October 27, 2025 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Welsh space manufacturing startup Space Forge releases video of unfolding test in zero-G of its Pridwen reusable heat shield
The test was on a zero-g plane. The shield design unfolds like an umbrella.
- Video of the launchpad rollout of China’s next manned capsule, Shenzhou-21, and its rocket, Long March 2F
The launch of this next crew to the Tiangong-3 station is scheduled for October 31, 2025.
- The priorities just released by China’s communist party for its next five-year plan (2026-2030) appear to explicitly include space
No details yet released but this is no surprise. For the past two decades China’s government has been using its space program as a training ground for its top political leadership, which means that the leadership it now has is guaranteed to be very pro-space. Stay tuned for more details.
- NASA administrator Sean Duffy tries to claim some credit for Japan’s just launched HTV-X1 cargo freighter
He quickly gets lambasted on X: “HTV-X is a Japanese spacecraft, built by a Japanese company, launched on a Japanese rocket, from Japan, to be captured by a Japanese astronaut driving a Canadian robotic arm. Trump is President of the USA, not Japan, and had no influence over the HTV-X, as Duffy implies.”
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Welsh space manufacturing startup Space Forge releases video of unfolding test in zero-G of its Pridwen reusable heat shield
The test was on a zero-g plane. The shield design unfolds like an umbrella.
- Video of the launchpad rollout of China’s next manned capsule, Shenzhou-21, and its rocket, Long March 2F
The launch of this next crew to the Tiangong-3 station is scheduled for October 31, 2025.
- The priorities just released by China’s communist party for its next five-year plan (2026-2030) appear to explicitly include space
No details yet released but this is no surprise. For the past two decades China’s government has been using its space program as a training ground for its top political leadership, which means that the leadership it now has is guaranteed to be very pro-space. Stay tuned for more details.
- NASA administrator Sean Duffy tries to claim some credit for Japan’s just launched HTV-X1 cargo freighter
He quickly gets lambasted on X: “HTV-X is a Japanese spacecraft, built by a Japanese company, launched on a Japanese rocket, from Japan, to be captured by a Japanese astronaut driving a Canadian robotic arm. Trump is President of the USA, not Japan, and had no influence over the HTV-X, as Duffy implies.”
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News
Russia claims to have successfully tested a low-flying nuclear-powered cruise missile

Artist’s rendering of Burevestnik. Click for source.
According to claims coming from Russia’s state-run press yesterday, it has successfully tested a low-flying nuclear-powered cruise missile, dubbed Burevestnik (“Storm Petrel” in English), that uses a nuclear-powered rocket engine.
Few technical details have been released. The flight itself supposedly lasted fifteen hours during which the missile flew about 8,700 miles, making its average speed about 580 miles per hour. That speed is a little higher than the cruising speed of most airplanes. According to Russia’s state-run press, Burevestnik flies at an altitude of 80 to 300 feet and has an unlimited range.
It appears the missile captures air as it flies, compresses it and then sends it through the nuclear reactor to be heated, which when released as exhaust provides the thrust. If true, this missile is the equivalent of an autonomous airplane that can fly below radar detection anywhere on the globe, and thus a major threat to Russia’s enemies (which is essentially now the whole world).
At the same time, Russia’s ability to design, build and complete any high-tech project has been suspect for decades. Its government makes a lot of promises, but has almost never delivered.
Regardless, this technology bears watching. Expect the defense industry to use this story as a wedge with Congress to get more funding.

Artist’s rendering of Burevestnik. Click for source.
According to claims coming from Russia’s state-run press yesterday, it has successfully tested a low-flying nuclear-powered cruise missile, dubbed Burevestnik (“Storm Petrel” in English), that uses a nuclear-powered rocket engine.
Few technical details have been released. The flight itself supposedly lasted fifteen hours during which the missile flew about 8,700 miles, making its average speed about 580 miles per hour. That speed is a little higher than the cruising speed of most airplanes. According to Russia’s state-run press, Burevestnik flies at an altitude of 80 to 300 feet and has an unlimited range.
It appears the missile captures air as it flies, compresses it and then sends it through the nuclear reactor to be heated, which when released as exhaust provides the thrust. If true, this missile is the equivalent of an autonomous airplane that can fly below radar detection anywhere on the globe, and thus a major threat to Russia’s enemies (which is essentially now the whole world).
At the same time, Russia’s ability to design, build and complete any high-tech project has been suspect for decades. Its government makes a lot of promises, but has almost never delivered.
Regardless, this technology bears watching. Expect the defense industry to use this story as a wedge with Congress to get more funding.
New data supports theory of dark matter, but suggests inexplicably that it acts differently depending on the galaxy’s mass
The uncertainty of science: Astronomers analyzing twelve small and faint galaxies have determined that the existence of some form of mysterious undetected dark matter is necessary to explain the motions of their stars, and that another theory dubbed MOND that would make dark matter unnecessary fails to explain the data.
The authors found that the galaxies’ internal gravitational fields cannot be explained by visible matter alone, and that MOND predictions fail to reproduce the observed behaviour. They then compared their results with theoretical models that assume instead that these galaxies are surrounded by a massive halo of dark matter. Run on the UK’s DiRAC National Supercomputer facility, these dark matter models gave a much better match to the data.
Sounds good, eh? Not so fast. The research also found that large and small galaxies inexplicably interact with gravity and dark matter differently.
The research, published in Astronomy & Astrophysics, also challenges a long-standing assumption about how galaxies behave. Astronomers have long believed there is a simple link between the amount of visible matter in a galaxy and the strength of the gravitational pull it produces – known as the “radial acceleration relation.” While this relationship still holds for larger systems, the new study shows that it starts to break down in the smallest galaxies.
In other words, we don’t know enough yet to really explain the formation and behavior of galaxies. This really isn’t surprising, considering the time scales involved (billions of years) and the distances (millions to billions of light years).
The uncertainty of science: Astronomers analyzing twelve small and faint galaxies have determined that the existence of some form of mysterious undetected dark matter is necessary to explain the motions of their stars, and that another theory dubbed MOND that would make dark matter unnecessary fails to explain the data.
The authors found that the galaxies’ internal gravitational fields cannot be explained by visible matter alone, and that MOND predictions fail to reproduce the observed behaviour. They then compared their results with theoretical models that assume instead that these galaxies are surrounded by a massive halo of dark matter. Run on the UK’s DiRAC National Supercomputer facility, these dark matter models gave a much better match to the data.
Sounds good, eh? Not so fast. The research also found that large and small galaxies inexplicably interact with gravity and dark matter differently.
The research, published in Astronomy & Astrophysics, also challenges a long-standing assumption about how galaxies behave. Astronomers have long believed there is a simple link between the amount of visible matter in a galaxy and the strength of the gravitational pull it produces – known as the “radial acceleration relation.” While this relationship still holds for larger systems, the new study shows that it starts to break down in the smallest galaxies.
In other words, we don’t know enough yet to really explain the formation and behavior of galaxies. This really isn’t surprising, considering the time scales involved (billions of years) and the distances (millions to billions of light years).
Now available in hardback and paperback as well as ebook!
From the press release: In this ground-breaking new history of early America, historian Robert Zimmerman not only exposes the lie behind The New York Times 1619 Project that falsely claims slavery is central to the history of the United States, he also provides profound lessons about the nature of human societies, lessons important for Americans today as well as for all future settlers on Mars and elsewhere in space.
Conscious Choice: The origins of slavery in America and why it matters today and for our future in outer space, is a riveting page-turning story that documents how slavery slowly became pervasive in the southern British colonies of North America, colonies founded by a people and culture that not only did not allow slavery but in every way were hostile to the practice.
Conscious Choice does more however. In telling the tragic history of the Virginia colony and the rise of slavery there, Zimmerman lays out the proper path for creating healthy societies in places like the Moon and Mars.
“Zimmerman’s ground-breaking history provides every future generation the basic framework for establishing new societies on other worlds. We would be wise to heed what he says.” —Robert Zubrin, founder of the Mars Society.
All editions are available at Amazon, Barnes & Noble, and all book vendors, with the ebook priced at $5.99 before discount. All editions can also be purchased direct from the ebook publisher, ebookit, in which case you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
Autographed printed copies are also available at discount directly from the author (hardback $29.95; paperback $14.95; Shipping cost for either: $6.00). Just send an email to zimmerman @ nasw dot org.
Luxembourg capsule startup Space Cargo signs partnership deal with French startup
The Luxembourg capsule startup Space Cargo today announced it has signed a partnership deal with the French startup Comat to work together to develop Space Cargo’s Bentobox orbital platform for in-space manufacturing, “which offers a pressurized and thermally controlled autonomous environment in orbit to operate industrial payloads and return them to Earth.”
COMAT, an experienced space equipment manufacturer, will provide extensive engineering and manufacturing capabilities in space systems, mechanical structures, and payload equipment to design and produce high-performance hardware for in-space manufacturing activities.
Bentobox is not a fully operational capsule. Its design up to now required it to be launched as part of another company’s returnable capsule. It appears this deal with Comat will provide Bentobox greater capabilities, though it is unclear whether it will allow it to return to Earth on its own.
The Luxembourg capsule startup Space Cargo today announced it has signed a partnership deal with the French startup Comat to work together to develop Space Cargo’s Bentobox orbital platform for in-space manufacturing, “which offers a pressurized and thermally controlled autonomous environment in orbit to operate industrial payloads and return them to Earth.”
COMAT, an experienced space equipment manufacturer, will provide extensive engineering and manufacturing capabilities in space systems, mechanical structures, and payload equipment to design and produce high-performance hardware for in-space manufacturing activities.
Bentobox is not a fully operational capsule. Its design up to now required it to be launched as part of another company’s returnable capsule. It appears this deal with Comat will provide Bentobox greater capabilities, though it is unclear whether it will allow it to return to Earth on its own.
Ispace signs deals with companies in India and Japan
The Japanese lunar lander startup Ispace today announced it has signed partnership deals with two different companies, OrbitAid in India and Toyota in Japan.
The startup OrbitAid is India’s first “on-orbit refueling company”. It will provide Ispace’s landers with standardized docking ports as well as refueling capabilities.
The two companies aim to demonstrate the critical capabilities required for mission extension in the cislunar environment, enabling long-duration lunar operations and paving the way for a sustainable lunar economy. The integration of OrbitAID’s SIDRP interface is expected to not only optimize refueling, recharging, and data transmission capabilities but also support ispace’s efforts to enhance the performance and reliability of its landers. By enabling lunar refueling, both companies plan to facilitate deep-space exploration beyond Earth’s orbit.
Toyota meanwhile will provide technical support to Ispace as it develops its own second generation lunar rover, dubbed Lunar Cruiser. Ispace is already prepping a smaller rover that will fly on its next lunar landing mission.
Ispace has been signing on a range of customers and commercial partners in recent months, even though its only two attempts to land on the Moon both failed just before touch down. It has contracts with NASA, ESA, and JAXA for future missions. These new deals appear designed to strengthen and extend its capabilities beyond simply landing on the Moon, but also to provide interplanetary spacecraft as well.
The Japanese lunar lander startup Ispace today announced it has signed partnership deals with two different companies, OrbitAid in India and Toyota in Japan.
The startup OrbitAid is India’s first “on-orbit refueling company”. It will provide Ispace’s landers with standardized docking ports as well as refueling capabilities.
The two companies aim to demonstrate the critical capabilities required for mission extension in the cislunar environment, enabling long-duration lunar operations and paving the way for a sustainable lunar economy. The integration of OrbitAID’s SIDRP interface is expected to not only optimize refueling, recharging, and data transmission capabilities but also support ispace’s efforts to enhance the performance and reliability of its landers. By enabling lunar refueling, both companies plan to facilitate deep-space exploration beyond Earth’s orbit.
Toyota meanwhile will provide technical support to Ispace as it develops its own second generation lunar rover, dubbed Lunar Cruiser. Ispace is already prepping a smaller rover that will fly on its next lunar landing mission.
Ispace has been signing on a range of customers and commercial partners in recent months, even though its only two attempts to land on the Moon both failed just before touch down. It has contracts with NASA, ESA, and JAXA for future missions. These new deals appear designed to strengthen and extend its capabilities beyond simply landing on the Moon, but also to provide interplanetary spacecraft as well.
Leaving Earth: Space Stations, Rival Superpowers, and the Quest for Interplanetary Travel, can be purchased as an ebook everywhere for only $3.99 (before discount) at amazon, Barnes & Noble, all ebook vendors, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit.
If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big oppressive tech companies and I get a bigger cut much sooner.
Winner of the 2003 Eugene M. Emme Award of the American Astronautical Society.
"Leaving Earth is one of the best and certainly the most comprehensive summary of our drive into space that I have ever read. It will be invaluable to future scholars because it will tell them how the next chapter of human history opened." -- Arthur C. Clarke
Astrobotic’s Griffin lunar lander delayed again
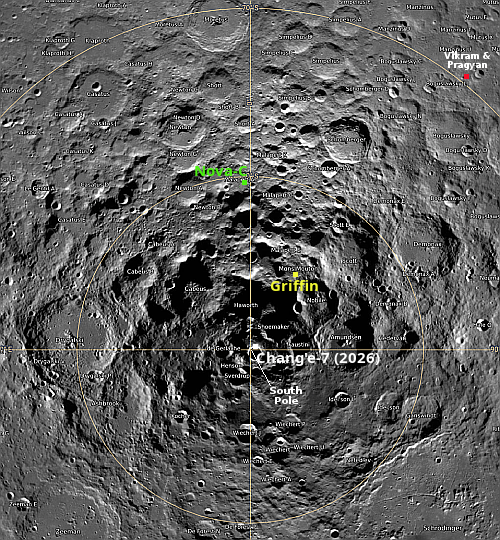
According to an update on the status of Astrobotic’s Griffin lunar lander posted on October 24, 2025, the company has now delayed the launch from the fall of 2025 to July 2026, apparently because the spacecraft is not yet assembled and its many components are still undergoing testing.
For example, none of Griffin’s four propellant tanks have yet been installed. Nor apparently has its core structure been fully integrated, with “tanks, ramps, attitude control thrusters, and solar panels” only now having completed “fit checks.”
The map to the right indicates the location where Griffin is supposed to land, about 100 miles from the Moon’s south pole. Nova-C, Intuitive Machines first attempt to soft land on the Moon, landed at the green dot, but failed when it fell over at landing. Intuitive Machines second lunar lander, Athena, also fell over when it landed in the same region that is now Griffin’s target landing zone.
Griffin has experienced repeated delays since the contract was issued to Astrobotic in 2020. The mission was originally supposed to launch in November 2023, carrying NASA’s Viper rover. In July 2022 however it was delayed one year to November 2024 because Astrobotic said it needed more time.
Sometime after the failure of Astrobotic’s first lunar lander, Peregrine, in January 2024, NASA once again delayed the Griffin mission, pushing it back another year to November 2025.
In July 2024 NASA canceled Viper, removing it as a payload from Griffin, because Viper was significantly overbudget and would not be ready for that fall 2025 launch. NASA however did not cancel Griffin. It appears however that Astrobotic wasn’t ready either for a launch in November, and thus this further delay.
Whether it will be ready by July remains unknown. Based on Astrobotic’s own update I have serious doubts. For a spacecraft that was supposed to originally launch in 2023, Griffin seems woefully unready now, two years past that date.

According to an update on the status of Astrobotic’s Griffin lunar lander posted on October 24, 2025, the company has now delayed the launch from the fall of 2025 to July 2026, apparently because the spacecraft is not yet assembled and its many components are still undergoing testing.
For example, none of Griffin’s four propellant tanks have yet been installed. Nor apparently has its core structure been fully integrated, with “tanks, ramps, attitude control thrusters, and solar panels” only now having completed “fit checks.”
The map to the right indicates the location where Griffin is supposed to land, about 100 miles from the Moon’s south pole. Nova-C, Intuitive Machines first attempt to soft land on the Moon, landed at the green dot, but failed when it fell over at landing. Intuitive Machines second lunar lander, Athena, also fell over when it landed in the same region that is now Griffin’s target landing zone.
Griffin has experienced repeated delays since the contract was issued to Astrobotic in 2020. The mission was originally supposed to launch in November 2023, carrying NASA’s Viper rover. In July 2022 however it was delayed one year to November 2024 because Astrobotic said it needed more time.
Sometime after the failure of Astrobotic’s first lunar lander, Peregrine, in January 2024, NASA once again delayed the Griffin mission, pushing it back another year to November 2025.
In July 2024 NASA canceled Viper, removing it as a payload from Griffin, because Viper was significantly overbudget and would not be ready for that fall 2025 launch. NASA however did not cancel Griffin. It appears however that Astrobotic wasn’t ready either for a launch in November, and thus this further delay.
Whether it will be ready by July remains unknown. Based on Astrobotic’s own update I have serious doubts. For a spacecraft that was supposed to originally launch in 2023, Griffin seems woefully unready now, two years past that date.
Two more launches, by China and SpaceX respectively
The global launch industry added two more launches to its 2025 launch totals since yesterday. First, China launched what its state-run press described as a Earth imaging satellite, its Long March 3B rocket lifting off from its Xichang spaceport in southwest China. No information was released as to where the rocket’s lower stages — using very toxic hypergolic fuels — crashed inside China.
Then early today SpaceX placed another 29 Starlink satellites into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida. The first stage completed its 24th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
With this launch, the U.S. set a new annual record for successful launches, 158, beating the record set in 2024. In both years, the record was almost entirely due to SpaceX and its Falcon 9. Rocket Lab’s numbers continue to rise, suggesting the company is about to finally begin launching more than once a month. All the other American rocket companies, especially ULA, have in the past two years failed to deliver the number of launches promised. All continue to promise big numbers in 2026. We shall see.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
139 SpaceX
65 China
13 Russia
13 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 139 to 107.
The global launch industry added two more launches to its 2025 launch totals since yesterday. First, China launched what its state-run press described as a Earth imaging satellite, its Long March 3B rocket lifting off from its Xichang spaceport in southwest China. No information was released as to where the rocket’s lower stages — using very toxic hypergolic fuels — crashed inside China.
Then early today SpaceX placed another 29 Starlink satellites into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida. The first stage completed its 24th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
With this launch, the U.S. set a new annual record for successful launches, 158, beating the record set in 2024. In both years, the record was almost entirely due to SpaceX and its Falcon 9. Rocket Lab’s numbers continue to rise, suggesting the company is about to finally begin launching more than once a month. All the other American rocket companies, especially ULA, have in the past two years failed to deliver the number of launches promised. All continue to promise big numbers in 2026. We shall see.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
139 SpaceX
65 China
13 Russia
13 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 139 to 107.
Japan launches a new upgraded version of its HTV cargo freighter
Japan today (October 26th in Japan) successfully launched to ISS a new upgraded version of its HTV cargo freighter, its H3 rocket lifting off from its Tanegashima spaceport in southern Japan.
The HTV-X1 carries more than freight. After its cargo is unloaded at ISS it will spend an additional three months flying independently in orbit, where engineers will conduct three additional experiments. JAXA, Japan’s space agency, hopes it can market HTV-X1 for use by the commercial space stations presently being developed. It is also marketing it as a potential orbital capsule that others can use for in-space manufacturing.
This was only the third launch by Japan in 2025, so there is no change to the 2025 leader board:
138 SpaceX
64 China
13 Russia
13 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 138 to 106.
Japan today (October 26th in Japan) successfully launched to ISS a new upgraded version of its HTV cargo freighter, its H3 rocket lifting off from its Tanegashima spaceport in southern Japan.
The HTV-X1 carries more than freight. After its cargo is unloaded at ISS it will spend an additional three months flying independently in orbit, where engineers will conduct three additional experiments. JAXA, Japan’s space agency, hopes it can market HTV-X1 for use by the commercial space stations presently being developed. It is also marketing it as a potential orbital capsule that others can use for in-space manufacturing.
This was only the third launch by Japan in 2025, so there is no change to the 2025 leader board:
138 SpaceX
64 China
13 Russia
13 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 138 to 106.
Nova Scotia spaceport wins $10 million credit line from Canadian government

Proposed Canadian spaceports
Maritime Launch Services, the startup that has been trying to establish a spaceport in Nova Scotia since 2016, without any success, was this week awarded a $10 million credit line from Canadian government’s Export Development agency (EDC).
EDC is Canada’s export credit agency, established in 1944 to help Canadian businesses of all sizes grow globally through trade financing, insurance, and market expertise. As part of its corporate strategy, EDC is committed to allocating strategic risk capital to developing trade-enabling infrastructure to help Canada become a more resilient, competitive, and secure global trading nation. EDC’s support of Maritime Launch as it develops Spaceport Nova Scotia will significantly strengthen Canada’s position in the defence and security sector, where space is an increasingly vital domain.
….The terms of the agreement provide development funding for Spaceport Nova Scotia’s next phase of construction, including launch pad and infrastructure development required to support future orbital missions.
This award is a bit puzzling, as Maritime has done nothing in the past decade to instill any confidence it is going to fulfill any of its promises. Its original plan, to offer satellite companies a launchpad and a rocket (made by a Ukrainian company) failed in 2022 when Russian invaded the Ukraine. Since the Maritime has struggled to get any other rocket companies interested in launching from Spaceport Nova Scotia.
Meanwhile, a second Canadian commercial spaceport, the Atlantic Spaceport in Newfoundland, was proposed only three years ago. It is developing its own rocket, and has already signed contracts with other companies for its mission control center and tracking stations. In addition, it twice attempted a suborbital test launch of a smaller rocket, though both attempts were scrubbed due to fuel leaks in ground systems.
Whether this grant can jump start Maritime’s spaceport remains an open question. Very clearly, the Canadian government hopes so.

Proposed Canadian spaceports
Maritime Launch Services, the startup that has been trying to establish a spaceport in Nova Scotia since 2016, without any success, was this week awarded a $10 million credit line from Canadian government’s Export Development agency (EDC).
EDC is Canada’s export credit agency, established in 1944 to help Canadian businesses of all sizes grow globally through trade financing, insurance, and market expertise. As part of its corporate strategy, EDC is committed to allocating strategic risk capital to developing trade-enabling infrastructure to help Canada become a more resilient, competitive, and secure global trading nation. EDC’s support of Maritime Launch as it develops Spaceport Nova Scotia will significantly strengthen Canada’s position in the defence and security sector, where space is an increasingly vital domain.
….The terms of the agreement provide development funding for Spaceport Nova Scotia’s next phase of construction, including launch pad and infrastructure development required to support future orbital missions.
This award is a bit puzzling, as Maritime has done nothing in the past decade to instill any confidence it is going to fulfill any of its promises. Its original plan, to offer satellite companies a launchpad and a rocket (made by a Ukrainian company) failed in 2022 when Russian invaded the Ukraine. Since the Maritime has struggled to get any other rocket companies interested in launching from Spaceport Nova Scotia.
Meanwhile, a second Canadian commercial spaceport, the Atlantic Spaceport in Newfoundland, was proposed only three years ago. It is developing its own rocket, and has already signed contracts with other companies for its mission control center and tracking stations. In addition, it twice attempted a suborbital test launch of a smaller rocket, though both attempts were scrubbed due to fuel leaks in ground systems.
Whether this grant can jump start Maritime’s spaceport remains an open question. Very clearly, the Canadian government hopes so.
SpaceX launches 28 Starlink satellites, sets new annual launch record
SpaceX this morning successfully launched another 28 Starlink satellites, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The first stage completed its 19th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Pacific.
With this launch SpaceX set a new record by a private company for the most successful launches in a single year, beating the record it set last year. In fact, this is the sixth year in a row that SpaceX has reset this particular record. Where once it was difficult for the world’s entire launch industry to complete 100 launches in a year — using government controlled rockets — SpaceX has shown that much greater things can happen if private enterprise, pursing profit, is given its head and allowed to run freely.
This launch also brought the U.S. launch total to 157, which matches the country’s record from last year. Expect a new record to be set before the week is out.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
138 SpaceX
64 China
13 Russia
13 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 138 to 105. Japan has a launch scheduled for later today, its H3 rocket carrying Japan’s upgraded HTV-X1 cargo freighter on a mission to ISS.
SpaceX this morning successfully launched another 28 Starlink satellites, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The first stage completed its 19th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Pacific.
With this launch SpaceX set a new record by a private company for the most successful launches in a single year, beating the record it set last year. In fact, this is the sixth year in a row that SpaceX has reset this particular record. Where once it was difficult for the world’s entire launch industry to complete 100 launches in a year — using government controlled rockets — SpaceX has shown that much greater things can happen if private enterprise, pursing profit, is given its head and allowed to run freely.
This launch also brought the U.S. launch total to 157, which matches the country’s record from last year. Expect a new record to be set before the week is out.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
138 SpaceX
64 China
13 Russia
13 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 138 to 105. Japan has a launch scheduled for later today, its H3 rocket carrying Japan’s upgraded HTV-X1 cargo freighter on a mission to ISS.
October 24, 2025 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
Deconstructed – How the bathyscaphe Trieste was the first to reach the ocean’s deepest point
October 24, 2025 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Everyday Astronaut asks great question: Why is NASA spending $700 million for developing new SLS upper stage when ULA’s Centaur-V is available for only $120 million?
Tim Dodd seems baffled, but then he is young and hasn’t lived through decades of NASA pork that accomplishes nothing. That new upper stage is just more of the same.
- NASA astronaut shows off Orion’s bathroom
Talk about overkill for a capsule. No wonder Orion is too heavy for almost every rocket available.
- Startup Apex to fly a commercially-developed space-based interceptor demo on its own dime
The company hopes the mission will convince defense contractors and satellite companies to buy its product.
- A rehash of Sierra Space’s Dream Chaser project
No real news, though overall the article underlines the failure of Sierra Space to get off the ground. It also provides evidence to explain why NASA abandoned Dream Chaser as an ISS cargo craft.
- Blue Origin touts the delivery of its 30th BE-4 engine to ULA
This gives ULA enough engines for at least fifteen launches of its Vulcan rocket, which is about the number of launches the company hopes to do in 2026
- In 2010 NASA analyzed what museums to send shuttles to and ranked Houston low
So what? These bureaucratic rankings meant nothing. All that mattered for choosing the cities that would get shuttles were political considerations, and Obama wished to reward blue states.
- Video of the demolition of one of the service towers for the Zenit rocket at Baikonur
Zenit was built by the Ukraine, now banned by Russia from Baikonur. Russia now wants to use this launchpad for its new Soyuz-5 rocket. Kazakhstan, which owns the site, has been resistant. It is unclear if this demolition means Kazakhstan has changed its mind.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Everyday Astronaut asks great question: Why is NASA spending $700 million for developing new SLS upper stage when ULA’s Centaur-V is available for only $120 million?
Tim Dodd seems baffled, but then he is young and hasn’t lived through decades of NASA pork that accomplishes nothing. That new upper stage is just more of the same.
- NASA astronaut shows off Orion’s bathroom
Talk about overkill for a capsule. No wonder Orion is too heavy for almost every rocket available.
- Startup Apex to fly a commercially-developed space-based interceptor demo on its own dime
The company hopes the mission will convince defense contractors and satellite companies to buy its product.
- A rehash of Sierra Space’s Dream Chaser project
No real news, though overall the article underlines the failure of Sierra Space to get off the ground. It also provides evidence to explain why NASA abandoned Dream Chaser as an ISS cargo craft.
- Blue Origin touts the delivery of its 30th BE-4 engine to ULA
This gives ULA enough engines for at least fifteen launches of its Vulcan rocket, which is about the number of launches the company hopes to do in 2026
- In 2010 NASA analyzed what museums to send shuttles to and ranked Houston low
So what? These bureaucratic rankings meant nothing. All that mattered for choosing the cities that would get shuttles were political considerations, and Obama wished to reward blue states.
- Video of the demolition of one of the service towers for the Zenit rocket at Baikonur
Zenit was built by the Ukraine, now banned by Russia from Baikonur. Russia now wants to use this launchpad for its new Soyuz-5 rocket. Kazakhstan, which owns the site, has been resistant. It is unclear if this demolition means Kazakhstan has changed its mind.
Two lawsuits filed against NASA at its Marshall Space Flight Center
Two lawsuits against NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center were announced yesterday, one by several employees citing discrimination and the second by the government union representing Marshall employees protesting the Trump executive order that strips it of its collective bargaining rights.
The timing of both announcements strongly suggests the lawsuits are a coordinated effort. The discrimination suit protests the demand of the Trump administration that government employees come back to the office to work. The suit says the agency has not made reasonable accommodation for the suing employees to work at home. It also appears that the lead employee in the suit has made it a habit of doing so, having already won $30K in a settlement of a 2024 lawsuit.
The second suit is of course more significant, as it challenges the president’s power.
The complaint, filed in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia, seeks to invalidate Executive Order 14343, issued by President Trump on Aug. 28. The order excludes NASA and five other agencies from coverage under the Federal Service Labor-Management Relations Statute (FSLMRS), effectively terminating their union representation rights on the grounds of “national security”.
According to the complaint, the Trump Administration justified the exclusion by claiming these agencies have a primary function of national security work and that collective bargaining is inconsistent with those requirements. A White House Fact Sheet accompanying the order stated that collective bargaining “can delay the implementation of time-sensitive national security measures”.
IFPTE vehemently disputes this characterization. The union argues that NASA’s primary mission is “not national security,” but rather scientific exploration for the “benefit of all humanity”. The complaint cites the National Aeronautics and Space Act, which states that “activities in space should be devoted to peaceful purposes for the benefit of all humankind”.
The existence of all these government unions comes originally from an executive order by President John Kennedy. It seems Trump should have the right to cancel that order. The lawsuit also argues no, that Trump is acting beyond his legal authority.
Isn’t it interesting how presidents who are Democrats always have the power to issue executive orders n matter how outrageous (such as was done frequently by Obama and Biden), but Republican presidents like Trump do not.
Two lawsuits against NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center were announced yesterday, one by several employees citing discrimination and the second by the government union representing Marshall employees protesting the Trump executive order that strips it of its collective bargaining rights.
The timing of both announcements strongly suggests the lawsuits are a coordinated effort. The discrimination suit protests the demand of the Trump administration that government employees come back to the office to work. The suit says the agency has not made reasonable accommodation for the suing employees to work at home. It also appears that the lead employee in the suit has made it a habit of doing so, having already won $30K in a settlement of a 2024 lawsuit.
The second suit is of course more significant, as it challenges the president’s power.
The complaint, filed in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia, seeks to invalidate Executive Order 14343, issued by President Trump on Aug. 28. The order excludes NASA and five other agencies from coverage under the Federal Service Labor-Management Relations Statute (FSLMRS), effectively terminating their union representation rights on the grounds of “national security”.
According to the complaint, the Trump Administration justified the exclusion by claiming these agencies have a primary function of national security work and that collective bargaining is inconsistent with those requirements. A White House Fact Sheet accompanying the order stated that collective bargaining “can delay the implementation of time-sensitive national security measures”.
IFPTE vehemently disputes this characterization. The union argues that NASA’s primary mission is “not national security,” but rather scientific exploration for the “benefit of all humanity”. The complaint cites the National Aeronautics and Space Act, which states that “activities in space should be devoted to peaceful purposes for the benefit of all humankind”.
The existence of all these government unions comes originally from an executive order by President John Kennedy. It seems Trump should have the right to cancel that order. The lawsuit also argues no, that Trump is acting beyond his legal authority.
Isn’t it interesting how presidents who are Democrats always have the power to issue executive orders n matter how outrageous (such as was done frequently by Obama and Biden), but Republican presidents like Trump do not.
SpaceX launches communications satellite for the Spanish government
SpaceX tonight successfully placed a Spanish communications satellite into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida.
The satellite will provide communications for Spain’s military and government. The first stage completed its 22nd flight, but because of the needs of the payload, there was not enough fuel left for it to land on a drone ship. This was its last flight, the stage falling into the Atlantic. The two fairings completed their 16th and 28th flights respectively.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
137 SpaceX
64 China
13 Russia
13 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 137 to 105.
SpaceX has now matched the annual launch record it set last year, and done it with more than two months left to go in 2025. Whether it can reach its goal of about 180 launches this year seems doubtful, but it will definitely come close. It is averaging about 14 launches per month, which means it could complete about 28 to 30 before the end of December.
SpaceX tonight successfully placed a Spanish communications satellite into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida.
The satellite will provide communications for Spain’s military and government. The first stage completed its 22nd flight, but because of the needs of the payload, there was not enough fuel left for it to land on a drone ship. This was its last flight, the stage falling into the Atlantic. The two fairings completed their 16th and 28th flights respectively.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
137 SpaceX
64 China
13 Russia
13 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 137 to 105.
SpaceX has now matched the annual launch record it set last year, and done it with more than two months left to go in 2025. Whether it can reach its goal of about 180 launches this year seems doubtful, but it will definitely come close. It is averaging about 14 launches per month, which means it could complete about 28 to 30 before the end of December.
Eivør & Danish National Symphony Orchestra – Trøllabundin
An evening pause: Performed live 2023 as part of a concert dubbed, “Viking.” From the comments on the webpage:
Trøllabundin means spellbound. In the viking age, ‘Galder’ was a kind of magic song that was used in seiðr (magic/witchcraft) practiced by mainly women, and to ‘galdra’ was to affect something by magic singing.
Hat tip Judd Clark.
October 23, 2025 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- AstroLab’s FLIP rover began thermal vacuum chamber testing in Los Angeles yesterday
This small unmanned rover will fly on Astrobotic’s Griffin lunar lander, and is intended as a testbed by AstroLab to prove the design of the larger manned rover it wants to build for NASA’s Artemis program. It also replaces NASA’s cancelled VIPER rover on Griffin.
- New Glenn’s first and second stages are now mated
This will be Blue Origin’s second launch of New Glenn, presently scheduled for November 9, 2025.
- Chinese pseudo-company Landspace completed the full rehearsal of its Zhuque-3 rocket in preparation for first launch
The rocket is essentially a copy of the Falcon 9, though Landspace will not attempt recovery of the first stage on the initial few flights.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- AstroLab’s FLIP rover began thermal vacuum chamber testing in Los Angeles yesterday
This small unmanned rover will fly on Astrobotic’s Griffin lunar lander, and is intended as a testbed by AstroLab to prove the design of the larger manned rover it wants to build for NASA’s Artemis program. It also replaces NASA’s cancelled VIPER rover on Griffin.
- New Glenn’s first and second stages are now mated
This will be Blue Origin’s second launch of New Glenn, presently scheduled for November 9, 2025.
- Chinese pseudo-company Landspace completed the full rehearsal of its Zhuque-3 rocket in preparation for first launch
The rocket is essentially a copy of the Falcon 9, though Landspace will not attempt recovery of the first stage on the initial few flights.
China launches a “communication technology test” satellite
Using its most powerful rocket, the Long March 5, China today placed in orbit what its state-run press called a “communication technology test satellite”, the rocket lifting off from China’s coastal Wenchang spaceport.
Though the rocket’s flight path over the ocean meant its lower stages would not crash on land, China did warn the Philippines that some of the drop zones were within its fishing regions, and that fishermen should stay out for about an hour this morning.
China’s state-run press provided no details about the satellite. That it needed a very powerful rocket suggests it is some variation of AST SpaceMobile’s very large Bluebird satellites for providing direct phone-to-satellite service. If so, this is just another example of China copying the work of a private company in the west.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
136 SpaceX
64 China
13 Russia
13 Rocket Lab
SpaceX still leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 136 to 105.
Using its most powerful rocket, the Long March 5, China today placed in orbit what its state-run press called a “communication technology test satellite”, the rocket lifting off from China’s coastal Wenchang spaceport.
Though the rocket’s flight path over the ocean meant its lower stages would not crash on land, China did warn the Philippines that some of the drop zones were within its fishing regions, and that fishermen should stay out for about an hour this morning.
China’s state-run press provided no details about the satellite. That it needed a very powerful rocket suggests it is some variation of AST SpaceMobile’s very large Bluebird satellites for providing direct phone-to-satellite service. If so, this is just another example of China copying the work of a private company in the west.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
136 SpaceX
64 China
13 Russia
13 Rocket Lab
SpaceX still leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 136 to 105.
Weird “What the heck?!” pedestal crater on Mars
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on August 26, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). While the full image shows what the camera team labels as the “ridges” that cover this area, the most prominent feature in the whole landscape is this half-mile-wide pedestal crater, sitting about 50 to 100 feet above the surrounding terrain.
What makes this strange butte so weird is the plateau on top, criss-crossed with ridges and hollows in a manner that defies any obvious geological explanation.
Pedestal craters are not uncommon on Mars, and in fact a bunch of others are found throughout this region. The theory for their formation is that they formed when the surface here was much higher. The impact made the crater floor more dense and resistant to erosion, so as the surrounding terrain wore aware the crater ended up being a butte.
However, pedestal craters usually have relatively smooth tops, making this crater another example of a “What the heck?” image.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on August 26, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). While the full image shows what the camera team labels as the “ridges” that cover this area, the most prominent feature in the whole landscape is this half-mile-wide pedestal crater, sitting about 50 to 100 feet above the surrounding terrain.
What makes this strange butte so weird is the plateau on top, criss-crossed with ridges and hollows in a manner that defies any obvious geological explanation.
Pedestal craters are not uncommon on Mars, and in fact a bunch of others are found throughout this region. The theory for their formation is that they formed when the surface here was much higher. The impact made the crater floor more dense and resistant to erosion, so as the surrounding terrain wore aware the crater ended up being a butte.
However, pedestal craters usually have relatively smooth tops, making this crater another example of a “What the heck?” image.
» Read more
European companies Airbus, Leonardo, and Thales merge their satellite divisions
The three European aerospace companies Airbus, Leonardo, and Thales today confirmed previous rumors and announced they are merging their satellite divisions into a new company, dubbed Project Bromo, in order to better compete with the giant satellite constellations in the U.S. and China.
The preliminary deal wraps up months of three-way talks and clears the path to create a single company with annual revenue of about €6.5 billion ($7.5 billion). Airbus will own 35% of the group, with the other two partners each holding 32.5% stakes, according to a joint release.
The alliance, dubbed Project Bromo, is seen as a key litmus test for Europe to consolidate its fragmented defense and space industries to better compete with US and Chinese competitors. It aims to unify Europe’s satellite efforts and provide more autonomy in a segment that has become commercially and geopolitically vital.
These companies are coming to this competition very late in the game. SpaceX already has more than 8,000 satellites in orbit, and new constellations by Amazon and several Chinese pseudo-companies have already begun launching satellites. Moreover, this smacks more of a consolidation resulting from these three companies inability to compete, rather than an effort to establish a new company capable of doing so.
The three European aerospace companies Airbus, Leonardo, and Thales today confirmed previous rumors and announced they are merging their satellite divisions into a new company, dubbed Project Bromo, in order to better compete with the giant satellite constellations in the U.S. and China.
The preliminary deal wraps up months of three-way talks and clears the path to create a single company with annual revenue of about €6.5 billion ($7.5 billion). Airbus will own 35% of the group, with the other two partners each holding 32.5% stakes, according to a joint release.
The alliance, dubbed Project Bromo, is seen as a key litmus test for Europe to consolidate its fragmented defense and space industries to better compete with US and Chinese competitors. It aims to unify Europe’s satellite efforts and provide more autonomy in a segment that has become commercially and geopolitically vital.
These companies are coming to this competition very late in the game. SpaceX already has more than 8,000 satellites in orbit, and new constellations by Amazon and several Chinese pseudo-companies have already begun launching satellites. Moreover, this smacks more of a consolidation resulting from these three companies inability to compete, rather than an effort to establish a new company capable of doing so.
Betelgeuse’s long predicted companion star confirmed

The image of the companion, released previously
in July 2025.
Astronomers have now confirmed prior observations announced in July 2025 of Betelgeuse’s long predicted companion star.
The July conclusions found faint evidence of the companion, shown to the right, from data collected by the Gemini telescope in Hawaii, when the modeling said the companion was at its farthest point from the central star.. This new research was based on new observations in December 2024 by the Hubble and Chandra space telescopes, taken at the same time.
During this ideal observational window, the Gemini North Telescope in Hawaii captured a faint image near Betelgeuse that could be its tiny companion. In a separate study, the Carnegie Mellon-led team used Chandra to collect X-ray data to determine the nature of the mysterious object. “It could have been a white dwarf. It could have been a neutron star. And those are very, very different objects,” O’Grady said. “If it was one of those objects, it would point to a very different evolutionary history for the system.”
But it wasn’t either. O’Grady and her collaborators found no evidence of accretion — a hallmark of compact objects like neutron stars or white dwarfs. Their findings, to be published in The Astrophysical Journal, point instead to a young stellar object roughly the size of the Sun. A companion paper from researchers at the Flatiron Institute, using Hubble data, helped narrow down the companion’s size.
You can read their paper here [pdf]. It estimates the companion to have a mass about 1.4 to 2 times that of the Sun.

The image of the companion, released previously
in July 2025.
Astronomers have now confirmed prior observations announced in July 2025 of Betelgeuse’s long predicted companion star.
The July conclusions found faint evidence of the companion, shown to the right, from data collected by the Gemini telescope in Hawaii, when the modeling said the companion was at its farthest point from the central star.. This new research was based on new observations in December 2024 by the Hubble and Chandra space telescopes, taken at the same time.
During this ideal observational window, the Gemini North Telescope in Hawaii captured a faint image near Betelgeuse that could be its tiny companion. In a separate study, the Carnegie Mellon-led team used Chandra to collect X-ray data to determine the nature of the mysterious object. “It could have been a white dwarf. It could have been a neutron star. And those are very, very different objects,” O’Grady said. “If it was one of those objects, it would point to a very different evolutionary history for the system.”
But it wasn’t either. O’Grady and her collaborators found no evidence of accretion — a hallmark of compact objects like neutron stars or white dwarfs. Their findings, to be published in The Astrophysical Journal, point instead to a young stellar object roughly the size of the Sun. A companion paper from researchers at the Flatiron Institute, using Hubble data, helped narrow down the companion’s size.
You can read their paper here [pdf]. It estimates the companion to have a mass about 1.4 to 2 times that of the Sun.
The second known asteroid discovered orbiting closer to the Sun than Venus
Using ground-based telescopes scanning the morning and evening sky, an astronomer has discovered only the second known asteroid circling the Sun within the orbit of Venus.
The manner of the discovery itself, by Scott Sheppard of the Carnegie Institution, also illustrated our modern world.
He first observed it using the Cerro Tololo Dark Energy Camera the night before leaving on a hiking trip. Because the object was moving fast, he knew it must be very close to the Sun, so he’d need to image it again and soon to confirm its orbit before it became lost in the Sun’s glare.
“I had to schedule new observations to re-observe the object while deep in the forest of Pennsylvania,” he says. “It is just amazing that even camp sites today have good Wi-Fi access — that allowed me to download the new second observations of this asteroid and determine its unique orbit that is interior to Venus.”
Astronomers have found so few asteroids close to the Sun because the Sun’s glare makes observations difficult. Some scientists like to speculate to the press that there could be a large unknown population, with some posing a threat to Earth. The computer predictions however say the population is small, because the push of the Sun’s light and radiation should easily shift their orbits outward or make them unstable.
The two asteroids so far found confirm these models in a counter-intuitive way. The new asteroid is estimated to be a little less than a half mile across, while the previously discovered asteroid is thought to have a diameter of more than a mile. Their larger size makes it harder for the Sun’s light and radiation to shift their orbit.
In other words, this inner population of asteroids is likely to be low in number, but made up of larger objects.
Using ground-based telescopes scanning the morning and evening sky, an astronomer has discovered only the second known asteroid circling the Sun within the orbit of Venus.
The manner of the discovery itself, by Scott Sheppard of the Carnegie Institution, also illustrated our modern world.
He first observed it using the Cerro Tololo Dark Energy Camera the night before leaving on a hiking trip. Because the object was moving fast, he knew it must be very close to the Sun, so he’d need to image it again and soon to confirm its orbit before it became lost in the Sun’s glare.
“I had to schedule new observations to re-observe the object while deep in the forest of Pennsylvania,” he says. “It is just amazing that even camp sites today have good Wi-Fi access — that allowed me to download the new second observations of this asteroid and determine its unique orbit that is interior to Venus.”
Astronomers have found so few asteroids close to the Sun because the Sun’s glare makes observations difficult. Some scientists like to speculate to the press that there could be a large unknown population, with some posing a threat to Earth. The computer predictions however say the population is small, because the push of the Sun’s light and radiation should easily shift their orbits outward or make them unstable.
The two asteroids so far found confirm these models in a counter-intuitive way. The new asteroid is estimated to be a little less than a half mile across, while the previously discovered asteroid is thought to have a diameter of more than a mile. Their larger size makes it harder for the Sun’s light and radiation to shift their orbit.
In other words, this inner population of asteroids is likely to be low in number, but made up of larger objects.
Lockheed Martin invests in rotating detonation rocket engine startup Venus Aerospace
The venture capital division at Lockheed Martin, which has previously invested in a number of aerospace startups, has now invested in the rocket engine startup Venus Aerospace, which is developing a new radical design called a rotating detonation rocket.
Venus Aerospace, based in Houston, Texas, has developed a rotating detonation rocket engine (RDRE) — a propulsion system that uses a continuously rotating detonation shockwave to generate thrust, promising more efficiency than conventional rocket engines. The company completed the first U.S. flight test of a 2,000-pound-thrust RDRE in May, launching the engine on a small rocket at Spaceport America in New Mexico. This engine could be used to replace solid rocket motors to power munitions and rockets, Sassie Duggleby, co-founder and chief executive of Venus Aerospace, said at Axios “Future of Defense” conference.
The amount of Lockheed Martin Ventures’ investment was not disclosed. Duggleby said the funding will “advance our capabilities to deliver at scale and deploy the engine.”
Venus Aerospace has already raised more than $100 million in private investment capital. This new influx from an established big space player will certainly strengthen its financial position.
Lockheed Martin has previously invested in rocket startups Rocket Lab, ABL, Orbex, and X-Bow. It has also invested in the orbital tug startup Orbit Fab, the orbital capsule company Inversion Space, and the satellite startup Terran Orbital, which it ended up buying entirely.
The venture capital division at Lockheed Martin, which has previously invested in a number of aerospace startups, has now invested in the rocket engine startup Venus Aerospace, which is developing a new radical design called a rotating detonation rocket.
Venus Aerospace, based in Houston, Texas, has developed a rotating detonation rocket engine (RDRE) — a propulsion system that uses a continuously rotating detonation shockwave to generate thrust, promising more efficiency than conventional rocket engines. The company completed the first U.S. flight test of a 2,000-pound-thrust RDRE in May, launching the engine on a small rocket at Spaceport America in New Mexico. This engine could be used to replace solid rocket motors to power munitions and rockets, Sassie Duggleby, co-founder and chief executive of Venus Aerospace, said at Axios “Future of Defense” conference.
The amount of Lockheed Martin Ventures’ investment was not disclosed. Duggleby said the funding will “advance our capabilities to deliver at scale and deploy the engine.”
Venus Aerospace has already raised more than $100 million in private investment capital. This new influx from an established big space player will certainly strengthen its financial position.
Lockheed Martin has previously invested in rocket startups Rocket Lab, ABL, Orbex, and X-Bow. It has also invested in the orbital tug startup Orbit Fab, the orbital capsule company Inversion Space, and the satellite startup Terran Orbital, which it ended up buying entirely.
Hungary becomes the 57th nation to sign the Artemis Accords
NASA’s acting administrator, Sean Duffy, announced yesterday in a tweet that Hungary has now signed the Artemis Accords.
There was no NASA press release because of the government shutdown.
Hungary is now the 57th nation to sign the accords. The full list of nations now part of this American space alliance: Angola, Argentina, Armenia, Australia, Austria, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Belgium, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, India, Israel, Italy, Japan, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Mexico, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Nigeria, Norway, Panama, Peru, Poland, Romania, Rwanda, Saudi Arabia, Senegal, Singapore, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Thailand, the United Kingdom, the United Arab Emirates, the Ukraine, the United States and Uruguay.
The addition of Hungary means that almost the entire European portion of the former Soviet bloc has now joined the alliance. I suspect the desire of these nations to ally with the U.S. and the west is a reflection of their fear of Russia, which has not been kind to its neighbors, both during the Cold War as well as recently.
It still remains to be seen if this alliance will be used by the American government to encourage property rights in space, something that the Outer Space Treaty presently outlaws. That appeared to be its original goal when the accords were created during the first Trump administration. That goal however was abandoned during the Biden administration, making the accords alliance more of a globalist collective in support of the Outer Space Treaty’s restrictions.
So far during Trump’s second administration no action has been taken to reassert those original goals.
NASA’s acting administrator, Sean Duffy, announced yesterday in a tweet that Hungary has now signed the Artemis Accords.
There was no NASA press release because of the government shutdown.
Hungary is now the 57th nation to sign the accords. The full list of nations now part of this American space alliance: Angola, Argentina, Armenia, Australia, Austria, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Belgium, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, India, Israel, Italy, Japan, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Mexico, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Nigeria, Norway, Panama, Peru, Poland, Romania, Rwanda, Saudi Arabia, Senegal, Singapore, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Thailand, the United Kingdom, the United Arab Emirates, the Ukraine, the United States and Uruguay.
The addition of Hungary means that almost the entire European portion of the former Soviet bloc has now joined the alliance. I suspect the desire of these nations to ally with the U.S. and the west is a reflection of their fear of Russia, which has not been kind to its neighbors, both during the Cold War as well as recently.
It still remains to be seen if this alliance will be used by the American government to encourage property rights in space, something that the Outer Space Treaty presently outlaws. That appeared to be its original goal when the accords were created during the first Trump administration. That goal however was abandoned during the Biden administration, making the accords alliance more of a globalist collective in support of the Outer Space Treaty’s restrictions.
So far during Trump’s second administration no action has been taken to reassert those original goals.
October 22, 2025 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
The Guys Downstairs – How Long Has This Been Going On
<An evening paus: A very nice cover.
Hat tip Cotour, who adds “These old guys have this piece nailed down!”
What bad news is NASA hiding about the heat shield it will use on the next Orion/SLS manned mission around the Moon?

Damage to Orion heat shield caused during re-entry in 2022,
including “cavities resulting from the loss of large chunks”
Even as our uneducated media goes bonkers over another Musk kerfuffle, this time with interim NASA administration Sean Duffy, it is ignoring what now appears to be a strong effort by NASA to cover up some serious issues with the Orion capsule’s heat shield, issues that might be far more serious than outlined in a May 2024 inspector general (IG) report.
That IG report [pdf] found the following:
Specifically, portions of the char layer wore away differently than NASA engineers predicted, cracking and breaking off the spacecraft in fragments that created a trail of debris rather than melting away as designed (see Figure 3 [shown to the right]). The unexpected behavior of the Avcoat creates a risk that the heat shield may not sufficiently protect the capsule’s systems and crew from the extreme heat of reentry on future missions. Moreover, while there was no evidence of impact with the Crew Module, the quantity and size of the debris could have caused enough structural damage to cause one of Orion’s parachutes to fail. Should the same issue occur on future Artemis missions, it could lead to the loss of the vehicle or crew.
In our judgment, the unexpected behavior of the heat shield poses a significant risk to the safety of
future crewed missions. [emphasis mine]
NASA spent the next few months reviewing the situation, and decided in December 2024 that it did not have the time or funding to redesign and replace the heat shield before the next flight. Instead, it chose to fly the next manned Orion mission — dubbed Artemis-2 and scheduled for the spring of 2026 carrying four astronauts around the Moon — using this same heat shield design but change the flight path during reentry to reduce stress on the shield.
NASA also admitted then that this heat shield design is defective, and that it will replace it beginning with the next mission, Artemis-3, the one that the agency hopes will land people back on the Moon.
The decision to fly humans in a capsule with such a known untrustworthy heat shield design is bad enough. Any rational person would not do this (as the inspector general above concluded). Yet NASA is going ahead, because it has determined that meeting its schedule, getting Americans back to the lunar surface ahead of China and during Trump’s present term of office, is more important than rational engineering and testing.
What now makes this decision even more worrisome is that it appears NASA is covering up the findings of its own engineers, completed in August 2024 but not made public until now.
» Read more
October 22, 2025 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Inversion Space touts its two autonomous drop test vehicles, Jaws and Big Tuna
The company has been using them in helicopter drops to test targeted precise reentry that its proposed Arc orbital capsule will require.
- Airbus, Thales, and Leonardo reportedly agree to merge their satellite divisions
The article speculates, without solid evidence, that the combined company will build a satellite constellation to compete with Starlink. Jay instead speculates (more accurately) that it “will will just lobby for laws that ban Starlink or tax the hell out of it.” After all, that is the European way in the 21st century.
- Chang’e-6 lunar sample is “a type of meteorite known as Ivuna-type carbonaceous chondrite”
What makes this find significant is that these types of primitive meteorites are very fragile, and almost never survive reentry on Earth. Finding this sample on the Moon will help scientists better determine the overall make-up of the solar system’s asteroid population, which will then allow them to better construct its early formation process.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Inversion Space touts its two autonomous drop test vehicles, Jaws and Big Tuna
The company has been using them in helicopter drops to test targeted precise reentry that its proposed Arc orbital capsule will require.
- Airbus, Thales, and Leonardo reportedly agree to merge their satellite divisions
The article speculates, without solid evidence, that the combined company will build a satellite constellation to compete with Starlink. Jay instead speculates (more accurately) that it “will will just lobby for laws that ban Starlink or tax the hell out of it.” After all, that is the European way in the 21st century.
- Chang’e-6 lunar sample is “a type of meteorite known as Ivuna-type carbonaceous chondrite”
What makes this find significant is that these types of primitive meteorites are very fragile, and almost never survive reentry on Earth. Finding this sample on the Moon will help scientists better determine the overall make-up of the solar system’s asteroid population, which will then allow them to better construct its early formation process.
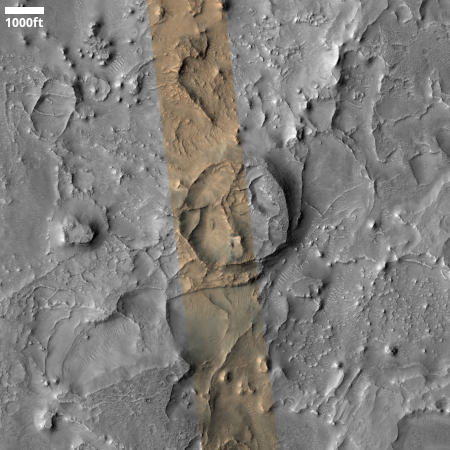
A somewhat typical volcanic vent on Mars
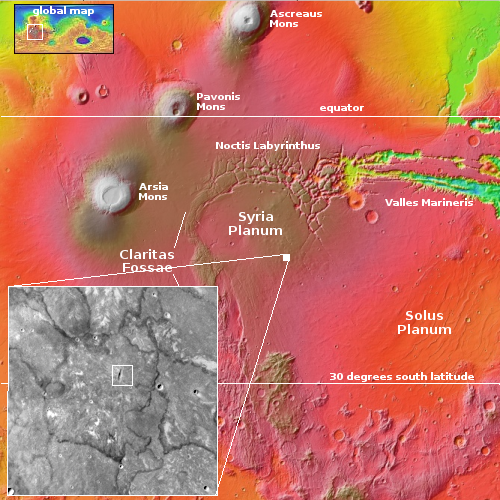
With today’s cool image we begin with the overview map to the right. The white dot marks the location, within the region on Mars dubbed the Tharsis Bulge, where four of its biggest volcanoes are located on a surface that has been pushed significantly above the red planet’s mean “sea level.”
The small rectangle in the inset shows the area covered by the cool image below. The focus is on a two-mile-long and half-mile-wide depression that sits on a relatively flat landscape of few craters.
If you look at the inset closely, you will notice this depression is surrounded by a dark borderline on all four sides, ranging in distance from three to thirteen miles. The grade to that borderline is downhill in all directions, with the drop ranging roughly from 800 to 1,000 feet.
So what are we looking at? » Read more

With today’s cool image we begin with the overview map to the right. The white dot marks the location, within the region on Mars dubbed the Tharsis Bulge, where four of its biggest volcanoes are located on a surface that has been pushed significantly above the red planet’s mean “sea level.”
The small rectangle in the inset shows the area covered by the cool image below. The focus is on a two-mile-long and half-mile-wide depression that sits on a relatively flat landscape of few craters.
If you look at the inset closely, you will notice this depression is surrounded by a dark borderline on all four sides, ranging in distance from three to thirteen miles. The grade to that borderline is downhill in all directions, with the drop ranging roughly from 800 to 1,000 feet.
So what are we looking at? » Read more




