One of Australia’s proposed spaceports moves
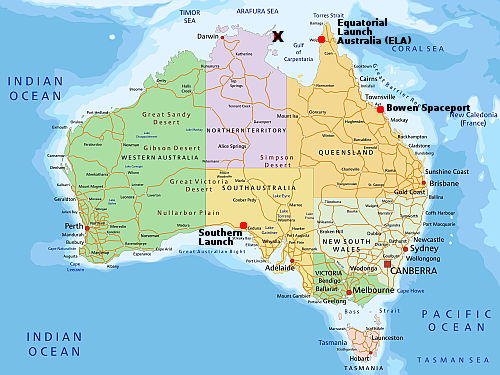
Australia’s spaceports
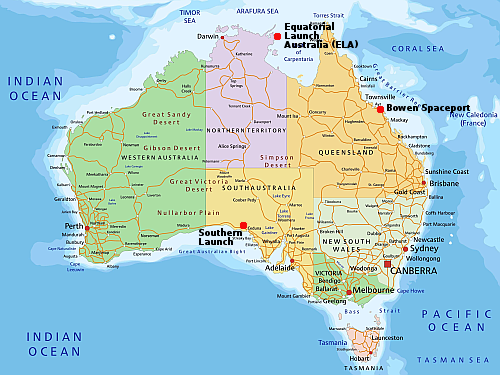
“I’m from the government and I’m here to help!” Because of its inability to get the proper permissions from a local council, the management of Equatorial Launch Australia (ELA) has abandoned its original spaceport location on the Gove peninsula in the Northwest Territory of Australia and shifted east to a new location on the York peninsula in Queensland.
On the map to the right the “X” shows the old location, with the new location near the town of Weipa on the west coast of the peninsula. The change was forced on the company when it could not get proper approvals from the Northern Land Council (NLC), which manages the Arnhem Land Aboriginal Land Trust where the original site was located.
In a statement late on Monday, ELA said its most recent attempt to finalise a lease for the expansion of the ASC in October had been unsuccessful, following three other failed attempts in the last 12 months. In each case, it said the NLC had “failed to meet its own specified deadline for the approval of the Head Lease” or “provide any official reason for the delay”, despite pleas from the NT government and the Gumatj Aboriginal Corporation.
Because ELA has a launch contract with a South Korea rocket startup Innospace that intends to launch next year, it decided the switch had to occur now to make sure it could meet its obligations under this launch contract.

Australia’s spaceports
“I’m from the government and I’m here to help!” Because of its inability to get the proper permissions from a local council, the management of Equatorial Launch Australia (ELA) has abandoned its original spaceport location on the Gove peninsula in the Northwest Territory of Australia and shifted east to a new location on the York peninsula in Queensland.
On the map to the right the “X” shows the old location, with the new location near the town of Weipa on the west coast of the peninsula. The change was forced on the company when it could not get proper approvals from the Northern Land Council (NLC), which manages the Arnhem Land Aboriginal Land Trust where the original site was located.
In a statement late on Monday, ELA said its most recent attempt to finalise a lease for the expansion of the ASC in October had been unsuccessful, following three other failed attempts in the last 12 months. In each case, it said the NLC had “failed to meet its own specified deadline for the approval of the Head Lease” or “provide any official reason for the delay”, despite pleas from the NT government and the Gumatj Aboriginal Corporation.
Because ELA has a launch contract with a South Korea rocket startup Innospace that intends to launch next year, it decided the switch had to occur now to make sure it could meet its obligations under this launch contract.