First image from Mars of interstellar Comet 3I/Atlas
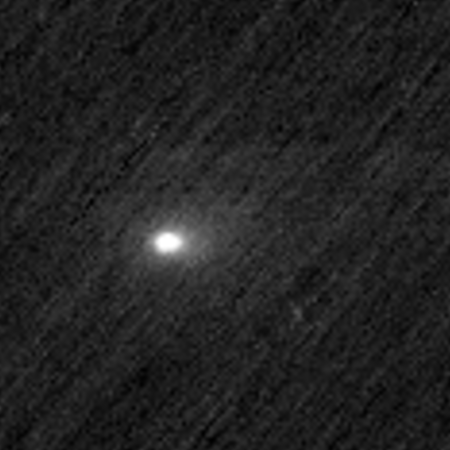
Using the Europe’s Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) presently orbiting Mars, scientists have successfully obtained the first images from Mars of interstellar Comet 3I/Atlas using its Colour and Stereo Surface Imaging System (CaSSIS).
They have compiled a short movie of those images, with one of those pictures to the right, cropped to post here. As expected, the observation was difficult and somewhat limited in the data it could obtain.
CaSSIS could not distinguish the nucleus from the coma, because 3I/ATLAS was too far away. Imaging this kilometre-wide nucleus would have been as impossible as seeing a mobile phone on the Moon from Earth.
But the coma, measuring a few thousand kilometres across, is clearly visible. The coma is created as 3I/ATLAS approaches the Sun. The Sun’s heat and radiation is bringing the comet to life, causing it to release gas and dust, which collects as this halo surrounding the nucleus. The full size of the coma could not be measured by CaSSIS because the brightness of the dust decreases quickly with distance from the nucleus. This means that the coma fades into the noise in the image.
Typically, material from the coma is swept into a long tail, which can grow up to millions of kilometres long as the comet moves closer to the Sun. The tail is much dimmer than the coma. We can’t see the tail in the CaSSIS images, but it may become more visible in future observations as the comet continues to heat up and release more ice.
The science team for Europe’s Mars Express orbiter also attempted to get data of the comet, but have not yet been able to detect it. Both orbiters also tried to get spectroscopy, but no data was obtained because the comet is presently too faint and distant for these instruments.
More observations are planned, not only from these orbiters but also from Europe’s Juice spacecraft on its way to Jupiter but presently in the inner solar system somewhat near the Sun. It will make its observations in November, but won’t be able to transmit the data back until February, after it has gotten more distant from the Sun.
Using the Europe’s Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) presently orbiting Mars, scientists have successfully obtained the first images from Mars of interstellar Comet 3I/Atlas using its Colour and Stereo Surface Imaging System (CaSSIS).
They have compiled a short movie of those images, with one of those pictures to the right, cropped to post here. As expected, the observation was difficult and somewhat limited in the data it could obtain.
CaSSIS could not distinguish the nucleus from the coma, because 3I/ATLAS was too far away. Imaging this kilometre-wide nucleus would have been as impossible as seeing a mobile phone on the Moon from Earth.
But the coma, measuring a few thousand kilometres across, is clearly visible. The coma is created as 3I/ATLAS approaches the Sun. The Sun’s heat and radiation is bringing the comet to life, causing it to release gas and dust, which collects as this halo surrounding the nucleus. The full size of the coma could not be measured by CaSSIS because the brightness of the dust decreases quickly with distance from the nucleus. This means that the coma fades into the noise in the image.
Typically, material from the coma is swept into a long tail, which can grow up to millions of kilometres long as the comet moves closer to the Sun. The tail is much dimmer than the coma. We can’t see the tail in the CaSSIS images, but it may become more visible in future observations as the comet continues to heat up and release more ice.
The science team for Europe’s Mars Express orbiter also attempted to get data of the comet, but have not yet been able to detect it. Both orbiters also tried to get spectroscopy, but no data was obtained because the comet is presently too faint and distant for these instruments.
More observations are planned, not only from these orbiters but also from Europe’s Juice spacecraft on its way to Jupiter but presently in the inner solar system somewhat near the Sun. It will make its observations in November, but won’t be able to transmit the data back until February, after it has gotten more distant from the Sun.