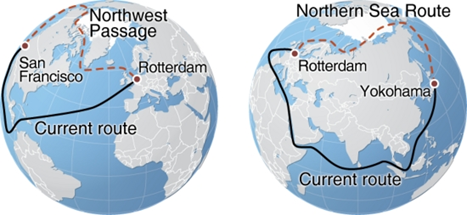
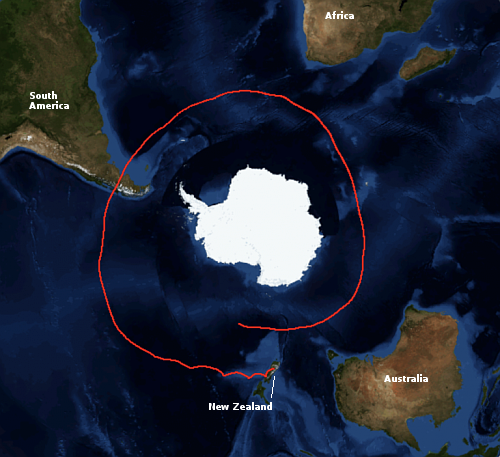
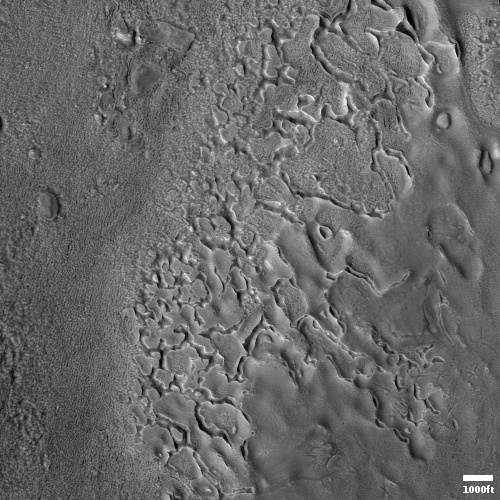
SpaceX successfully launches Falcon 9 from Cape Canaveral
SpaceX today successfully used its Falcon 9 rocket to put a SES communications satellite into orbit.
The first stage successfully completed its eighth flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
The company also attempted to complete a second launch just a little more than three hours later from Cape Canaveral, but the countdown of the Falcon Heavy rocket aborted just 59 seconds prior to liftoff. No word on what happened, though the company has another launch window beginning around 7:30 pm Eastern time tomorrow. If successful it would be the second Falcon Heavy launch in 2023, using two side boosters flying their eighth and third flights respectively. Because of the fuel needs of the payload, neither the side boosters or the core stage will be recovered.
The leaders in the 2023 launch race:
27 SpaceX
16 China
6 Russia
3 Rocket Lab
3 India
American private enterprise now leads China 30 to 16 in the national rankings, and the entire world combined 30 to 28. SpaceX by itself trails the rest of the world, including other American companies, 27 to 31.
SpaceX today successfully used its Falcon 9 rocket to put a SES communications satellite into orbit.
The first stage successfully completed its eighth flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
The company also attempted to complete a second launch just a little more than three hours later from Cape Canaveral, but the countdown of the Falcon Heavy rocket aborted just 59 seconds prior to liftoff. No word on what happened, though the company has another launch window beginning around 7:30 pm Eastern time tomorrow. If successful it would be the second Falcon Heavy launch in 2023, using two side boosters flying their eighth and third flights respectively. Because of the fuel needs of the payload, neither the side boosters or the core stage will be recovered.
The leaders in the 2023 launch race:
27 SpaceX
16 China
6 Russia
3 Rocket Lab
3 India
American private enterprise now leads China 30 to 16 in the national rankings, and the entire world combined 30 to 28. SpaceX by itself trails the rest of the world, including other American companies, 27 to 31.