Musk provides update to his Boca Chica crew
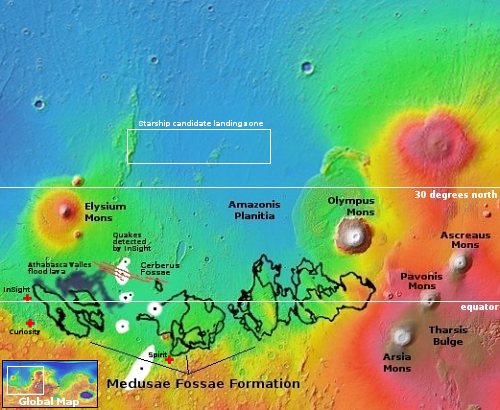
The candidate landing zone on Mars for Starship
Elon Musk yesterday gave a 44-minute update on Starship/Superheavy to his team in Boca Chica, outlining what he now expects in the next two years as well as in the next two decades.
You can watch his presentation here. Musk began by once again describing his fundamental goal behind the company, to make the human race multi-planetary, for its own survival, and that Mars is at this time the best choice for doing so. He then provided some details about the on-going development of Starship/Superheavy:
- SpaceX will be ready to launch 4th test flight in early May
- There is an 80-90% chance they will attempt a tower landing of Superheavy, caught by its chopstick arms, by the end of this year
- Starship will require at least two precision ocean landings before they attempt a tower landing
- To provide tower redundancy for these test landings, by next year they will have 2 towers at Boca Chica, 2 at Cape Canaveral, with Cape Canaveral operational by next year
- In 2024 they hope to build 6 Superheavys and Starships for test flights
- By 2025 they plan to test full refueling of Starship in orbit
- The third iteration of Starship/Superheavy will be capable of placing 200 tons in orbit
- That third iteration will cost less to launch than Falcon 1, $2-3 million
- To make a base on Mars self-sufficient quickly, he anticipates sending large fleets of Starships every two years, everytime the flight window to Mars opens.
- The preferred landing sites will be in the low mid-latitudes, 30-40 degrees, with elevations two kilometers below the Martian “sea level”, to take advantage of a thick atmosphere.
- If all goes as planned, Musk expects SpaceX to establish a Mars colony in about two decades
That next-to-last bullet point fits perfectly with the region north of Amazonis Planitia, as shown on the map above, where SpaceX has requested numerous images from the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It is two kilometers below the “sea level” of Mars. It is at a latitude either on or close to 40 degrees north latitude. It is a region that orbital data says has lots of very near-surface ice. And it is flat, making those first landings relatively safe.

The candidate landing zone on Mars for Starship
Elon Musk yesterday gave a 44-minute update on Starship/Superheavy to his team in Boca Chica, outlining what he now expects in the next two years as well as in the next two decades.
You can watch his presentation here. Musk began by once again describing his fundamental goal behind the company, to make the human race multi-planetary, for its own survival, and that Mars is at this time the best choice for doing so. He then provided some details about the on-going development of Starship/Superheavy:
- SpaceX will be ready to launch 4th test flight in early May
- There is an 80-90% chance they will attempt a tower landing of Superheavy, caught by its chopstick arms, by the end of this year
- Starship will require at least two precision ocean landings before they attempt a tower landing
- To provide tower redundancy for these test landings, by next year they will have 2 towers at Boca Chica, 2 at Cape Canaveral, with Cape Canaveral operational by next year
- In 2024 they hope to build 6 Superheavys and Starships for test flights
- By 2025 they plan to test full refueling of Starship in orbit
- The third iteration of Starship/Superheavy will be capable of placing 200 tons in orbit
- That third iteration will cost less to launch than Falcon 1, $2-3 million
- To make a base on Mars self-sufficient quickly, he anticipates sending large fleets of Starships every two years, everytime the flight window to Mars opens.
- The preferred landing sites will be in the low mid-latitudes, 30-40 degrees, with elevations two kilometers below the Martian “sea level”, to take advantage of a thick atmosphere.
- If all goes as planned, Musk expects SpaceX to establish a Mars colony in about two decades
That next-to-last bullet point fits perfectly with the region north of Amazonis Planitia, as shown on the map above, where SpaceX has requested numerous images from the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It is two kilometers below the “sea level” of Mars. It is at a latitude either on or close to 40 degrees north latitude. It is a region that orbital data says has lots of very near-surface ice. And it is flat, making those first landings relatively safe.