super Heavy operations at LC-39A. The No Action Alternative would not meet the purpose and need. [emphasis mine]
In other words, rejecting SpaceX’s request would not fulfill the FAA’s obligation to serve the public. It would also not fulfill the FAA’s obligation to serve a fellow government agency, NASA, which has already approved this SpaceX request in a 2019 environmental assessment.
It appears a final decision by the FAA is imminent. A nice summary of this FAA document can be found here, which notes that if approved, it will give SpaceX license approval to launch Starship/Superheavy as much as 146 times per year, from its launchpads at Boca Chica, Kennedy, and Cape Canaveral. Note too that this FAA assessment is independent of the Air Force’s environment assessment, which has already approved 76 launches per year at the SLC-37 launchpad.