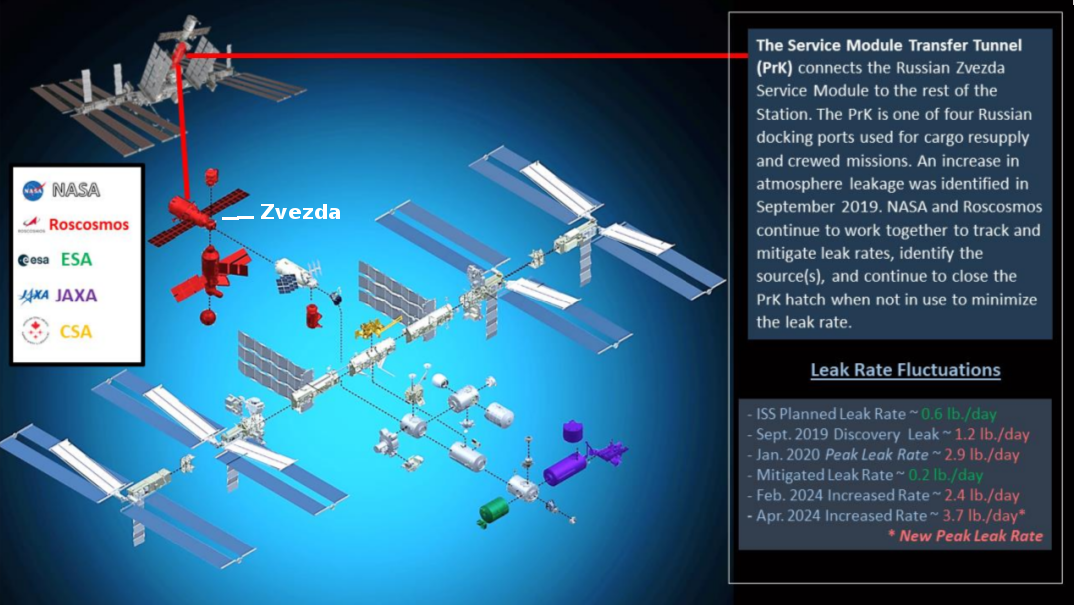
Charon’s surface, completely unlike Pluto

Click for full resolution. For original images go here, here, and here.

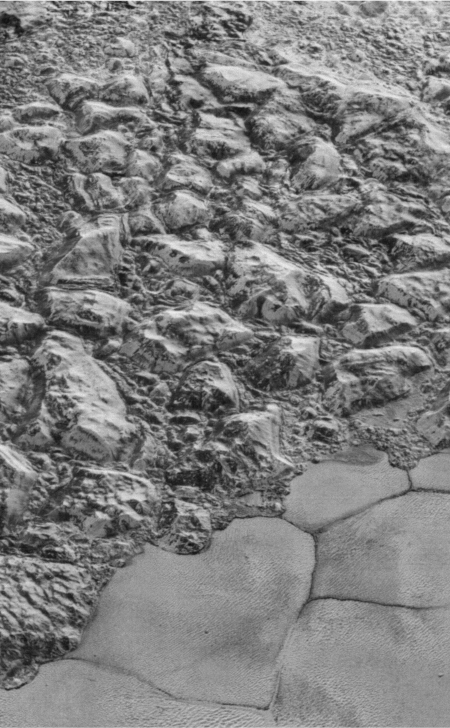
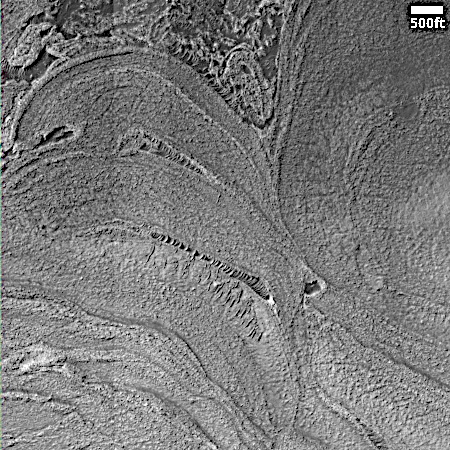
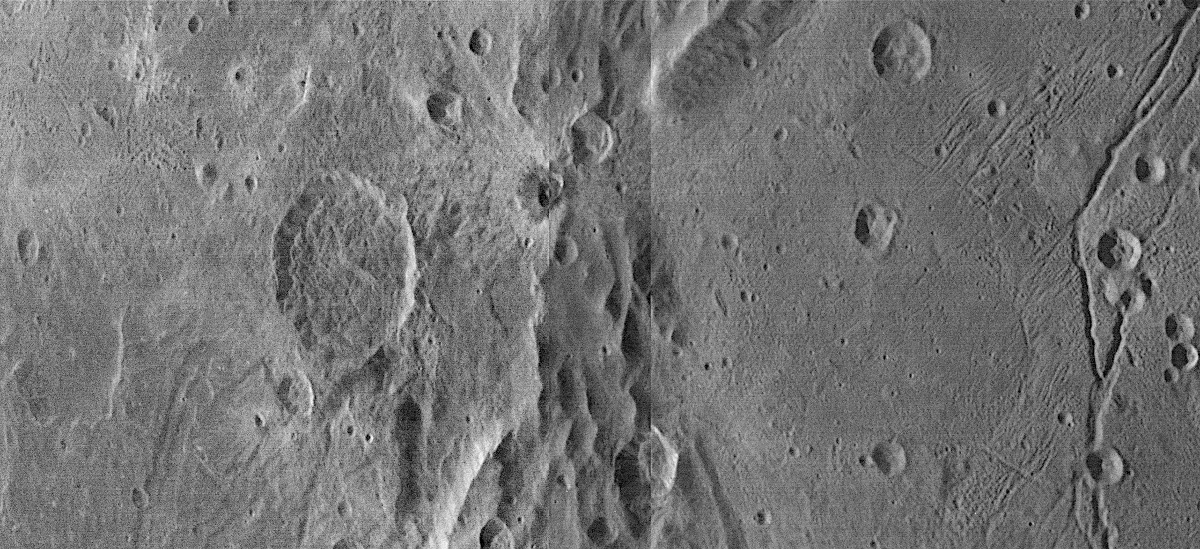
Cool image time! The panorama above, created from three images taken by New Horizons as it began its July 14, 2015 fly-by of the Pluto-Charon double planet system (found here, here, and here), show in close-up one specific swath of Charon cutting across its equatorial regions.
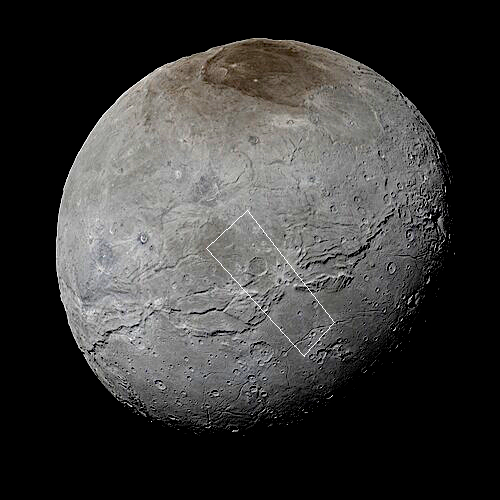
The true color global image of Charon to the right shows the approximate area covered by the panorama above. For scale, Charon has a diameter of about 750 miles, about half that of Pluto. For clarity I have rotated the panorama so that it more closely aligns with the rectangle of global image.
One of the most remarkable discoveries made during New Horizons’ fly-by was how completely different Pluto and Charon appeared, despite their likely formation together at the same time and in the same location of the early solar system. While Pluto had frozen nitrogen seas and water ice mountains floating at the shores, Charon more resembled Mercury, cratered with many large ridges and canyons criss-crossing its service. Both planets appear to be icy, but somehow Charon appears to lack the large differentiated variety of materials seen on Pluto.

Click for full resolution. For original images go here, here, and here.

Cool image time! The panorama above, created from three images taken by New Horizons as it began its July 14, 2015 fly-by of the Pluto-Charon double planet system (found here, here, and here), show in close-up one specific swath of Charon cutting across its equatorial regions.
The true color global image of Charon to the right shows the approximate area covered by the panorama above. For scale, Charon has a diameter of about 750 miles, about half that of Pluto. For clarity I have rotated the panorama so that it more closely aligns with the rectangle of global image.
One of the most remarkable discoveries made during New Horizons’ fly-by was how completely different Pluto and Charon appeared, despite their likely formation together at the same time and in the same location of the early solar system. While Pluto had frozen nitrogen seas and water ice mountains floating at the shores, Charon more resembled Mercury, cratered with many large ridges and canyons criss-crossing its service. Both planets appear to be icy, but somehow Charon appears to lack the large differentiated variety of materials seen on Pluto.