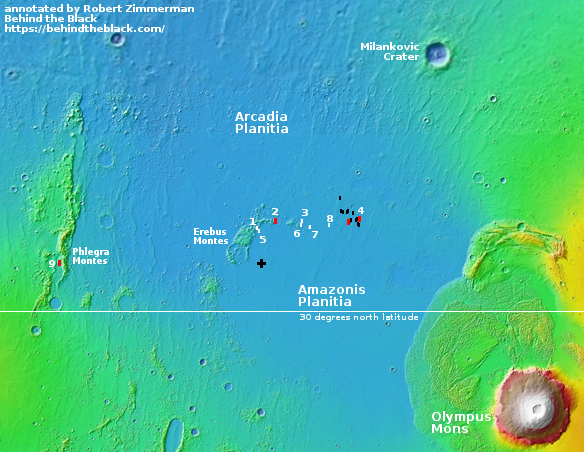
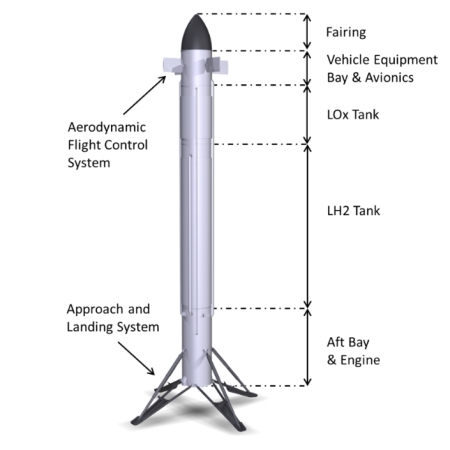
NASA and Northrop Grumman work out rendezvous plan to get Cygnus to ISS
UPDATE: The plan worked and Cygnus is safely berthed at ISS.
According to a press release tonight, NASA and Northrop Grumman have figured out a new rendezvous plan to get Cygnus to ISS after its previous engine burns yesterday cut off prematurely and left it in the wrong orbit.
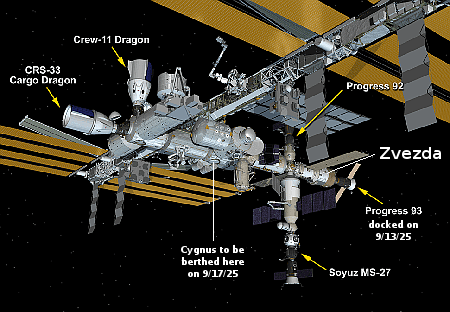
NASA and Northrop Grumman are targeting the safe arrival of the company’s Cygnus XL at approximately 7:18 a.m. EDT Thursday, Sept. 18, to the International Space Station. The Cygnus XL now will conduct a series of burns to bring the spacecraft to the space station for its robotic capture and installation.
NASA astronaut Jonny Kim is scheduled to capture Cygnus XL using the station’s Canadarm2 robotic arm with backup support from NASA astronaut Zena Cardman. After capture, the spacecraft will be installed on the Unity module’s Earth-facing port and will remain at the space station until March 2026.
The release also added this detail about why that engine burn ended too soon:
Data shared by the spacecraft confirmed that Cygnus XL operated as intended during two planned maneuvers when an early warning system initiated a shutdown command and ended the main engine burn because of a conservative safeguard in the software settings.
Apparently this cause has reassured them that the engine is in good shape for the final rendezvous burns.
UPDATE: The plan worked and Cygnus is safely berthed at ISS.
According to a press release tonight, NASA and Northrop Grumman have figured out a new rendezvous plan to get Cygnus to ISS after its previous engine burns yesterday cut off prematurely and left it in the wrong orbit.
NASA and Northrop Grumman are targeting the safe arrival of the company’s Cygnus XL at approximately 7:18 a.m. EDT Thursday, Sept. 18, to the International Space Station. The Cygnus XL now will conduct a series of burns to bring the spacecraft to the space station for its robotic capture and installation.
NASA astronaut Jonny Kim is scheduled to capture Cygnus XL using the station’s Canadarm2 robotic arm with backup support from NASA astronaut Zena Cardman. After capture, the spacecraft will be installed on the Unity module’s Earth-facing port and will remain at the space station until March 2026.
The release also added this detail about why that engine burn ended too soon:
Data shared by the spacecraft confirmed that Cygnus XL operated as intended during two planned maneuvers when an early warning system initiated a shutdown command and ended the main engine burn because of a conservative safeguard in the software settings.
Apparently this cause has reassured them that the engine is in good shape for the final rendezvous burns.