October 21, 2025 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- NASA’s administrator touts the installation of Orion to SLS for next year’s Artemis II mission
I wonder if Duffy is even aware of the heat shield issues or the lack of testing of the capsule’s environmental system. That NASA is poo-pooing both makes this manned mission around the Moon essentially a repeat of Challenger and Columbia, placing schedule above engineering.
- On board video from Dawn Aerospace’s Mk-II Aurora record-breaking flight in November 2024
On the flight this small scale unmanned prototype was the first commercial plane to break the sound barrier since the Concorde.
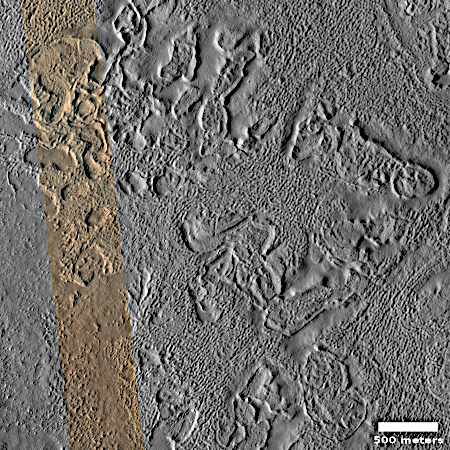
- Video of a Chinese rocket booster crashing into a ranch in Guinan County, Hainan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai province on October 13, 2025
This was the launch that day of a Long March 2D rocket from China’s northwest Jiquan spaceport. The rocket uses very toxic hypergolic fuels (note the red clouds) that can dissolve skin. Bad news for this ranch.
- Video of launchpad static fire test of China’s Zhuque-3 rocket
It is a copy of SpaceX’s Falcon 9, with a tentative launch date of November 3, 2025, according to Jay. It is built by the pseudo-company Landspace, which won’t try recovering the first stage until later launches in 2026.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- NASA’s administrator touts the installation of Orion to SLS for next year’s Artemis II mission
I wonder if Duffy is even aware of the heat shield issues or the lack of testing of the capsule’s environmental system. That NASA is poo-pooing both makes this manned mission around the Moon essentially a repeat of Challenger and Columbia, placing schedule above engineering.
- On board video from Dawn Aerospace’s Mk-II Aurora record-breaking flight in November 2024
On the flight this small scale unmanned prototype was the first commercial plane to break the sound barrier since the Concorde.
- Video of a Chinese rocket booster crashing into a ranch in Guinan County, Hainan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai province on October 13, 2025
This was the launch that day of a Long March 2D rocket from China’s northwest Jiquan spaceport. The rocket uses very toxic hypergolic fuels (note the red clouds) that can dissolve skin. Bad news for this ranch.
- Video of launchpad static fire test of China’s Zhuque-3 rocket
It is a copy of SpaceX’s Falcon 9, with a tentative launch date of November 3, 2025, according to Jay. It is built by the pseudo-company Landspace, which won’t try recovering the first stage until later launches in 2026.