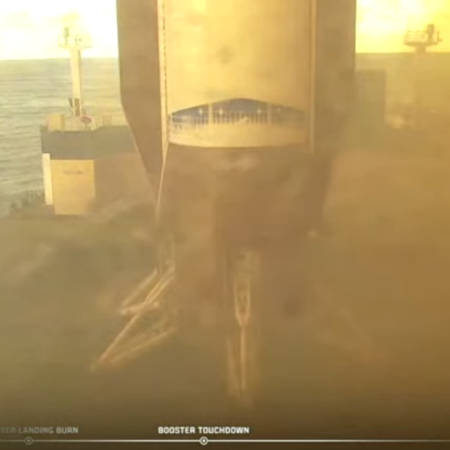
New Glenn first stage after landing
Blue Origin today successfully placed two the NASA Escapade Mars orbiters into space, its New Glenn rocket launching for the second time from Cape Canaveral in Florida.
More significantly, the company successfully landed the rocket’s first stage on a barge in the Atlantic. New Glenn is now the second rocket company capable of vertically landing and recovering an orbital first stage, after SpaceX.
Several take-aways: First, this first stage recovery took place almost exactly a decade after Blue Origin successfully landed vertically its suborbital New Shepard rocket, and almost a decade after SpaceX successfully did it with its Falcon 9 orbital rocket. It is a shame that it took Blue Origin so long to get to this point. It is also magnificent that it has finally made it happen. The United States now has two reusable rockets, with two more (by Rocket Lab and Stoke Space) expected to launch by next year.
Blue Origin is not likely to reuse this particular first stage, but its recovery will make future reuses likely and soon.
Second, Blue Origin made one interesting broadcast choice that I like. It listed the rocket’s altitude and speed in feet/miles and miles per hour, not kilometers. The engineers might have been using metric, but the audience is American, so using the traditional Imperial numbers is smart. Good for Blue Origin.
Third, Blue Origin’s announcers were once again annoying, distracting, ignorant, and childishly emotional. And they simply would not shut up, preventing the audience from hearing critical reports from mission control. They also seemed oblivious to reality, bragging repeatedly about the ten year gap between the first New Shepard landing and this landing, as if this was somehow a good thing. It was embarrassing to listen to.
The company would do a far better job selling itself by hiring announcers who are more serious and professional. Sadly, I have noted this problem from Blue Origin’s announcers now for almost a decade, with little change.
Finally, this success is a very big deal, both for Blue Origin and the United States. The company is now primed to begin regular launches next year, including the 27 launches Amazon has purchased for its Kuiper constellation.
For the U.S., this finally gives us a solid competitor to SpaceX. And that competition is finally going to force launch prices to drop significantly. SpaceX dropped prices, but not as far as it could because there was no pressure to do so from anyone else. Now there is that pressure.
As this was only the second launch by Blue Origin in 2025, the leader board for the 2025 launch race remains unchanged:
147 SpaceX
70 China
14 Rocket Lab
13 Russia
SpaceX still leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 147 to 116. Note that ULA hopes to launch its Atlas-5 rocket tonight.