Next manned Dragon mission to ISS delayed until September 24, 2024
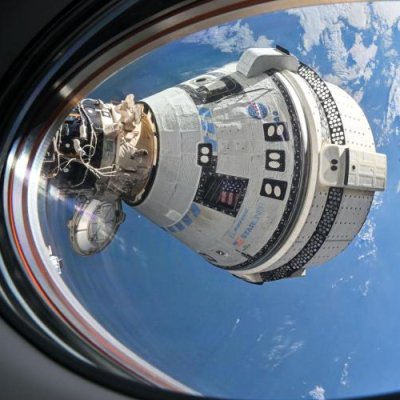
NASA tonight announced that the next manned Dragon mission to ISS has been delayed until September 24, 2024, a pushback of more than a month caused by the thruster issues on Boeing’s Starliner capsule presently docked to the station.
This adjustment allows more time for mission managers to finalize return planning for the agency’s Boeing Crew Flight Test currently docked to the orbiting laboratory. Starliner ground teams are taking their time to analyze the results of recent docked hot-fire testing, finalize flight rationale for the spacecraft’s integrated propulsion system, and confirm system reliability ahead of Starliner’s return to Earth. NASA and Boeing continue to evaluate the spacecraft’s readiness, and no decisions have been made regarding Starliner’s return.
Since both manned capsule use the same port, Starliner must undock before a Dragon can arrive.
The schedule change also eliminates scheduling conflicts with a Soyuz capsule bringing Russian astronauts to the station in mid-September, and will also allow the launch to switch launchpads so as to not conflict with the SpaceX launch of Europa Clipper, scheduled for October 10, 2024 (though that launch remains in doubt due to other problems with the spacecraft itself).
NASA will be holding a briefing on the status of Starliner at 12:30 pm (Eastern) on Wednesday, August 7, 2024.
NASA tonight announced that the next manned Dragon mission to ISS has been delayed until September 24, 2024, a pushback of more than a month caused by the thruster issues on Boeing’s Starliner capsule presently docked to the station.
This adjustment allows more time for mission managers to finalize return planning for the agency’s Boeing Crew Flight Test currently docked to the orbiting laboratory. Starliner ground teams are taking their time to analyze the results of recent docked hot-fire testing, finalize flight rationale for the spacecraft’s integrated propulsion system, and confirm system reliability ahead of Starliner’s return to Earth. NASA and Boeing continue to evaluate the spacecraft’s readiness, and no decisions have been made regarding Starliner’s return.
Since both manned capsule use the same port, Starliner must undock before a Dragon can arrive.
The schedule change also eliminates scheduling conflicts with a Soyuz capsule bringing Russian astronauts to the station in mid-September, and will also allow the launch to switch launchpads so as to not conflict with the SpaceX launch of Europa Clipper, scheduled for October 10, 2024 (though that launch remains in doubt due to other problems with the spacecraft itself).
NASA will be holding a briefing on the status of Starliner at 12:30 pm (Eastern) on Wednesday, August 7, 2024.