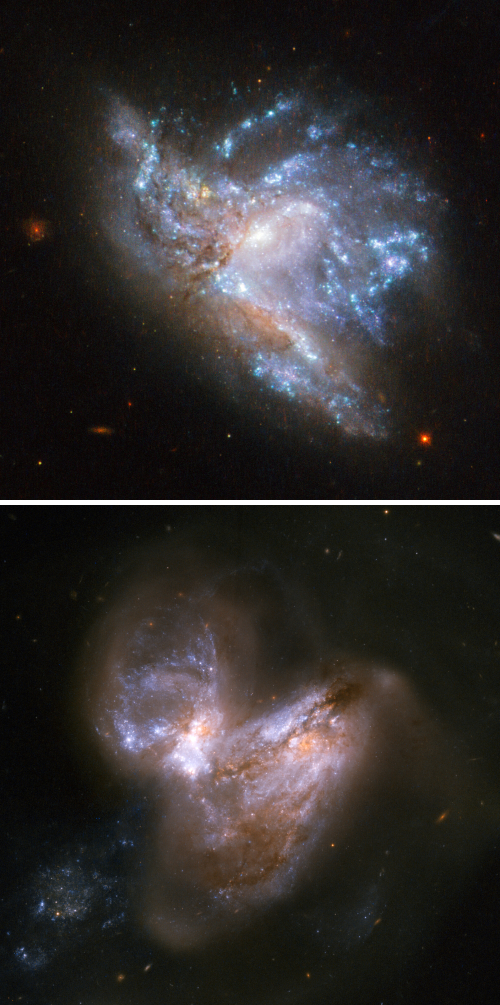
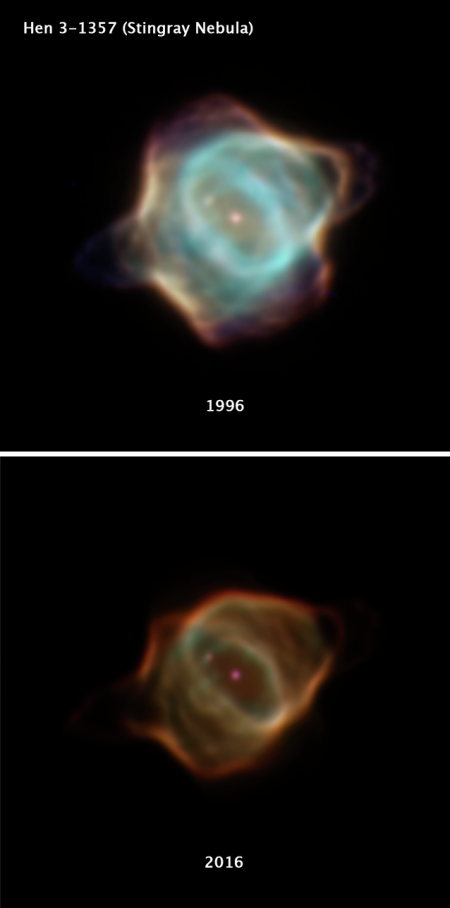
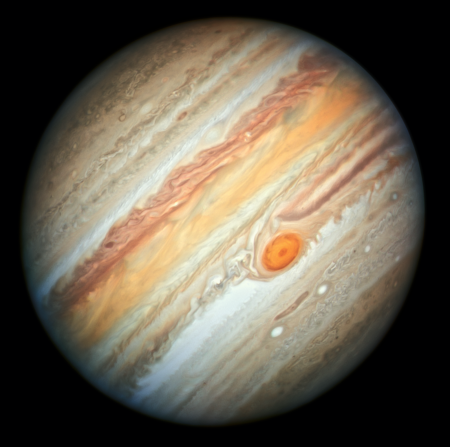
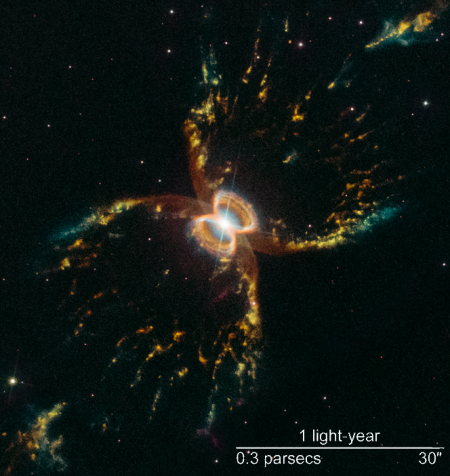
Hubble’s wide field camera returns to operation
Though the Hubble Space Telescope returned to science operations on March 12th after going into safe mode, its wide field camera did not.
Engineers however now report that they have successfully restored the camera to operations as well. The reason for the delayed restoration exemplifies Hubble’s aging status.
Analysis showed that voltage levels in WFC3 power supplies have slowly decreased over time as their electronics aged. The electronics experience colder temperatures when the hardware is turned off in safe mode. This factor coupled with the power the instrument components draw as they are turned back on contributed to the small voltage fluctuation that suspended WFC3 recovery operations. Further detailed analysis indicated that it would be safe to slightly reduce the low voltage limit to avoid a future suspend, and it would be safe to recover the instrument to its science state.
The instrument has now been safely recovered. Standard calibration of the instrument and other pre-observation activities will be conducted this week.
All the telescope’s equipment has been adjusted in recent years to deal with the varying ages of its instruments and its main structure. For example, this wide field camera was installed during the last shuttle serving mission in 2009, and is therefore one of Hubble’s newest components. It however is now more than a decade old, and thus needs careful handling to function properly.
Other components are far older, such as the primary motor to open and close the telescope’s “lens cap”. That failed during this safe mode, forcing engineers to switch to a back up motor to control the cap. Whether they can recover that primary motor is presently unclear, though unlikely.
Expect more such issues in the coming years.
Though the Hubble Space Telescope returned to science operations on March 12th after going into safe mode, its wide field camera did not.
Engineers however now report that they have successfully restored the camera to operations as well. The reason for the delayed restoration exemplifies Hubble’s aging status.
Analysis showed that voltage levels in WFC3 power supplies have slowly decreased over time as their electronics aged. The electronics experience colder temperatures when the hardware is turned off in safe mode. This factor coupled with the power the instrument components draw as they are turned back on contributed to the small voltage fluctuation that suspended WFC3 recovery operations. Further detailed analysis indicated that it would be safe to slightly reduce the low voltage limit to avoid a future suspend, and it would be safe to recover the instrument to its science state.
The instrument has now been safely recovered. Standard calibration of the instrument and other pre-observation activities will be conducted this week.
All the telescope’s equipment has been adjusted in recent years to deal with the varying ages of its instruments and its main structure. For example, this wide field camera was installed during the last shuttle serving mission in 2009, and is therefore one of Hubble’s newest components. It however is now more than a decade old, and thus needs careful handling to function properly.
Other components are far older, such as the primary motor to open and close the telescope’s “lens cap”. That failed during this safe mode, forcing engineers to switch to a back up motor to control the cap. Whether they can recover that primary motor is presently unclear, though unlikely.
Expect more such issues in the coming years.