Ferris Akel – Snow Geese Takeoff, March 20, 2021
An evening pause: Wait for it — a moment that tells us even on Earth there is alien things going on all around us. Makes for a good start to the weekend.
Hat tip Ferris.
An evening pause: Wait for it — a moment that tells us even on Earth there is alien things going on all around us. Makes for a good start to the weekend.
Hat tip Ferris.
In a press briefing this morning officials from NASA, Boeing, and ULA confirmed the new June 1, 12:25 pm (Eastern) launch date for the first manned flight of Boeing’s Starliner manned capsule.
The officials provided a more detailed explanation of the helium leak in a valve that effects the capsule’s service module attitude thruster system, noting that it is not a design flaw but some specific issue in this particular valve. Because of this, they are confident the system can function safely even with the leak, which is relatively small.
However, the officials also noted that during their reviews in the past two weeks they discovered a new software issue in the spacecraft’s de-orbit engines that — under very unusual and unlikely circumstances — could actually cause those engines to fail to operate. They have figured out a work-around, whereby they fire the engines at a lower thrust in two stages rather than once.
Should the launch on June 1st be scrubbed for weather, they have back up dates on the next few days, though by June 4th ULA might have to swap out batteries on its Atlas-5 rocket that will require a longer stand down of several additional days.
Click for original image at high resolution.
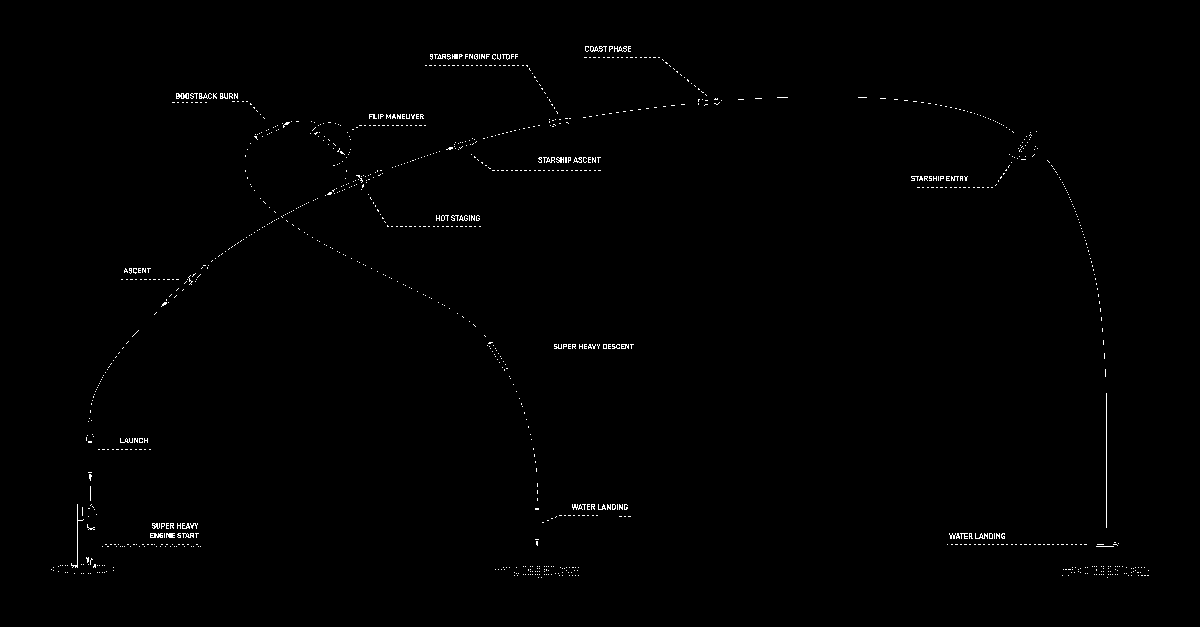
SpaceX today tentatively announced a June 5, 2024 launch date for the fourth Starship/Superheavy orbital test launch.
Before going into any details of the flight plan, as shown in the flight profile above, it is important to quote the first sentence in the announcement:
The fourth flight test of Starship could launch as soon as June 5, pending regulatory approval. [emphasis mine]
SpaceX has not yet gotten a launch permit from the FAA. It is likely it has inside information from the agency suggesting that permit will be issued by this date. It is also likely that SpaceX by making this announcement is applying pressure to the FAA to either get its paperwork done or waive the need so its red tape doesn’t delay the flight unnecessarily.
As for the flight itself, the flight profile is essentially the same as the previous test flight, with the Starship’s orbit designed for safety to bring it down in the Indian Ocean.
The fourth flight test turns our focus from achieving orbit to demonstrating the ability to return and reuse Starship and Super Heavy. The primary objectives will be executing a landing burn and soft splashdown in the Gulf of Mexico with the Super Heavy booster, and achieving a controlled entry of Starship.
To accomplish this, several software and hardware upgrades have been made to increase overall reliability and address lessons learned from Flight 3. The SpaceX team will also implement operational changes, including the jettison of the Super Heavy’s hot-stage following boostback to reduce booster mass for the final phase of flight.
All in all, this announcement is good news. SpaceX is ready to launch.
More bunny action. SpaceX tonight successfully launched another 23 Starlink satellites, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida.
The first stage completed its thirteenth flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
Increasingly, SpaceX is treating its rockets and launchpads like the airlines treat their airplanes: They only have value if they are flying, and SpaceX is trying to keep both rockets and launchpads flying at all times.
The leaders in the 2024 launch race:
55 SpaceX
23 China
7 Russia
5 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise now leads the world combined in successful launches, 62 to 36, while SpaceX by itself leads the entire world, including other American companies, 55 to 43.
Superheavy/Starship lifting off on March 14, 2024
According to the FAA, SpaceX has officially asked the FAA to allow it to launch the next Starship/Superheavy test orbital launch before the agency officially completes its mishap investigation into the previous flight in March.
In a statement sent to ValleyCentral, the FAA stated that on April 5, SpaceX requested the FAA make a “public safety determination” as part of the Starship flight test mishap. “If the FAA agrees no public safety issues were involved in the mishap, the operator may return to flight while the mishap investigation remains open, provided all other license requirements are met.”
With this modification in place, SpaceX would be able to launch the fourth Starship test flight while the mishap investigation of the third flight is still open.
When these requests are received, the FAA evaluates safety-critical systems, the nature of the consequences of the mishap, adequacy of existing flight analysis, safety organization performance and environmental factors, the statement added. The FAA stated it is reviewing the request and will be “guided by data and safety at every step of the process.”
What does this request tell us? First, as expected SpaceX has completed its own investigation into the March launch and installed the upgrades it considers necessary. Second, the FAA however has not, even though the FAA has absolutely no competence in this matter. It is merely retyping the SpaceX report.
Third, SpaceX now realizes that the FAA will not have finished that retyping when SpaceX is ready to launch sometime in the next three weeks. Rather than sit and wait, as it did on the previous two test launches, it wants the FAA to recognize reality and let it proceed. Why wait when the FAA is literally contributing nothing to the process?
Will the FAA do so? I suspect there are people in the FAA who would very much like to. I also know that there are others both in the FAA and higher up the command chain (mostly in the White House) that like the idea of slowing SpaceX down, mostly for petty political reasons. We should not be surprised if those higher ups use their clout and insist the FAA reject this request.
If so, the fourth test launch of Starship/Superheavy will likely be further delayed, though by how much is unclear. Shortly after the March test launch I predicted that the next flight would occur in the June/July timeframe, not early May as SpaceX was then predicting, and the delay will be mostly because of FAA red tape. It now appears that prediction will be correct.
In a brief update posted today by NASA, the agency announced that Boeing, NASA, and ULA have a new 12:25 pm (Eastern) June 1, 2024 launch date for the first manned flight of Boeing’s Starliner capsule.
The announcement was incredibly obscure about what the issues are that have caused this additional week delay:
Work continues to assess Starliner performance and redundancy following the discovery of a small helium leak in the spacecraft’s service module. As part of this work, and unrelated to the current leak which remains stable, teams are in the process of completing a follow-on propulsion system assessment to understand potential helium system impacts on some Starliner return scenarios. NASA also will conduct a Delta-Agency Flight Test Readiness Review to discuss the work that was performed since the last CFT launch attempt on May 6, and to evaluate issue closure and flight rationale ahead of the next attempt, as part of NASA’s process for assessing readiness. The date of the upcoming Flight Test Readiness Review is under consideration and will be announced once selected.
It appears that engineers are worried the leak — which is linked to one of the attitude thrusters in the capsule’s service module — might impact the ability of Starliner to return to Earth safely. It also appears there is concern about the spacecraft sitting on the launchpad for more than a month, and an evaluation is on-going on whether this might be an issue as well.
I am guessing however. A more detailed explanation might be forth-coming after press update scheduled for 11 am (Eastern) tomorrow.
March on bunny! SpaceX last night successfully launched another 23 Starlink satellites, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida.
The first stage completed its eighth flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
The leaders in the 2024 launch race:
54 SpaceX
23 China
7 Russia
5 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise now leads the world combined in successful launches, 61 to 36, while SpaceX by itself leads the entire world, including other American companies, 54 to 43.
The European Space Agency (ESA) today awarded contracts worth 25 million euros each to two European companies — the French startup The Exploration Company and the established Italian contractor Thales-Alenia — to begin development of their own unmanned freighters capable of bringing cargo to and from orbit.
During phase 1 development, the selected companies will mature the design of their respective vehicles, focusing on mission requirements, architectures, technology maturation, and de-risking activities. This phase of development is expected to run from June 2024 to June 2026.
Phase 2 of the initiative will see the companies develop and execute a demonstration mission that must be launched by the end of 2028. However, the commencement of Phase 2 will be subject to decisions and appropriations made at ESA’s next ministerial-level council meeting, which will take place in late 2025.
These contracts only cover phase 1. If successful, these capsules will compete with the cargo capsules that SpaceX, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Space fly in providing supplies to the four commercial space stations presently being built.
SpaceX last night successfully placed a National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) reconnaissance payload into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg in California. Because of the classified nature of the flight, it is unclear whether the payload is one or several satellites.
The first stage completed its 16th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Pacific. The fairings completed their 12th and 3rd flights respectively.
The leaders in the 2024 launch race:
53 SpaceX
23 China
7 Russia
5 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise still leads the world combined in successful launches, 60 to 36, while SpaceX by itself still leads the entire world, including other American companies, 53 to 43.
In a very terse statement that apparently was only sent out by email to some sources, NASA and Boeing announced last night that the May 25, 2024 launch of the first manned Starliner mission on ULA’s Atlas-5 rocket had been postponed, with no new launch date set.
NASA, Boeing, and ULA are foregoing the Saturday, May 25 launch attempt for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test. The team has been in meetings for two consecutive days, assessing flight rationale, system performance, and redundancy. There is still forward work in these areas, and the next possible launch opportunity is still being discussed.
NASA will share more details once we have a clearer path forward,
The first launch scrub prior to the first launch date of May 6th was due to a valve issue on the Atlas-5 rocket. ULA quickly replaced that valve and the launch was rescheduled for May 17th. Then Boeing engineers detected a helium leak related to one of the attitude thrusters in the capsule’s service module. The launch was first delayed until May 21st, then delayed again until May 25th. Now it is delayed indefinitely.
Whether that helium leak remains the cause of this new delay remains unknown. That no new launch date has been proposed suggests the need to bring the rocket and capsule back to the assembly building to destack it in order to fix the problem. That NASA, Boeing, and ULA are being so coy about revealing any details suggests however that some additional issue might have been uncovered.
Regardless, this new extended delay is very bad publicity for Boeing. While the comparison is somewhat unfair, it continues to make Starliner look like an American version of a Yugo, not the kind of vehicle one would nonchalantly climb into for a flight into space.
Capitalism in space: Sierra Space’s Tenacity Dream Chaser mini-shuttle has finally arrived at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida for its final testing and assembly onto ULA’s Vulcan rocket.
Upon arrival at Kennedy, teams moved Dream Chaser Tenacity to the high bay inside the Space Systems Processing Facility, where it will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing ahead of its launch scheduled for later this year.
…The remaining pre-flight activities at Kennedy include acoustic and electromagnetic interference and compatibility testing, completion of work on the spaceplane’s thermal protection system, and final payload integration.
If all goes right, Tenacity’s first mission will last 45 days, delivery about 7,800 pounds of cargo to ISS, and prove out the reusable mini-shuttle for up to seven more flights to ISS.
In an announcement today, the European Space Agency (ESA) narrowed the launch window for the first launch of its new Ariane-6 rocket to the first two weeks in July.
It also stated that the final launch date will be revealed in the first week of June, during presentations at an air show in Berlin, Germany.
In the next month the rocket will undergo a full dress rehearsal countdown on the launchpad. It will then be “drained of fuel in preparation” for the actual launch.
This rocket is built and mostly owned by the private consortium ArianeGroup, made up of a partnership of Airbus and Safran, and working in conjunction with ESA. Though Arianespace, ESA’s long time commercial arm, is mentioned as ESA’s “launch service provider” for this launch, it is very clear that it is being pushed aside and will soon become irrelevant. The rocket is four years behind schedule and being entirely expendable it is too expensive to compete in the modern launch market. The member nations of ESA have rejected it, and so they are shifting to a capitalism in space model, whereby they no longer have a government commercial “launch service provider” like Arianespace, but instead buy launch services from competing private European rocket companies.
Europe’s problem is that it will take time to develop these private companies. In the interim it will be forced to use Ariane-6, but likely only for a few years. There are at least five new rocket companies in Europe, with three (Rocket Factory Augsburg, PLD, and Hyimpulse) having already completed their first launch tests.
Blue Origin yesterday flew its first suborbital New Shepard flight since a failure during an unmanned flight in 2022, flying six passengers on a short ten-minute jump.
This suborbital flight got a lot of press yesterday and today, but I consider these suborbital tourist flights somewhat old news. Had they occurred two decades ago, in the 2000s as promised, they could have helped trigger the commercial space industry. Instead, both Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic took another two decades to get started, and by that time orbital tourist flights were taking place.
There might be money to be made in suborbital hops like this, but the future of space exploration lies elsewhere.
As for Blue Origin, this flight confirms that the company has fixed the nozzle issues that caused the September 2022 launch failure. During ascent just after launch the spacecraft’s abort system activated, sending the New Shepard capsule free from the first stage booster, which subsequently crashed. The capsule landed safely with parachutes.
The investigation then stretched out over more than two years. It remains unclear why it took so long, though the FAA’s regulatory burden appears to have been one factor, with Blue Origin’s own sluggish pace of operations another.
Though not yet confirmed a 90-pound piece of burned debris that crashed on a Canadian farm and found in late April appears to be a section from the trunk section of a SpaceX Dragon service module.
Jonathan McDowell, who tracks space launches and re-entries, posted on X (formerly Twitter) that the trunk from the private Axiom Space Ax-3 mission fell over Saskatchewan on Feb. 26.
This incident, along with several others over the last few years, tells us that not everything engineers thought would burn up upon re-entry does so. A major rethinking of how objects are de-orbited could be necessary.
The National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) has agreed to suspend one of its cases against SpaceX while the company’s lawsuit challenging the board’s constitutional authority proceeds.
SpaceX alleged that the NLRB’s in-house enforcement proceedings violate its constitutional right to a jury trial. It also said limits on the removal of the NLRB’s board members and administrative judges violates the Constitution. Amazon, Starbucks, and Trader Joe’s have asserted similar claims in recent months.
A second NLRB case has already been suspended by the federal 5th Court of Appeals, for the same reasons.
This bunny never stops. SpaceX today successfully launched 23 more Starlink satellites, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral.
The first stage set a new record for reflights, completing its 21st flight after landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic. The company has said it is upgrading these stages to last for 40 launches instead of 20, and this launch clearly is the first step in that direction.
The leaders in the 2024 launch race:
52 SpaceX
21 China
7 Russia
5 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise now leads the world combined in successful launches, 59 to 34, while SpaceX by itself still leads the rest of the world, including other American companies, 52 to 41.
Boeing, ULA, and NASA have decided to delay the first manned flight of Boeing’s Starliner capsule another four days to 3:09 pm (Eastern) on May 25, 2024.
The additional time allows teams to further assess a small helium leak in the Boeing Starliner spacecraft’s service module traced to a flange on a single reaction control system thruster. Pressure testing performed on May 15 on the spacecraft’s helium system showed the leak in the flange is stable and would not pose a risk at that level during the flight. The testing also indicated the rest of the thruster system is sealed effectively across the entire service module. Boeing teams are working to develop operational procedures to ensure the system retains sufficient performance capability and appropriate redundancy during the flight.
It appears they simply want to give themselves extra time to review their data thoroughly, with no rush, before lighting the rocket.
NASA yesterday signed a new agreement with the European Space Agency (ESA) that confirmed its previous commitment to help land ESA’s Franklin rover on Mars.
With this memorandum of understanding, the NASA Launch Services Program will procure a U.S. commercial launch provider for the Rosalind Franklin rover. The agency will also provide heater units and elements of the propulsion system needed to land on Mars.
Previously NASA had committed $30 million to pay for that launch provider, as yet undetermined. It now wants $49 million for the Franklin mission, with the extra money likely to pay for the new additional equipment outlined in this agreement.
Whether NASA gets this money from Congress however remains unknown. It has not yet been appropriated.
This overall European project has been fraught with problems. It was first designed as a partnership with NASA. Then Obama pulled NASA out in 2012, and ESA switched to a partnership with Russia, which was to provide the rocket and lander. Then in 2022 Russia invaded the Ukraine and Europe broke off all its partnerships with Russia.
Since then ESA has signed a deal with the company Thales Alenia to build the lander.
As these political foibles were going on, the rover also had parachute issues that forced ESA to cancel its original launch date in 2022, using the Russian rocket.
It is likely Congress will approve this additional funding, though it seems to me that Europe should be able to afford paying for its own launch, especially if it is buying that service from the much cheaper U.S. market.
An evening pause: Performed at an October 2022 concert celebrating the life of Loretta Lynn.
Hat tip Diane Zimmerman.
Link here. The NPR article is a long detailed look at NASA on-going review of the proposal by billionaire astronaut Jared Isaacman and SpaceX to to do a maintenance mission to the Hubble Space Telescope.
The NPR spin is subtly hostile to the mission, because it would be funded privately and run entirely by private citizens, not the government. Like all modern leftist news outlets, it can only imagine the government capable of doing such things properly.
Reading between the lines, however, what I instead sense is that NASA and the scientific community is generally quite enthusiastic about this proposal, but wants to make sure it not only is done safely but does nothing to harm Hubble in any way, both completely reasonable concerns. While there appear to be some individuals who are opposed for purely political and egotistically reasons — a desire to keep control of this turf no matter what — I don’t see that faction having much influence long term.
Whether this project can go forward I think will be largely determined by the success or failure of Isaacman’s next manned flight, dubbed Polaris Dawn and scheduled for this summer. On it he will attempt the first spacewalk by a private citizen, using SpaceX’s Resilience capsule and EVA spacesuit. If that spacewalk is a success, and he can demonstrate the ability to accomplish some complex tasks during the EVA, it will certainly ease the concerns of many about a follow-up repair mission to Hubble.
If it does proceed, the goal appears to be to attach new gyroscope hardware to the outside of Hubble, rather than replace the failed gyroscopes already in place. Such an approach will be simpler and more in line with the capabilities of a Dragon capsule, compared to the repair work the astronauts did on the space shuttle.
AST SpaceMobile, which launched in 2022 its first satellite for direct cellphone-to-satellite communications and has been successfully testing it since, has now signed a deal with ATT, which wants to use the company’s planned constellation of five such satellites, scheduled for launch this summer.
Nor is this the only satellite company launching such satellites. SpaceX has already launched several dozen Starlink satellites adapted for direct cell-to-satellite service. In addition, it appears that all the companies making smart phones are adding features to their phones that would allow this capability in the future.
Once operational, these satellites will act as orbiting cell towers, and will thus eliminate most of the dead zones in all the populated regions on Earth.
One of the satellites in the commercial satellite constellation run by the Australian company HEO Robotics to monitor objects in space successfully took a picture of ISS this week as it zipped by only 43 miles away.
That picture is to the right, reduced to post here. The relative speeds between the satellite and ISS was about 3.7 miles a second. The station’s main truss, which holds up its solar panels and heat radiators, is the vertical structure going from upper left to lower right. The habitable modules cross this at right angles, with what appears to be the Russian section on the right with a Soyuz or Progress docked to the port at the end. A Dragon capsule can be seen at the opposite end, docked to the American section on the left.
The company’s satellites have previously provided imagery of other objects in orbit, including the ERS-2 satellite just before it was de-orbited as well as China’s Tiangong-3 space station during its assembly.
The new FAA authorization bill that that House approved yesterday and was passed previously by the Senate includes a short extension to the end of the year of the so-called “learning period” that is supposed to restrict the agency’s ability to regulate the new commercial space industry.
That limitation was first established in 2004 with a time period of eight years. It has been extended numerous times since then. The most recent extensions however have been very short, suggesting Congress (mostly from the Democrat side of the aile) wants to soon eliminate it. Whether that happens when it comes up for extension again at the end of 2024 will depend greatly on which party is in control after the election.
It really doesn’t matter. Everything the FAA has been doing in the past three years suggests this learning period no longer exists anyway. The agency has been demanding every new American company or rocket or spacecraft meet much higher regulatory requirements, which appears to have slowed significantly the development of those new companies, rockets, or spacecraft in the past two years.
Lithuania yesterday became the 40th nation to sign the Artemis Accords, joining the American alliance for exploring the solar system.
The alliance now includes these nations: Angola, Argentina, Australia, Bahrain, Belgium, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, Columbia, Czech Republic, Ecuador, France, Germany, Greece, Iceland, India, Israel, Italy, Japan, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Mexico, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Nigeria, Poland, Romania, Rwanda, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Slovenia, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, the United Arab Emirates, the Ukraine, the United States and Uruguay.
The press release for this announcement differed slightly from the last few, all of which emphasized how the accords were designed to “reinforce” the Outer Space Treaty, the exact opposite of its original goals, which was to build an alliance of nations focused on getting around or eliminating the restrictions of the Outer Space Treaty on private property in space. Today the press release was more vague:
NASA, along with the Department of State and seven other nations, established the Artemis Accords in 2020 to lay out a set of principles grounded in the Outer Space Treaty of 1967 and three related space treaties. With the commitment of now 40 nations, the accords community will facilitate a long-term and peaceful presence of deep space exploration for the benefit of humanity.
Does this mean the Biden administration is going to return to the accords’ original goal? I doubt it. I think instead they decided they needed to be less obvious about their new intentions, which increasingly appears to be to use this alliance to foster globalist international cooperation aimed at keeping all power and legal control in the hands of the governments themselves.