Martian rootless cones
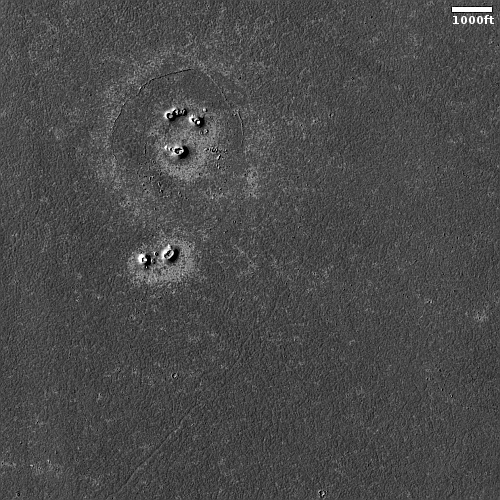
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on March 8, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
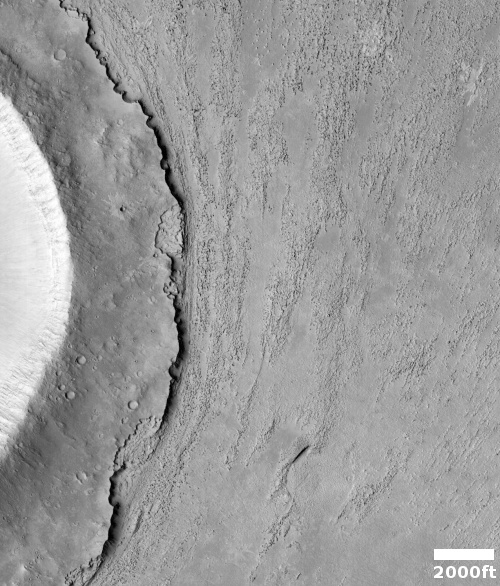
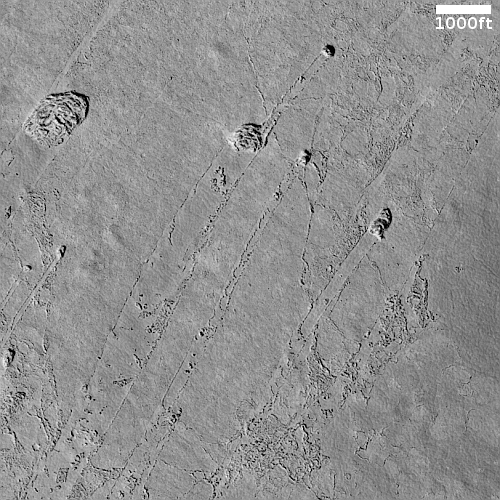
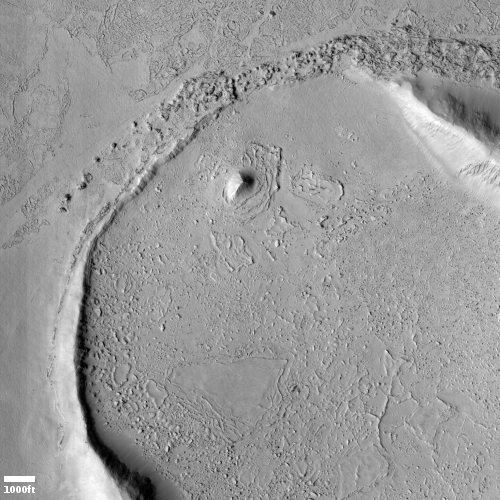
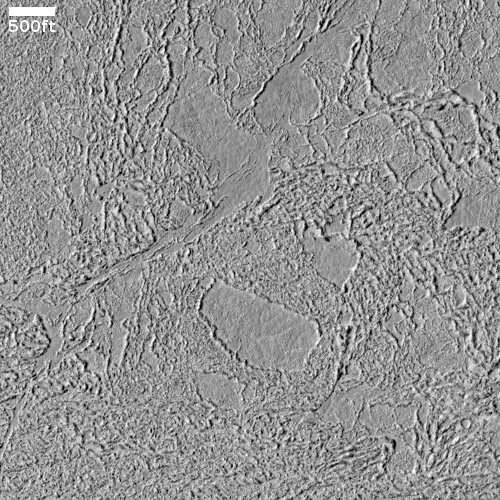
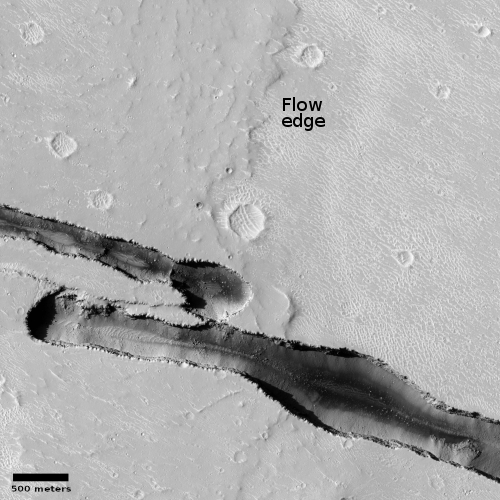
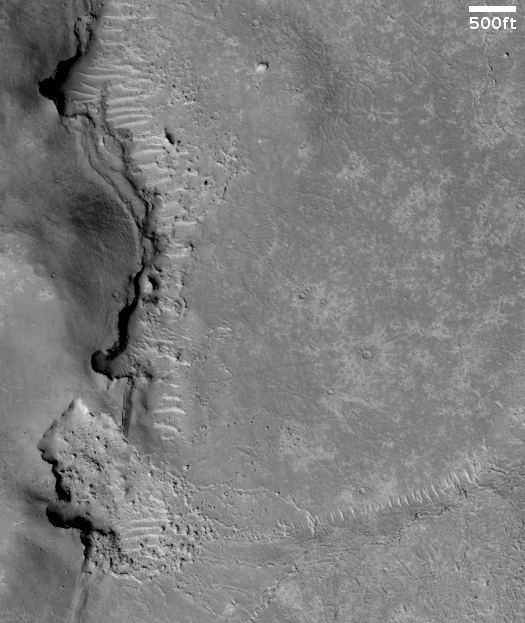
The camera team labeled this picture simply “Rootless Cones,” which is a feature that is created when the lava that covers the surface is thin, allowing the heated material below (which is not lava) to burst upward, producing the cone and caldera. If you look at the full image you will see other similar clusters of cones scattered about on this very flat and featureless plain. Apparently, the material that this lava plain covered had several similar bursts in a number of areas.
Such cones in this particular lava field are not rare, and in fact are evidence that this particular field is young.
» Read more
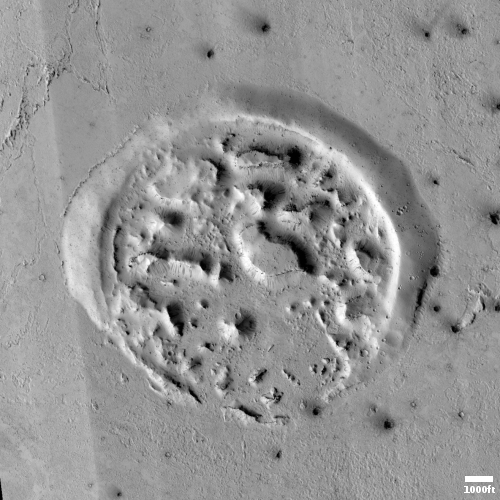
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on March 8, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The camera team labeled this picture simply “Rootless Cones,” which is a feature that is created when the lava that covers the surface is thin, allowing the heated material below (which is not lava) to burst upward, producing the cone and caldera. If you look at the full image you will see other similar clusters of cones scattered about on this very flat and featureless plain. Apparently, the material that this lava plain covered had several similar bursts in a number of areas.
Such cones in this particular lava field are not rare, and in fact are evidence that this particular field is young.
» Read more