Cargo Dragon successfully returns to Earth
A cargo Dragon capsule successfully splashed down in the Pacific late Thursday, February 26, 2026, bringing back several thousand pounds of hardware and experiments.
The ship had been docked at ISS for the past six months, during which it used its engines six different times to raise the station’s orbit. That capability has traditionally been done by Russian Progress freighters, but NASA has been testing other options as they are unsure Russia will remain with the station after 2028. Furthermore, there are risks using Progress to do these reboosts, as the burns take place when Progress is docked to its Zvezda module port, and the hull of the Zvezda module has been developing stress fractures in the past five years that could catastrophically fail.
Not only has Dragon now demonstrated this boost capability, so has Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus capsule.
I strongly expect Russia to stick with ISS for as long as it can, mainly because its own proposed new space station is not likely to launch as presently scheduled later this decade. Since the fall of the Soviet Union, Roscosmos has consistently been unable to complete almost any new proposed projects, and the few it has completed launched literally decades late.
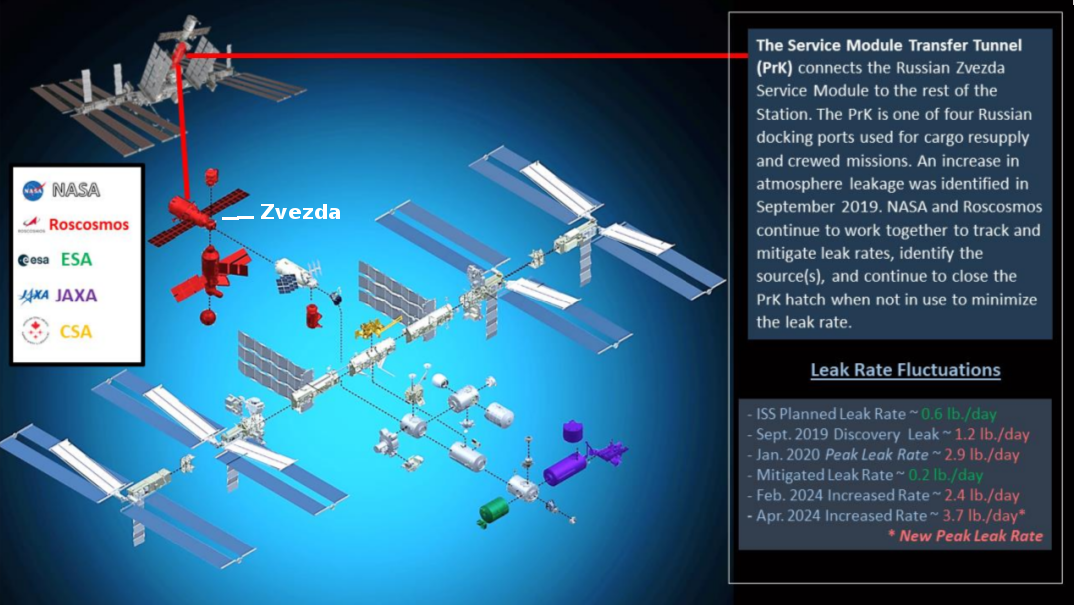
Figure 3 from September 2024 Inspector General report, showing Zvezda’s location on ISS, as well as the station’s leak rate at that time. The leaks in Zvezda now appear to have been sealed, but there is no guarantee more stress fractures will not appear as dockings continue at its port.
A cargo Dragon capsule successfully splashed down in the Pacific late Thursday, February 26, 2026, bringing back several thousand pounds of hardware and experiments.
The ship had been docked at ISS for the past six months, during which it used its engines six different times to raise the station’s orbit. That capability has traditionally been done by Russian Progress freighters, but NASA has been testing other options as they are unsure Russia will remain with the station after 2028. Furthermore, there are risks using Progress to do these reboosts, as the burns take place when Progress is docked to its Zvezda module port, and the hull of the Zvezda module has been developing stress fractures in the past five years that could catastrophically fail.
Not only has Dragon now demonstrated this boost capability, so has Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus capsule.
I strongly expect Russia to stick with ISS for as long as it can, mainly because its own proposed new space station is not likely to launch as presently scheduled later this decade. Since the fall of the Soviet Union, Roscosmos has consistently been unable to complete almost any new proposed projects, and the few it has completed launched literally decades late.

Figure 3 from September 2024 Inspector General report, showing Zvezda’s location on ISS, as well as the station’s leak rate at that time. The leaks in Zvezda now appear to have been sealed, but there is no guarantee more stress fractures will not appear as dockings continue at its port.