Astronomers detect neutron star merger in both light and gravitational waves
Big news! Astronomers from dozens of telescopes on the ground and in space have observed for the first time the light burst caused by the merger of two neutron stars because earlier observations of the merger’s gravitational wave and gamma ray burst told them where to look in the sky.
On 17 August 2017 the NSF’s Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) in the United States, working with the Virgo Interferometer in Italy, detected gravitational waves passing the Earth. This event, the fifth ever detected, was named GW170817. About two seconds later, two space observatories, NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope and ESA’s INTErnational Gamma Ray Astrophysics Laboratory (INTEGRAL), detected a short gamma-ray burst from the same area of the sky.
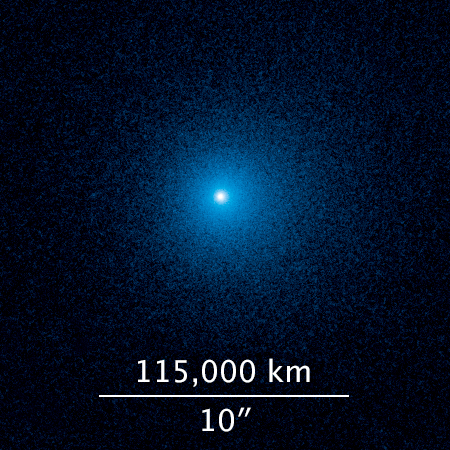
The LIGO–Virgo observatory network positioned the source within a large region of the southern sky, the size of several hundred full Moons and containing millions of stars. As night fell in Chile many telescopes peered at this patch of sky, searching for new sources. These included ESO’s Visible and Infrared Survey Telescope for Astronomy (VISTA) and VLT Survey Telescope (VST) at the Paranal Observatory, the Italian Rapid Eye Mount (REM) telescope at ESO’s La Silla Observatory, the LCO 0.4-meter telescope at Las Cumbres Observatory, and the American DECam at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory. The Swope 1-metre telescope was the first to announce a new point of light. It appeared very close to NGC 4993, a lenticular galaxy in the constellation of Hydra, and VISTA observations pinpointed this source at infrared wavelengths almost at the same time. As night marched west across the globe, the Hawaiian island telescopes Pan-STARRS and Subaru also picked it up and watched it evolve rapidly.
Press releases today from numerous other observatories are too numerous to link here, and most essentially say the same thing. The key facts so far gleaned however are intriguing:
Distance estimates from both the gravitational wave data and other observations agree that GW170817 was at the same distance as NGC 4993, about 130 million light-years from Earth. This makes the source both the closest gravitational wave event detected so far and also one of the closest gamma-ray burst sources ever seen
This event also highlights the advantages of observing the universe in as many ways as possible. Some phenomenon get to us sooner, and thus provide us clues on where to look with other tools. Without the gravitational wave and gamma ray burst detectors, on Earth and in space, the other optical and infrared telescopes would have almost certainly not have recorded this merger.
Big news! Astronomers from dozens of telescopes on the ground and in space have observed for the first time the light burst caused by the merger of two neutron stars because earlier observations of the merger’s gravitational wave and gamma ray burst told them where to look in the sky.
On 17 August 2017 the NSF’s Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) in the United States, working with the Virgo Interferometer in Italy, detected gravitational waves passing the Earth. This event, the fifth ever detected, was named GW170817. About two seconds later, two space observatories, NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope and ESA’s INTErnational Gamma Ray Astrophysics Laboratory (INTEGRAL), detected a short gamma-ray burst from the same area of the sky.
The LIGO–Virgo observatory network positioned the source within a large region of the southern sky, the size of several hundred full Moons and containing millions of stars. As night fell in Chile many telescopes peered at this patch of sky, searching for new sources. These included ESO’s Visible and Infrared Survey Telescope for Astronomy (VISTA) and VLT Survey Telescope (VST) at the Paranal Observatory, the Italian Rapid Eye Mount (REM) telescope at ESO’s La Silla Observatory, the LCO 0.4-meter telescope at Las Cumbres Observatory, and the American DECam at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory. The Swope 1-metre telescope was the first to announce a new point of light. It appeared very close to NGC 4993, a lenticular galaxy in the constellation of Hydra, and VISTA observations pinpointed this source at infrared wavelengths almost at the same time. As night marched west across the globe, the Hawaiian island telescopes Pan-STARRS and Subaru also picked it up and watched it evolve rapidly.
Press releases today from numerous other observatories are too numerous to link here, and most essentially say the same thing. The key facts so far gleaned however are intriguing:
Distance estimates from both the gravitational wave data and other observations agree that GW170817 was at the same distance as NGC 4993, about 130 million light-years from Earth. This makes the source both the closest gravitational wave event detected so far and also one of the closest gamma-ray burst sources ever seen
This event also highlights the advantages of observing the universe in as many ways as possible. Some phenomenon get to us sooner, and thus provide us clues on where to look with other tools. Without the gravitational wave and gamma ray burst detectors, on Earth and in space, the other optical and infrared telescopes would have almost certainly not have recorded this merger.