State Department blasts the European Union’s proposed Space Act

This label would be more accurate if it read
“NOT made in the European Union”
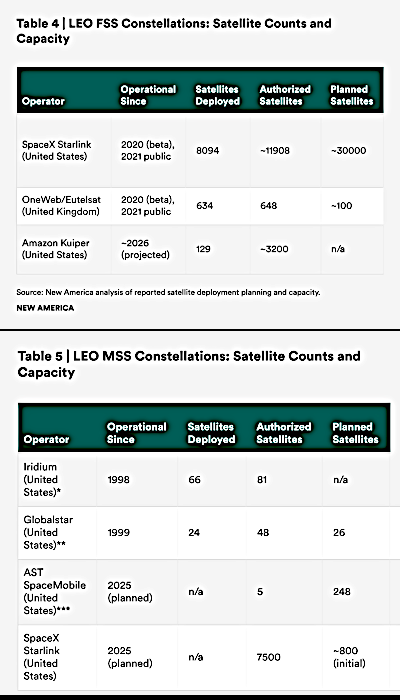
In a comment the State Department posted on November 4, 2025 on the European Commission’s website for public comment in connection with the European Union’s proposed Space Act, the Trump administration lambasted that law as imposing “unacceptable regulatory burdens on U.S. providers of space services to European customers.”
As a general matter, the United States expresses deep concern regarding measures in the proposed Act that would impose unacceptable regulatory burdens on U.S. providers of space services to European customers.
As close partners in civil, commercial, and security aspects of space cooperation for decades, the EU should proceed cautiously when developing and refining the proposed EU Space Act to ensure it provides a permissive and adaptable framework that promotes innovation, investment, and fair competition for the U.S., EU, and EU member states commercial sectors, while respecting each other’s sovereignty. Otherwise, the ability of the United States, the EU, and EU members to maintain government-to-government burden-sharing partnerships could be threatened. These non-tariff barriers would introduce challenges in the areas of space weather, remote sensing, space exploration, spaceflight safety, space debris mitigation and remediation, communications, as well as cooperations with the European Space Agency.
No one should be surprised by this response. Trump has always been aggressive in his desire to limit regulation. He has also been passionate about defending U.S. sovereignty. As I noted in June 2025 when the law was first released,
» Read more

This label would be more accurate if it read
“NOT made in the European Union”
In a comment the State Department posted on November 4, 2025 on the European Commission’s website for public comment in connection with the European Union’s proposed Space Act, the Trump administration lambasted that law as imposing “unacceptable regulatory burdens on U.S. providers of space services to European customers.”
As a general matter, the United States expresses deep concern regarding measures in the proposed Act that would impose unacceptable regulatory burdens on U.S. providers of space services to European customers.
As close partners in civil, commercial, and security aspects of space cooperation for decades, the EU should proceed cautiously when developing and refining the proposed EU Space Act to ensure it provides a permissive and adaptable framework that promotes innovation, investment, and fair competition for the U.S., EU, and EU member states commercial sectors, while respecting each other’s sovereignty. Otherwise, the ability of the United States, the EU, and EU members to maintain government-to-government burden-sharing partnerships could be threatened. These non-tariff barriers would introduce challenges in the areas of space weather, remote sensing, space exploration, spaceflight safety, space debris mitigation and remediation, communications, as well as cooperations with the European Space Agency.
No one should be surprised by this response. Trump has always been aggressive in his desire to limit regulation. He has also been passionate about defending U.S. sovereignty. As I noted in June 2025 when the law was first released,
» Read more