October 4, 2024 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- ASTSpaceMobile’s 1st Bluebird cell-to-satellite satellite in orbit is about to go operational
The satellites are the largest commercial arrays ever placed in orbit, 700 square feet in area.
- German startup Polaris Spaceplanes raises €7.1 million in private investment capital
It will use the funds to develop its “Aurora multipurpose spaceplane and hypersonic transport system.”
- On this day in 1957, the Soviet Union opened the space age by launching the first artificial satellite, Sputnik
And as they say, the rest is history.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- ASTSpaceMobile’s 1st Bluebird cell-to-satellite satellite in orbit is about to go operational
The satellites are the largest commercial arrays ever placed in orbit, 700 square feet in area.
- German startup Polaris Spaceplanes raises €7.1 million in private investment capital
It will use the funds to develop its “Aurora multipurpose spaceplane and hypersonic transport system.”
- On this day in 1957, the Soviet Union opened the space age by launching the first artificial satellite, Sputnik
And as they say, the rest is history.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News
Frozen Martian eddies at the confluence of two glacier rivers
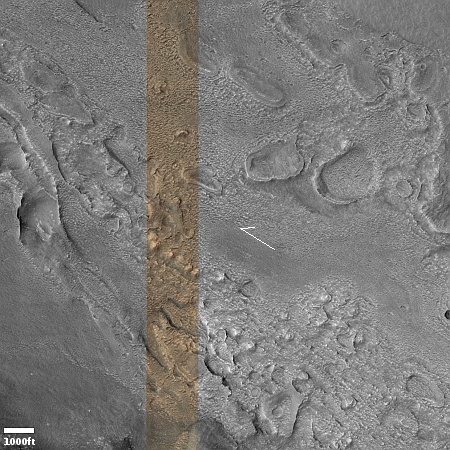
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on July 3, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The science team labels the photo as capturing a “contact near Reull Vallis,” a 1,000-mile-long Martian canyon that flows down the eastern slopes of Hellas Basin, the death valley of Mars.
What I see isn’t a geological contact but a complex jumble of odd-shaped depressions and mesas, surrounded by an eroded surface that seems squashed and deformed by some process. If this is all we had to go on, I would simply label this as another “What the heck?” image on Mars and move on. However, the larger context of the overview map helps explain it all, at least as best as we can explain using orbital data.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on July 3, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The science team labels the photo as capturing a “contact near Reull Vallis,” a 1,000-mile-long Martian canyon that flows down the eastern slopes of Hellas Basin, the death valley of Mars.
What I see isn’t a geological contact but a complex jumble of odd-shaped depressions and mesas, surrounded by an eroded surface that seems squashed and deformed by some process. If this is all we had to go on, I would simply label this as another “What the heck?” image on Mars and move on. However, the larger context of the overview map helps explain it all, at least as best as we can explain using orbital data.
» Read more
NASA pushes discrimination to favor minorities in its education workshops

NASA: dedicated to the new segregation!
“Segregation today, segregation tomorrow, segregation forever!” A NASA press release today proudly touted what it called a “Culturally Inclusive Planetary Engagement in Colorado,” one of a series of recent science/education workships designed specifically to help “black and Latinx youth and their families.”
Though the events are apparently not segregated, it also appears that white and Asian kids and their parents were not really welcome.
Planetary scientists and engineers from Boulder, as well as scientists from Florida, Maryland, and Alaska participated. ReaCH partnered with the Boys & Girls Clubs of Metro Denver, whose staff participated in the workshop to share their perspectives. Other educators local to the Denver area also participated, along with an educational specialist from NASA@ My Library (another Science Activation program). The workshop culminated in an event at the Shopneck Boys & Girls Club in Brighton, CO; workshop participants facilitated a variety of hands-on planetary activities for approximately 120 children. Workshop participants also shared information about college pathways into science professions with teenagers at the Club.
The location and the local organizations were specifically chosen to aid these specific minorites above anyone else.
» Read more
Now available in hardback and paperback as well as ebook!
From the press release: In this ground-breaking new history of early America, historian Robert Zimmerman not only exposes the lie behind The New York Times 1619 Project that falsely claims slavery is central to the history of the United States, he also provides profound lessons about the nature of human societies, lessons important for Americans today as well as for all future settlers on Mars and elsewhere in space.
Conscious Choice: The origins of slavery in America and why it matters today and for our future in outer space, is a riveting page-turning story that documents how slavery slowly became pervasive in the southern British colonies of North America, colonies founded by a people and culture that not only did not allow slavery but in every way were hostile to the practice.
Conscious Choice does more however. In telling the tragic history of the Virginia colony and the rise of slavery there, Zimmerman lays out the proper path for creating healthy societies in places like the Moon and Mars.
“Zimmerman’s ground-breaking history provides every future generation the basic framework for establishing new societies on other worlds. We would be wise to heed what he says.” —Robert Zubrin, founder of the Mars Society.
All editions are available at Amazon, Barnes & Noble, and all book vendors, with the ebook priced at $5.99 before discount. All editions can also be purchased direct from the ebook publisher, ebookit, in which case you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
Autographed printed copies are also available at discount directly from the author (hardback $29.95; paperback $14.95; Shipping cost for either: $6.00). Just send an email to zimmerman @ nasw dot org.
Sierra Space wins Air Force contract to develop orbital cargo delivery system
The Air Force has now awarded Sierra Space a contract to develop its proposed “Space Ghost” satellite spacecraft, designed to be launched into a stand-by orbit carrying needed cargo, where it can upon command deliver that cargo within 90 minutes anywhere on Earth.
Sierra Space won a contract of undisclosed value as part of the AFRL’s Rocket Experimentation for Global Agile Logistics (REGAL) program. The Air Force is exploring the potential of space vehicles to rapidly transport critical supplies from orbital warehouses back to Earth. This could include reusable reentry vehicles capable of delivering payloads from prepositioned stocks in orbit.
Sierra Space, based in Louisville, Colorado, said its defense technology team designed the Ghost system to be capable of remaining in orbit for up to five years, storing and delivering essential supplies on-demand. Once fully developed, the spacecraft could be used for missions such as delivering rescue kits for downed pilots, medical supplies for disaster relief or logistical support for military operations.
The company began doing drop tests of a Space Ghost prototype heat shield in March, and apparently the data satisfied the Air Force enough to issue this development contract. Whether such a system however makes sense remains unknown. To be able to deliver cargo anywhere on Earth will require putting up a large constellation of Space Ghost satellites, in many different orbits. Moreover, it is unclear how much cargo each satellite would carry.
The Air Force has now awarded Sierra Space a contract to develop its proposed “Space Ghost” satellite spacecraft, designed to be launched into a stand-by orbit carrying needed cargo, where it can upon command deliver that cargo within 90 minutes anywhere on Earth.
Sierra Space won a contract of undisclosed value as part of the AFRL’s Rocket Experimentation for Global Agile Logistics (REGAL) program. The Air Force is exploring the potential of space vehicles to rapidly transport critical supplies from orbital warehouses back to Earth. This could include reusable reentry vehicles capable of delivering payloads from prepositioned stocks in orbit.
Sierra Space, based in Louisville, Colorado, said its defense technology team designed the Ghost system to be capable of remaining in orbit for up to five years, storing and delivering essential supplies on-demand. Once fully developed, the spacecraft could be used for missions such as delivering rescue kits for downed pilots, medical supplies for disaster relief or logistical support for military operations.
The company began doing drop tests of a Space Ghost prototype heat shield in March, and apparently the data satisfied the Air Force enough to issue this development contract. Whether such a system however makes sense remains unknown. To be able to deliver cargo anywhere on Earth will require putting up a large constellation of Space Ghost satellites, in many different orbits. Moreover, it is unclear how much cargo each satellite would carry.
Avio completes testing of new redesigned nozzle for its Vega-C second stage
The Italian rocket company Avio yesterday successfully completed the second of two static fire engine tests of the newly redesigned nozzle for the second stage of its Vega-C rocket, paving the way for the company to resume launches after the nozzle design failed both during a launch in 2022 and then again during a static fire test in 2023 after its first redesign.
A launch date has tentatively been scheduled for November, but this date is not yet confirmed. For this and the next several launches in 2025, the rocket will still be managed by the European Space Agency’s (ESA) commercial arm, Arianespace. Beginning late next year however Avio will regain complete control of its rocket and will be able to market it internationally, no longer required to deal with this unneeded government middleman. The launch price will then certainly go down, making Vega-C more competitive.
The Italian rocket company Avio yesterday successfully completed the second of two static fire engine tests of the newly redesigned nozzle for the second stage of its Vega-C rocket, paving the way for the company to resume launches after the nozzle design failed both during a launch in 2022 and then again during a static fire test in 2023 after its first redesign.
A launch date has tentatively been scheduled for November, but this date is not yet confirmed. For this and the next several launches in 2025, the rocket will still be managed by the European Space Agency’s (ESA) commercial arm, Arianespace. Beginning late next year however Avio will regain complete control of its rocket and will be able to market it internationally, no longer required to deal with this unneeded government middleman. The launch price will then certainly go down, making Vega-C more competitive.
Leaving Earth: Space Stations, Rival Superpowers, and the Quest for Interplanetary Travel, can be purchased as an ebook everywhere for only $3.99 (before discount) at amazon, Barnes & Noble, all ebook vendors, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit.
If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big oppressive tech companies and I get a bigger cut much sooner.
Winner of the 2003 Eugene M. Emme Award of the American Astronautical Society.
"Leaving Earth is one of the best and certainly the most comprehensive summary of our drive into space that I have ever read. It will be invaluable to future scholars because it will tell them how the next chapter of human history opened." -- Arthur C. Clarke
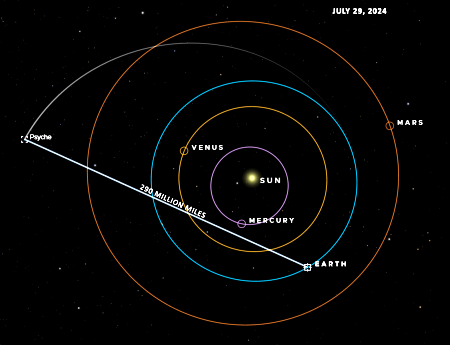
Engineers set new laser communications record to asteroid probe Psyche
As part of a continuing test program, engineers have set a new long distance laser communications record, exceeding 290 million miles, by successfully using a laser to send communicate with the asteroid probe Psyche from Earth.
The graph to the right, not to scale, shows the orbital configuation of the laser record. It appears however that little actual data was sent in this last test. It merely demonstrated that a link could be established. An actual data transfer record by laser occurred in June.
On June 24, when Psyche was about 240 million miles (390 million kilometers) from Earth — more than 2½ times the distance between our planet and the Sun — the project achieved a sustained downlink data rate of 6.25 megabits per second, with a maximum rate of 8.3 megabits per second. While this rate is significantly lower than the experiment’s maximum, it is far higher than what a radio frequency communications system using comparable power can achieve over that distance.
The high data rates promised by laser communications will significantly improve deep space operations. Most especially, the ability to get data back in much larger packets more quickly will reduce the antenna bottleneck on Earth that limits the number of missions as well as the data can be returned daily. More missions will be able to fly, and scientists and engineers will get their results faster.
As part of a continuing test program, engineers have set a new long distance laser communications record, exceeding 290 million miles, by successfully using a laser to send communicate with the asteroid probe Psyche from Earth.
The graph to the right, not to scale, shows the orbital configuation of the laser record. It appears however that little actual data was sent in this last test. It merely demonstrated that a link could be established. An actual data transfer record by laser occurred in June.
On June 24, when Psyche was about 240 million miles (390 million kilometers) from Earth — more than 2½ times the distance between our planet and the Sun — the project achieved a sustained downlink data rate of 6.25 megabits per second, with a maximum rate of 8.3 megabits per second. While this rate is significantly lower than the experiment’s maximum, it is far higher than what a radio frequency communications system using comparable power can achieve over that distance.
The high data rates promised by laser communications will significantly improve deep space operations. Most especially, the ability to get data back in much larger packets more quickly will reduce the antenna bottleneck on Earth that limits the number of missions as well as the data can be returned daily. More missions will be able to fly, and scientists and engineers will get their results faster.
FAA: No Starship/Superheavy launch before late November
In response to speculation that the fifth Starship/Superheavy test launch could happen in mid-October — based on a recent notice to mariners from the Coast Guard, the FAA on Wednesday made it clear that its stonewalling of SpaceX will continue.
“We are not issuing launch authorization for a launch to occur in the next two weeks — it’s not happening,” an FAA spokesman said Wednesday afternoon. “Late November is still our target date.”
The report comes from the San-Antonio Express-News, and as is typical of the reporting in the propaganda press, the article only gives the FAA’s side of this story, making absolutely no mention of SpaceX’s detailed and very public objections. As far as this news outlet is concerned, the FAA is god, whatever it says must be true. So much for a skeptical free press whose goal is supposed to be to hold government accountable.
In response to speculation that the fifth Starship/Superheavy test launch could happen in mid-October — based on a recent notice to mariners from the Coast Guard, the FAA on Wednesday made it clear that its stonewalling of SpaceX will continue.
“We are not issuing launch authorization for a launch to occur in the next two weeks — it’s not happening,” an FAA spokesman said Wednesday afternoon. “Late November is still our target date.”
The report comes from the San-Antonio Express-News, and as is typical of the reporting in the propaganda press, the article only gives the FAA’s side of this story, making absolutely no mention of SpaceX’s detailed and very public objections. As far as this news outlet is concerned, the FAA is god, whatever it says must be true. So much for a skeptical free press whose goal is supposed to be to hold government accountable.
ULA successfully completes second test launch of its new Vulcan rocket
ULA this morning successfully completed the second test launch of its new Vulcan rocket, lifting off from Cape Canaveral from Florida.
It placed a dummy test payload into orbit in order to obtain from the Space Force certification that will allow the company to begin operational military launches and actually make money from the rocket. ULA hopes to launch two such Vulcan launches before the end of the year, and then hopes to do ten more Vulcan launches in 2025, along with ten Atlas-5 launches as it closes out that rocket’s inventory before retiring it.
UPDATE: An explosion on of Vulcun’s two solid-fueled strap-on boosters during the launch today might prevent a quick certification from the military. Though the rocket successfully put the payload into its correct orbit, it appears the nozzle failed on that booster, throwing it out sideways, fortunately away from the rocket. The video here shows this clearly. I was startled by this explosion during the launch, but then forgot about it (until my readers reminded me) when the payload reached orbit as planned.
The strap-on boosters are manufactured by Northrop Grumman. Before using them again ULA needs to get clarity on this issue. We also must wonder if the FAA will step in as it has for SpaceX to ground ULA. At the moment it has decided not to do so.
This was ULA’s fifth launch in 2024, so there is no change in the 2024 launch race leader board.
95 SpaceX
44 China
11 Russia
11 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise now leads the rest of the world combined in successful launches 112 to 67, while SpaceX by itself now leads the entire world, including American companies, 95 to 84.
ULA this morning successfully completed the second test launch of its new Vulcan rocket, lifting off from Cape Canaveral from Florida.
It placed a dummy test payload into orbit in order to obtain from the Space Force certification that will allow the company to begin operational military launches and actually make money from the rocket. ULA hopes to launch two such Vulcan launches before the end of the year, and then hopes to do ten more Vulcan launches in 2025, along with ten Atlas-5 launches as it closes out that rocket’s inventory before retiring it.
UPDATE: An explosion on of Vulcun’s two solid-fueled strap-on boosters during the launch today might prevent a quick certification from the military. Though the rocket successfully put the payload into its correct orbit, it appears the nozzle failed on that booster, throwing it out sideways, fortunately away from the rocket. The video here shows this clearly. I was startled by this explosion during the launch, but then forgot about it (until my readers reminded me) when the payload reached orbit as planned.
The strap-on boosters are manufactured by Northrop Grumman. Before using them again ULA needs to get clarity on this issue. We also must wonder if the FAA will step in as it has for SpaceX to ground ULA. At the moment it has decided not to do so.
This was ULA’s fifth launch in 2024, so there is no change in the 2024 launch race leader board.
95 SpaceX
44 China
11 Russia
11 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise now leads the rest of the world combined in successful launches 112 to 67, while SpaceX by itself now leads the entire world, including American companies, 95 to 84.
Van Halen – Jump
An evening pause: Its an “official video,” so much of this is lip synched footage cobbled together to make what looks like a single performance. Much of it however is the actual performance, and the song is good.
Hat tip James Street.
October 3, 2024 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Axiom’s co-founder touts the nearly completed hull of its first space station module
It is being built by Thales-Alenia in Italy, and will be shipped soon to Houston. The company has been posting pictures like this for the past year-plus, but for some reason that module never gets finished.
- Major solar flare in progress
As Jay notes, “Regular news outlets are picking this up with the usual apocalypse chatter.” The big issue is how this might effect emergency communications using ham radio.
- Hera mission to Didymos/Dimorphos asteroid binary came in under budget by $20 million; still targeting October 7th launch, despite SpaceX grounding
ESA used that $20 million to cobble together a mission to Apophis, using Hera architecture.
- Starlink free for 30 days for those impacted by Hurricane Helene or doing rescue work
As always, private citizens and companies are acting faster and smarter than the government, which has actually moved to block such efforts, even threatening volunteers with arrest for providing aid.
- India approves joint India-Japan lunar project now dubbed Chandrayaan-5
It will include a lander built by India and a rover built by Japan.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Axiom’s co-founder touts the nearly completed hull of its first space station module
It is being built by Thales-Alenia in Italy, and will be shipped soon to Houston. The company has been posting pictures like this for the past year-plus, but for some reason that module never gets finished.
- Major solar flare in progress
As Jay notes, “Regular news outlets are picking this up with the usual apocalypse chatter.” The big issue is how this might effect emergency communications using ham radio.
- Hera mission to Didymos/Dimorphos asteroid binary came in under budget by $20 million; still targeting October 7th launch, despite SpaceX grounding
ESA used that $20 million to cobble together a mission to Apophis, using Hera architecture.
- Starlink free for 30 days for those impacted by Hurricane Helene or doing rescue work
As always, private citizens and companies are acting faster and smarter than the government, which has actually moved to block such efforts, even threatening volunteers with arrest for providing aid.
- India approves joint India-Japan lunar project now dubbed Chandrayaan-5
It will include a lander built by India and a rover built by Japan.
Pushback: Fired teacher wins $575K free speech settlement from school board

Peter Vlaming
Fight! Fight! Fight! In 2018 Peter Vlaming, a long time French teacher in the West Point School District in Virgina was fired because he would not use the preferred pro-nouns of one of his students. The firing was especially offensive in that Vlaming had done everything reasonable to accommodate the student, including using her preferred male-sounding name while avoiding the use of pronouns. He just could not use male pronouns for a female student. It violated his core beliefs.
The school board considered his silence on this point abusive to the student, and fired him. In 2019 he sued, and on September 30, 2024 his attorneys from the non-profit legal firm, the Alliance Defending Freedom, won him a $575K settlement from school board.
[T]he West Point School Board has agreed to pay $575,000 in damages and attorneys’ fees. In addition, the school board cleared Peter Vlaming’s firing from his record, and separate from the settlement agreement, changed its policies to conform to the new Virginia education policies established by Gov. Glenn Youngkin that respect fundamental free speech and parental rights.

Peter Vlaming
Fight! Fight! Fight! In 2018 Peter Vlaming, a long time French teacher in the West Point School District in Virgina was fired because he would not use the preferred pro-nouns of one of his students. The firing was especially offensive in that Vlaming had done everything reasonable to accommodate the student, including using her preferred male-sounding name while avoiding the use of pronouns. He just could not use male pronouns for a female student. It violated his core beliefs.
The school board considered his silence on this point abusive to the student, and fired him. In 2019 he sued, and on September 30, 2024 his attorneys from the non-profit legal firm, the Alliance Defending Freedom, won him a $575K settlement from school board.
[T]he West Point School Board has agreed to pay $575,000 in damages and attorneys’ fees. In addition, the school board cleared Peter Vlaming’s firing from his record, and separate from the settlement agreement, changed its policies to conform to the new Virginia education policies established by Gov. Glenn Youngkin that respect fundamental free speech and parental rights.
ULA’s big plans for 2025
As ULA prepares for the second launch of its new Vulcan rocket, presently scheduled for launch tomorrow at 6 am (Eastern), it held a press briefing on October 2, 2024 to provide an update on the rocket’s present and future status.
The key takeaways, assuming this launch succeeds as planned, as noted in a tweet by reporter Jeff Foust from Space News:
- ULA still plans on completing two national security Vulcan flights before the end of the year
- It is targeting 20 launches in 2025, half with Vulcan and half with Atlas-5
- The first Atlas-5 launch of Amazon’s Kuiper satellites won’t happen until 2025
- When Sierra Space says Dream Chaser is ready, ULA will launch it
Completing three Vulcan launches in the next three months will almost match the four launches the company has so far completed in the first nine months of the year. Furthermore, considering that ULA’s previous record for launches in a single year is 16, set in 2009, and that the company has not completed more than ten launches in a year since 2016, these plans are very ambitious indeed.
If it succeeds however in just getting close to these numbers, ULA will be doing very well indeed.
As ULA prepares for the second launch of its new Vulcan rocket, presently scheduled for launch tomorrow at 6 am (Eastern), it held a press briefing on October 2, 2024 to provide an update on the rocket’s present and future status.
The key takeaways, assuming this launch succeeds as planned, as noted in a tweet by reporter Jeff Foust from Space News:
- ULA still plans on completing two national security Vulcan flights before the end of the year
- It is targeting 20 launches in 2025, half with Vulcan and half with Atlas-5
- The first Atlas-5 launch of Amazon’s Kuiper satellites won’t happen until 2025
- When Sierra Space says Dream Chaser is ready, ULA will launch it
Completing three Vulcan launches in the next three months will almost match the four launches the company has so far completed in the first nine months of the year. Furthermore, considering that ULA’s previous record for launches in a single year is 16, set in 2009, and that the company has not completed more than ten launches in a year since 2016, these plans are very ambitious indeed.
If it succeeds however in just getting close to these numbers, ULA will be doing very well indeed.
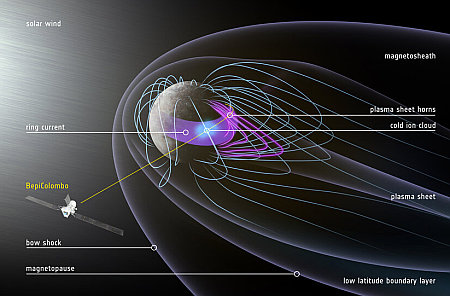
A new map of the magnetosphere of Mercury
Using data obtained during the June 2023 fly-by by the European-Japanese probe BepiColombo, scientists have now published a new detailed map of the magnetic field that surrounds Mercury.
That map is to the right. From the caption:
A textured sphere representing Mercury is shown with magnetic field lines compressed on the sunward side and streaming out into a tail on the nightside. The BepiColombo spacecraft’s trajectory is drawn passing through the magnetosphere from dawn to dusk, close to the planet’s surface. Various features in the magnetosphere are depicted and labelled with text. Following the order in which they were detected by the spacecraft, this includes the bow shock, magnetopause, low-latitude boundary layer, cold ion cloud, plasma sheet horn and ring current.
You can read the peer-reviewed paper here [pdf]. Note that this research does not include data obtained during BepiColumbo’s fourth fly-by of Mercury in September. Furthermore, the spacecraft will do two more fly-bys before arriving in orbit in 2026, where it will then separate into two separate orbiters in complementary orbits. Thus, this magnetic map of Mercury is merely a rough draft, and will be significantly refined by the end of the mission.
Using data obtained during the June 2023 fly-by by the European-Japanese probe BepiColombo, scientists have now published a new detailed map of the magnetic field that surrounds Mercury.
That map is to the right. From the caption:
A textured sphere representing Mercury is shown with magnetic field lines compressed on the sunward side and streaming out into a tail on the nightside. The BepiColombo spacecraft’s trajectory is drawn passing through the magnetosphere from dawn to dusk, close to the planet’s surface. Various features in the magnetosphere are depicted and labelled with text. Following the order in which they were detected by the spacecraft, this includes the bow shock, magnetopause, low-latitude boundary layer, cold ion cloud, plasma sheet horn and ring current.
You can read the peer-reviewed paper here [pdf]. Note that this research does not include data obtained during BepiColumbo’s fourth fly-by of Mercury in September. Furthermore, the spacecraft will do two more fly-bys before arriving in orbit in 2026, where it will then separate into two separate orbiters in complementary orbits. Thus, this magnetic map of Mercury is merely a rough draft, and will be significantly refined by the end of the mission.
Scientists confirm theory that thunderstorms on Earth also produce gamma ray bursts
Prior to the 1990s, the origin of gamma ray bursts (GRBs) was uttlerly known. First detected by satellites in the early 1970s, astronomers has no idea what caused them because without a parallel detection in optical light they had no way to determine their distance. Theories suggested the bursts could be coming from billions of light years away, from within the Milky Way, from inside the solar system, and from even the Earth’s upper atmosphere.
In the 1990s it was finally proven that GRBs almost all come from very distant cosmic events, billions of light years away, each signaling the formation of a black hole.
Now researchers have confirmed the theory that GRBs are also occuring within the Earth’s atmosphere, though these GRBs have no resemblance to the astronomical ones.
During thunderclouds, two different hard radiation phenomena have so far been known to originate: Terrestrial Gamma-ray Flashes (TGFs) and gamma-ray glows. This third phenomenon, observed and named FGFs by Østgaard et al. [2024] resembles the other two, while at the same time revealing certain characteristics separating FGFs from the others. Most noteworthy may be that FGFs are pulses of gamma-rays not associated with any detectable optical or radio signals.
“We think that FGFs could be the missing link between TGFs and gamma-ray glows, whose absence has been puzzling the atmospheric electricity community for two decades”, says lead author and Professor Nikolai Østgaard at the University of Bergen.
More information on this research can be found here. The research not only confirms the early theories as well as later detections, it adds significant nuance to the data. As noted at this second link:
“The dynamics of gamma-glowing thunderclouds starkly contradicts the former quasi-stationary picture of glows, and rather resembles that of a huge gamma-glowing boiling pot both in pattern and behavior,” said Martino Marisaldi, professor of physics and technology at the University of Bergen.
Given the size of a typical thunderstorm in the tropics, which get much larger than storms at other latitudes, this suggests that more than half of all thunderstorms in the tropics are radioactive. The researchers postulate that this low-level production of gamma radiation acts like steam boiling off a pot of water and limits how much energy can be built up inside.
This data will help refined the computer models that attempt to predict weather patterns, as it appears the phenomenon impacts the formation of thunderstorms.
Prior to the 1990s, the origin of gamma ray bursts (GRBs) was uttlerly known. First detected by satellites in the early 1970s, astronomers has no idea what caused them because without a parallel detection in optical light they had no way to determine their distance. Theories suggested the bursts could be coming from billions of light years away, from within the Milky Way, from inside the solar system, and from even the Earth’s upper atmosphere.
In the 1990s it was finally proven that GRBs almost all come from very distant cosmic events, billions of light years away, each signaling the formation of a black hole.
Now researchers have confirmed the theory that GRBs are also occuring within the Earth’s atmosphere, though these GRBs have no resemblance to the astronomical ones.
During thunderclouds, two different hard radiation phenomena have so far been known to originate: Terrestrial Gamma-ray Flashes (TGFs) and gamma-ray glows. This third phenomenon, observed and named FGFs by Østgaard et al. [2024] resembles the other two, while at the same time revealing certain characteristics separating FGFs from the others. Most noteworthy may be that FGFs are pulses of gamma-rays not associated with any detectable optical or radio signals.
“We think that FGFs could be the missing link between TGFs and gamma-ray glows, whose absence has been puzzling the atmospheric electricity community for two decades”, says lead author and Professor Nikolai Østgaard at the University of Bergen.
More information on this research can be found here. The research not only confirms the early theories as well as later detections, it adds significant nuance to the data. As noted at this second link:
“The dynamics of gamma-glowing thunderclouds starkly contradicts the former quasi-stationary picture of glows, and rather resembles that of a huge gamma-glowing boiling pot both in pattern and behavior,” said Martino Marisaldi, professor of physics and technology at the University of Bergen.
Given the size of a typical thunderstorm in the tropics, which get much larger than storms at other latitudes, this suggests that more than half of all thunderstorms in the tropics are radioactive. The researchers postulate that this low-level production of gamma radiation acts like steam boiling off a pot of water and limits how much energy can be built up inside.
This data will help refined the computer models that attempt to predict weather patterns, as it appears the phenomenon impacts the formation of thunderstorms.
European phone companies demand the FCC stop SpaceX’s cell-to-satellite Starlink plans
Several European phone companies have now submitted a request to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to block a waiver that would allow SpaceX to operate its new cell-to-satellite Starlink satellites at radio frequencies normally not permitted.
This request follows similar requests by Verizon and AT&T to the FCC. The fear is that the use of these frequencies in the low orbit of Starlink satellites will interfere with satellites in the much higher geosynchronous orbits that these phone companies presently use.
While those concerns might be valid (SpaceX says no), these companies also fear the competition of Starlink itself, as its low orbit means it can provide better service, and are clearly hoping the FCC will act to protect them from that competition.
In a more sane world, the FCC would decide this issue on purely technical grounds. It was formed expressly to police the frequencies so that users would not interfere or pirate each others licenses, and had done that job quite well for decades.
Sadly, the FCC no longer confines itself to this one job. For the past four years the FCC has arbitrarily decided its job should include many other things not listed in its statutory authority, such as policing the de-orbiting of satellites and determining the acceptable lifespans of orbiting spacecraft, while also making many decisions based entirely on political factors, sometimes even favoring some companies over others for partisan reasons.
Thus we should have no confidence that the FCC will make this decision on purely technical grounds, especially since it has shown a clear hostility to SpaceX in its recent decisions.
Several European phone companies have now submitted a request to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to block a waiver that would allow SpaceX to operate its new cell-to-satellite Starlink satellites at radio frequencies normally not permitted.
This request follows similar requests by Verizon and AT&T to the FCC. The fear is that the use of these frequencies in the low orbit of Starlink satellites will interfere with satellites in the much higher geosynchronous orbits that these phone companies presently use.
While those concerns might be valid (SpaceX says no), these companies also fear the competition of Starlink itself, as its low orbit means it can provide better service, and are clearly hoping the FCC will act to protect them from that competition.
In a more sane world, the FCC would decide this issue on purely technical grounds. It was formed expressly to police the frequencies so that users would not interfere or pirate each others licenses, and had done that job quite well for decades.
Sadly, the FCC no longer confines itself to this one job. For the past four years the FCC has arbitrarily decided its job should include many other things not listed in its statutory authority, such as policing the de-orbiting of satellites and determining the acceptable lifespans of orbiting spacecraft, while also making many decisions based entirely on political factors, sometimes even favoring some companies over others for partisan reasons.
Thus we should have no confidence that the FCC will make this decision on purely technical grounds, especially since it has shown a clear hostility to SpaceX in its recent decisions.
Water on the Moon? New data analysis from two different lunar orbiters say yes
Two papers in the past month using data from two different lunar orbiters have claimed the presence of water on Moon, based on the detection of evidence of hydrogen on the surface.
First, on September 16, 2024 scientists published a paper [pdf] that analyzed data collected in 2009 by India’s Chandrayaan-1 lunar orbiter, and concluded, as stated enthusiastically in the press release:
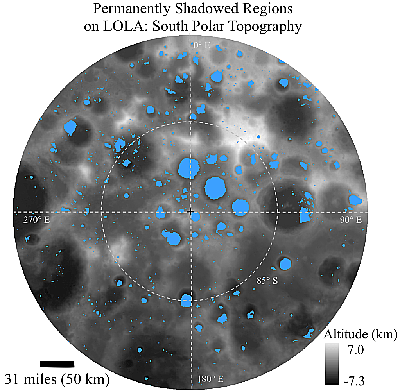
From the second paper, a map of permanently shadowed
regions at the Moon’s south pole. Click for original.
“Future astronauts may be able to find water even near the equator by exploiting these water-rich areas. Previously, it was thought that only the polar region, and in particular, the deeply shadowed craters at the poles were where water could be found in abundance,” said Roger Clark, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute and lead author of “The Global Distribution of Water and Hydroxyl on the Moon as Seen by the Moon Mineralogy Mapper (M3)” that appears in the Planetary Science Journal. “Knowing where water is located not only helps to understand lunar geologic history, but also where astronauts may find water in the future.”
Then today NASA announced the publication of a new paper [pdf] that looked at the data collected over the last decade by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), and have concluded that “hydrogen-bearing volatiles are observed to be concentrated, likely in the form of water ice, within most of the Moon’s permanently shadowed regions (PSRs), poleward of 77°.” The press release, which included the map to the right of permanently shadowed areas at the Moon’s south pole, was more enthusiastic:
» Read more
Two papers in the past month using data from two different lunar orbiters have claimed the presence of water on Moon, based on the detection of evidence of hydrogen on the surface.
First, on September 16, 2024 scientists published a paper [pdf] that analyzed data collected in 2009 by India’s Chandrayaan-1 lunar orbiter, and concluded, as stated enthusiastically in the press release:

From the second paper, a map of permanently shadowed
regions at the Moon’s south pole. Click for original.
“Future astronauts may be able to find water even near the equator by exploiting these water-rich areas. Previously, it was thought that only the polar region, and in particular, the deeply shadowed craters at the poles were where water could be found in abundance,” said Roger Clark, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute and lead author of “The Global Distribution of Water and Hydroxyl on the Moon as Seen by the Moon Mineralogy Mapper (M3)” that appears in the Planetary Science Journal. “Knowing where water is located not only helps to understand lunar geologic history, but also where astronauts may find water in the future.”
Then today NASA announced the publication of a new paper [pdf] that looked at the data collected over the last decade by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), and have concluded that “hydrogen-bearing volatiles are observed to be concentrated, likely in the form of water ice, within most of the Moon’s permanently shadowed regions (PSRs), poleward of 77°.” The press release, which included the map to the right of permanently shadowed areas at the Moon’s south pole, was more enthusiastic:
» Read more
Viewing Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS
While the newly discovered Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS in the past week reached naked eye visibility in the dawn sky, in the next few weeks it will shift into the evening sky on October 11, 2024 while brightening to peak levels.
Although Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS will be visible in both hemispheres, the northern one is favored because the comet tracks north. Also, sunsets are getting earlier and twilights shorter, while the opposite is happening in southern latitudes.
Observers should be aware that the Moon will interfere for several nights, from about Oct. 15-20 (full Moon is on Oct. 17th), around the same time the comet climbs out of twilight.
As it begins to fade, the comet will be visible at an increasing height above the horizon each night through the end of October. At its brightest it is expected to be one of the brightest objects in the sky.
While the newly discovered Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS in the past week reached naked eye visibility in the dawn sky, in the next few weeks it will shift into the evening sky on October 11, 2024 while brightening to peak levels.
Although Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS will be visible in both hemispheres, the northern one is favored because the comet tracks north. Also, sunsets are getting earlier and twilights shorter, while the opposite is happening in southern latitudes.
Observers should be aware that the Moon will interfere for several nights, from about Oct. 15-20 (full Moon is on Oct. 17th), around the same time the comet climbs out of twilight.
As it begins to fade, the comet will be visible at an increasing height above the horizon each night through the end of October. At its brightest it is expected to be one of the brightest objects in the sky.
October 2, 2024 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
Santana – Flor de Luna
An evening pause: Performed live 1977. The filmwork leaves a lot to be desired, and the sound might not come from this particular performance. No matter. Just listen to the music.
Hat tip Judd Clark.
October 2, 2024 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Astrobotic successfully completes ground communications tests between its Griffin lunar lander and NASA’s Deep Space Network
The launch is presently scheduled for 2025 on a Falcon Heavy rocket.
- New Horizons is now 60 times as far from the Sun as Earth, and has almost doubled Pluto’s distance from the Sun since flying past it in 2015
It is flying 300 million miles farther out each year.
- ESA touts new antenna in its own deep space network
Now all Europe has to do is launch some deep space probes.
- ISRO is hopeful its first unmanned test orbital Gangayaan mission will happen before the end of this year
This isn’t really news, as the agency has been saying this for quite some time. If anything, the story hints that the mission will likely be delayed until early next year.
- Russian prime minister claims the first 300 satellites in its own “Starlink” constellation will be launched by 2027
And if you believe him I have bridge in Brooklyn I could sell you cheap!
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Astrobotic successfully completes ground communications tests between its Griffin lunar lander and NASA’s Deep Space Network
The launch is presently scheduled for 2025 on a Falcon Heavy rocket.
- New Horizons is now 60 times as far from the Sun as Earth, and has almost doubled Pluto’s distance from the Sun since flying past it in 2015
It is flying 300 million miles farther out each year.
- ESA touts new antenna in its own deep space network
Now all Europe has to do is launch some deep space probes.
- ISRO is hopeful its first unmanned test orbital Gangayaan mission will happen before the end of this year
This isn’t really news, as the agency has been saying this for quite some time. If anything, the story hints that the mission will likely be delayed until early next year.
- Russian prime minister claims the first 300 satellites in its own “Starlink” constellation will be launched by 2027
And if you believe him I have bridge in Brooklyn I could sell you cheap!
Sunspot update: Sunspot activity crashes in September
As it is the start of the month, it is time another monthly sunspot update, in which I provide some context and analysis to NOAA’s most recent update of its monthly graph tracking the number of sunspots on the Sun’s Earth-facing hemisphere.
After several months in which the number of sunspots rose considerably each month, in September the sunspot count crashed, dropping precipitously to levels closer to the various predictions of solar scientists, but still far above what they had all expected at this time of the solar maximum.
The strange terrain of the Martian southern ice cap
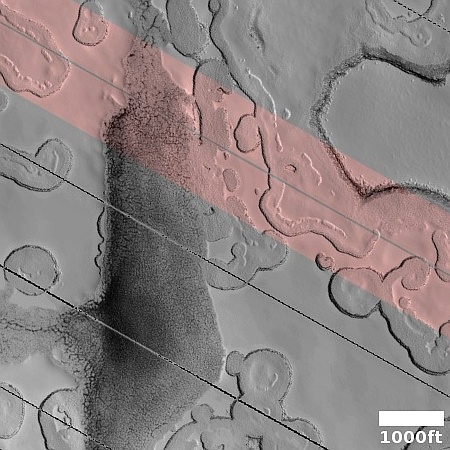
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, and sharpened to post here, was taken on July 29, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a section at the Martian south pole at the very high latitude of 87 degrees south, only about 100 miles from the pole itself.
The label for this picture is “possible water ice and mesas,” suggesting we are looking at an ice cap of water that is partly sublimated away.
In truth, things are much more complicated. It was summer when this photo was taken. Note the drainage in the lower right and the dark spidery lines there. In the winter on Mars atmospheric carbon dioxide falls as snow and coats the poles to about 60 degrees latitude with a thin mantle of dry ice. In the spring this mantle sublimates away, but does so in an counter-intuitive manner. The sublimation first occurs at the mantle’s base, and the trapped gas flows up until it finds a weak spot in the mantle and cracks through, spewing out and deposting dark splotches of dust.
At the south pole this upward flow always follows the same paths, producing the dark spidery patterns we see here. In the case of the drainage in the lower right, this is a drainage of gas eastward until it pops out at the slope, causing that depression to become darkly stained.
This is only part of the story of this complex geology, however.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, and sharpened to post here, was taken on July 29, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a section at the Martian south pole at the very high latitude of 87 degrees south, only about 100 miles from the pole itself.
The label for this picture is “possible water ice and mesas,” suggesting we are looking at an ice cap of water that is partly sublimated away.
In truth, things are much more complicated. It was summer when this photo was taken. Note the drainage in the lower right and the dark spidery lines there. In the winter on Mars atmospheric carbon dioxide falls as snow and coats the poles to about 60 degrees latitude with a thin mantle of dry ice. In the spring this mantle sublimates away, but does so in an counter-intuitive manner. The sublimation first occurs at the mantle’s base, and the trapped gas flows up until it finds a weak spot in the mantle and cracks through, spewing out and deposting dark splotches of dust.
At the south pole this upward flow always follows the same paths, producing the dark spidery patterns we see here. In the case of the drainage in the lower right, this is a drainage of gas eastward until it pops out at the slope, causing that depression to become darkly stained.
This is only part of the story of this complex geology, however.
» Read more
Mid-October date for the 5th Starship/Superheavy test orbital launch?
A US Coast Guard announcement issued today includes a notice to mariners of a rocket launch window at Boca Chica from October 12th to October 19th, suggesting that SpaceX has gotten an update from the FAA that a launch license will be issued for those dates, more than a month earlier than previously predicted by the FAA.
It must be emphasized that this notice is from the Coast Guard, not the FAA. The FAA has said nothing new about SpaceX’s launch license application. This notice suggests several possiblilites, all or none of which may be true:
1. The FAA has told SpaceX privately that it expects to issue that license in time for a launch in two weeks, and SpaceX then moved quickly to get the Coast Guard in line.
2. SpaceX and the Coast Guard are working together to increase the pressure on the FAA to get out of the way.
3. The public condemnations of the FAA by SpaceX in the past few weeks have worked to force that agency to back off its hardnosed regulatory over-reach.
All of this is wild speculation. For all we know, this Coast Guard notice is something it always issues prior to major static fire tests at Boca Chica. We shall have to wait to get a better sense of what is happening.
Hat tip to reader Steve Richter.
A US Coast Guard announcement issued today includes a notice to mariners of a rocket launch window at Boca Chica from October 12th to October 19th, suggesting that SpaceX has gotten an update from the FAA that a launch license will be issued for those dates, more than a month earlier than previously predicted by the FAA.
It must be emphasized that this notice is from the Coast Guard, not the FAA. The FAA has said nothing new about SpaceX’s launch license application. This notice suggests several possiblilites, all or none of which may be true:
1. The FAA has told SpaceX privately that it expects to issue that license in time for a launch in two weeks, and SpaceX then moved quickly to get the Coast Guard in line.
2. SpaceX and the Coast Guard are working together to increase the pressure on the FAA to get out of the way.
3. The public condemnations of the FAA by SpaceX in the past few weeks have worked to force that agency to back off its hardnosed regulatory over-reach.
All of this is wild speculation. For all we know, this Coast Guard notice is something it always issues prior to major static fire tests at Boca Chica. We shall have to wait to get a better sense of what is happening.
Hat tip to reader Steve Richter.
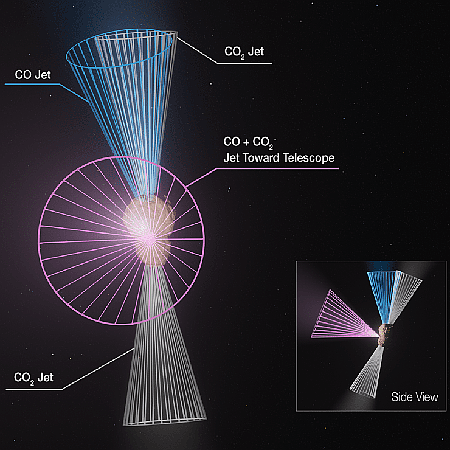
Scientists detect jets of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide from asteroid
Using the spectroscopy from the Webb Space Telescope, scientists have now detected jets of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide spewing from the very active asteroid 29P/Schwassmann-Wachmann-1 (29P).
Based on the data gathered by Webb, the team created a 3D model of the jets to understand their orientation and origin. They found through their modeling efforts that the jets were emitted from different regions on the centaur’s nucleus, even though the nucleus itself cannot be resolved by Webb. The jets’ angles suggest the possibility that the nucleus may be an aggregate of distinct objects with different compositions; however, other scenarios can’t yet be excluded.
The graphic to the right illustrates the modeling of these jets. That the center of this two-lobed asteroid could have been created from distinct objects suggests a very complex formation process, since those objects would have had to have formed themselves in different locations in the solar system and then somehow come together.
Using the spectroscopy from the Webb Space Telescope, scientists have now detected jets of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide spewing from the very active asteroid 29P/Schwassmann-Wachmann-1 (29P).
Based on the data gathered by Webb, the team created a 3D model of the jets to understand their orientation and origin. They found through their modeling efforts that the jets were emitted from different regions on the centaur’s nucleus, even though the nucleus itself cannot be resolved by Webb. The jets’ angles suggest the possibility that the nucleus may be an aggregate of distinct objects with different compositions; however, other scenarios can’t yet be excluded.
The graphic to the right illustrates the modeling of these jets. That the center of this two-lobed asteroid could have been created from distinct objects suggests a very complex formation process, since those objects would have had to have formed themselves in different locations in the solar system and then somehow come together.
ESA awards Polish rocket startup €2.4 million contract
The European Space Agency (ESA) has awarded a Polish rocket startup, dubbed SpaceForest, €2.4 million to upgrade its suborbital Perun rocket that the company has test launched twice in last year.
Perun runs on modified paraffin, commonly used as candle wax, and so its propellant is non-toxic. The rocket can be launched on a mobile launch pad, allowing for easy deployment at launch facilities around Europe. Last year, SpaceForest launched two full-scale models of its Perun rocket that flew to 22 km and 13 km altitude from the coastal town of Ustka, Poland, on the Baltic Sea.
This company is now the second Polish rocket startup to have successfully tested its rocket. The Łukasiewicz Institute of Aviation has completed suborbital test flights of its ILR-33 Amber 2K rocket, and has a deal to fly its next test from Norway’s commercial Andoya spaceport.
The European Space Agency (ESA) has awarded a Polish rocket startup, dubbed SpaceForest, €2.4 million to upgrade its suborbital Perun rocket that the company has test launched twice in last year.
Perun runs on modified paraffin, commonly used as candle wax, and so its propellant is non-toxic. The rocket can be launched on a mobile launch pad, allowing for easy deployment at launch facilities around Europe. Last year, SpaceForest launched two full-scale models of its Perun rocket that flew to 22 km and 13 km altitude from the coastal town of Ustka, Poland, on the Baltic Sea.
This company is now the second Polish rocket startup to have successfully tested its rocket. The Łukasiewicz Institute of Aviation has completed suborbital test flights of its ILR-33 Amber 2K rocket, and has a deal to fly its next test from Norway’s commercial Andoya spaceport.
ISRO reveals design of its Chandrayaan-4 lunar sample return mission
India’s space agency ISRO yesterday unveiled its design concept for its Chandrayaan-4 lunar sample return mission, requiring two launches and five modules that will dock in Earth orbit before traveling to the Moon.
“After two launches, the stacks will be docked together in elliptical Earth orbit to form an integrated stack. Subsequent to docking, the Integrated Stack will perform the first set of Earth-bound manoeuvres with the PM propulsion system. Once the PM is depleted, it gets jettisoned from the Integrated stack,” Isro said Tuesday.
The integrated stack then performs all the manoeuvres to achieve the lunar orbit, such that the orbit plane has the pre-determined landing site. In the final lunar orbit, the descender module and ascender module get separated from the transfer module and re-entry module. The descender and ascender modules then undergo powered descent to achieve a soft landing on the lunar surface.
Both a robot arm and a drill will then grab samples, deposit them separately in the ascender, which will then launch and redock with the stack. It will then take the re-entry module back toward Earth, where it will be released prior to its return.
This plan is essentially the same as the first proposal last year, but with many more added details.
A landing site has apparently not yet been chosen.
India’s space agency ISRO yesterday unveiled its design concept for its Chandrayaan-4 lunar sample return mission, requiring two launches and five modules that will dock in Earth orbit before traveling to the Moon.
“After two launches, the stacks will be docked together in elliptical Earth orbit to form an integrated stack. Subsequent to docking, the Integrated Stack will perform the first set of Earth-bound manoeuvres with the PM propulsion system. Once the PM is depleted, it gets jettisoned from the Integrated stack,” Isro said Tuesday.
The integrated stack then performs all the manoeuvres to achieve the lunar orbit, such that the orbit plane has the pre-determined landing site. In the final lunar orbit, the descender module and ascender module get separated from the transfer module and re-entry module. The descender and ascender modules then undergo powered descent to achieve a soft landing on the lunar surface.
Both a robot arm and a drill will then grab samples, deposit them separately in the ascender, which will then launch and redock with the stack. It will then take the re-entry module back toward Earth, where it will be released prior to its return.
This plan is essentially the same as the first proposal last year, but with many more added details.
A landing site has apparently not yet been chosen.
Orbital tug startup Impulse Space raises $150 million
The orbital tug startup Impulse Space announced yesterday that it has raised $150 million in private investment capital, money it will use to develop its planned two tugs, dubbed Mira and Helios.
So far the company, founded by former SpaceX engineer Tom Mueller, has only flown one mission, a demo mission of Mira last year that had some communications and software problems but was still declared a success.
Both Mira and Helios use chemical propulsion systems that offer large amounts of delta-v, or change in velocity, that can be provided quickly. Impulse said when it announced Helios that the vehicle could take a five-ton satellite from low Earth orbit to geostationary orbit in less than a day.
It hopes to fly an upgraded version of Mira late next year, and the first Helios mission in 2026.
The orbital tug startup Impulse Space announced yesterday that it has raised $150 million in private investment capital, money it will use to develop its planned two tugs, dubbed Mira and Helios.
So far the company, founded by former SpaceX engineer Tom Mueller, has only flown one mission, a demo mission of Mira last year that had some communications and software problems but was still declared a success.
Both Mira and Helios use chemical propulsion systems that offer large amounts of delta-v, or change in velocity, that can be provided quickly. Impulse said when it announced Helios that the vehicle could take a five-ton satellite from low Earth orbit to geostationary orbit in less than a day.
It hopes to fly an upgraded version of Mira late next year, and the first Helios mission in 2026.
Carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide found on the surface of Pluto’s moon Charon
Using spectroscopic data from the Webb Space Telescope, scientists have detected both carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide on the surface of Pluto’s moon Charon, adding these chemicals to the previously detected water ice and ammonia-bearing chemicals that give the planet its gray and red colors.
The team compared the spectroscopic observations with laboratory measurements and detailed spectral models of the surface, concluding that carbon dioxide is present primarily as a surface veneer on a water ice-rich subsurface. “Our preferred interpretation is that the upper layer of carbon dioxide originates from the interior and has been exposed to the surface through cratering events. Carbon dioxide is known to be present in regions of the protoplanetary disk from which the Pluto system formed,” Protopapa said.
The presence of hydrogen peroxide on the surface of Charon clearly indicates that the water ice-rich surface is altered by solar ultraviolet light and energetic particles from the solar wind and galactic cosmic rays. Hydrogen peroxide forms from oxygen and hydrogen atoms originating from the breakup of water ice due to incoming ions, electrons or photons.
The theory proposing the dry ice comes from the interior is interesting, but there simply is not enough data to take it very seriously at this point.
Using spectroscopic data from the Webb Space Telescope, scientists have detected both carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide on the surface of Pluto’s moon Charon, adding these chemicals to the previously detected water ice and ammonia-bearing chemicals that give the planet its gray and red colors.
The team compared the spectroscopic observations with laboratory measurements and detailed spectral models of the surface, concluding that carbon dioxide is present primarily as a surface veneer on a water ice-rich subsurface. “Our preferred interpretation is that the upper layer of carbon dioxide originates from the interior and has been exposed to the surface through cratering events. Carbon dioxide is known to be present in regions of the protoplanetary disk from which the Pluto system formed,” Protopapa said.
The presence of hydrogen peroxide on the surface of Charon clearly indicates that the water ice-rich surface is altered by solar ultraviolet light and energetic particles from the solar wind and galactic cosmic rays. Hydrogen peroxide forms from oxygen and hydrogen atoms originating from the breakup of water ice due to incoming ions, electrons or photons.
The theory proposing the dry ice comes from the interior is interesting, but there simply is not enough data to take it very seriously at this point.
Russia delays first launch of new Soyuz-5 rocket to 2026
According to Russia’s state-run press, the first launch of its new Soyuz-5 rocket will not occur in 2025 as previously predicted, but has been delayed to 2026.
No reason for the delay was given, but I suspect it is because Russia has still been unable to negotiate a deal with Kazakhstan for the use of the planned launchpad at Baikonur. In 2023 Kazakhstan seized control of the Soyuz-5 launchpad, and has apparently so far refused to agree to a new deal for allowing Russia to use it.
These negotiating delays with Kazakhstan are not the Soyuz-5 rocket’s only issues. Russia first announced the rocket in 2015, with its first launch planned for 2022. Thus, long before Kazakhstan retook its launchpad in 2023 the project was behind schedule. Other plans in 2019 to launch it from the former commercial Sea Launch platform that Russia took over have come to nothing.
Kazakhstan’s unwillingness to negotiate almost certainly stems from Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine. It now fears Russia, and is very reluctant to give it more control of Kazakhstan’s assets.
According to Russia’s state-run press, the first launch of its new Soyuz-5 rocket will not occur in 2025 as previously predicted, but has been delayed to 2026.
No reason for the delay was given, but I suspect it is because Russia has still been unable to negotiate a deal with Kazakhstan for the use of the planned launchpad at Baikonur. In 2023 Kazakhstan seized control of the Soyuz-5 launchpad, and has apparently so far refused to agree to a new deal for allowing Russia to use it.
These negotiating delays with Kazakhstan are not the Soyuz-5 rocket’s only issues. Russia first announced the rocket in 2015, with its first launch planned for 2022. Thus, long before Kazakhstan retook its launchpad in 2023 the project was behind schedule. Other plans in 2019 to launch it from the former commercial Sea Launch platform that Russia took over have come to nothing.
Kazakhstan’s unwillingness to negotiate almost certainly stems from Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine. It now fears Russia, and is very reluctant to give it more control of Kazakhstan’s assets.