China begins hurried preparations to launch rescue Shenzhou capsule to Tiangong-3
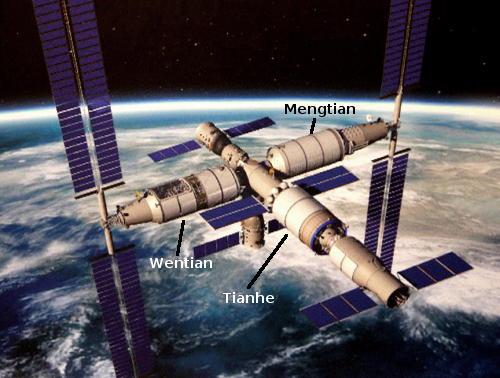
The Tiangong-3 station, as presently configured
According to China’s state run press, it has begun emergency procedures to quickly launch the Shenzhou-22 capsule — originally scheduled to carry the next crew to its Tiangong-3 station in April 2026 — in order to provide the present station crew a lifeboat and a return capsule.
The China Manned Space Agency has started preparations for the launch of an unmanned spacecraft to carry a full cargo load, including provisions for astronauts and equipment for the Tiangong space station, according to a senior engineer. Zhou Yaqiang, who works with the agency’s general technical bureau, told China Central Television on Saturday that all systems involved in the upcoming Shenzhou-22 cargo mission “are busy getting ready for it, testing the rocket and the spaceship and preparing the payloads”.
The Shenzhou-22 spacecraft will be launched in due course to dock with the Tiangong space station, the agency said.
The report provided no details on when this launch would occur, though another Chinese report said getting the rocket (a Long March 2F) and capsule ready in the next 10 to 20 days would be “difficult.”
At the moment, the three astronauts on Tiangong-3 have no lifeboat. Should anything go wrong at the station before that launch they will have no way to get back to Earth, unless they use the damaged Shenzhou-21 capsule still docked to the station. That capsule has cracks in a window, caused by what the Chinese think was an impact from “space debris.” The Chinese have already determined it is not safe for human travel. Thus, using it in an emergency would be a desperate act.
Since the first space station, Salyut-1, was launched and occupied in 1971, this is the first time that a crew has been in space with absolutely no way to get home. The press last year repeatedly claimed the Starliner crew was “stranded” on ISS, but that wasn’t so. They could have always come home on their Starliner craft, as was proven when it returned unmanned with no problems. NASA had simply made the decision to be cautious and wait for the launch of next Dragon to bring them home instead.

The Tiangong-3 station, as presently configured
According to China’s state run press, it has begun emergency procedures to quickly launch the Shenzhou-22 capsule — originally scheduled to carry the next crew to its Tiangong-3 station in April 2026 — in order to provide the present station crew a lifeboat and a return capsule.
The China Manned Space Agency has started preparations for the launch of an unmanned spacecraft to carry a full cargo load, including provisions for astronauts and equipment for the Tiangong space station, according to a senior engineer. Zhou Yaqiang, who works with the agency’s general technical bureau, told China Central Television on Saturday that all systems involved in the upcoming Shenzhou-22 cargo mission “are busy getting ready for it, testing the rocket and the spaceship and preparing the payloads”.
The Shenzhou-22 spacecraft will be launched in due course to dock with the Tiangong space station, the agency said.
The report provided no details on when this launch would occur, though another Chinese report said getting the rocket (a Long March 2F) and capsule ready in the next 10 to 20 days would be “difficult.”
At the moment, the three astronauts on Tiangong-3 have no lifeboat. Should anything go wrong at the station before that launch they will have no way to get back to Earth, unless they use the damaged Shenzhou-21 capsule still docked to the station. That capsule has cracks in a window, caused by what the Chinese think was an impact from “space debris.” The Chinese have already determined it is not safe for human travel. Thus, using it in an emergency would be a desperate act.
Since the first space station, Salyut-1, was launched and occupied in 1971, this is the first time that a crew has been in space with absolutely no way to get home. The press last year repeatedly claimed the Starliner crew was “stranded” on ISS, but that wasn’t so. They could have always come home on their Starliner craft, as was proven when it returned unmanned with no problems. NASA had simply made the decision to be cautious and wait for the launch of next Dragon to bring them home instead.