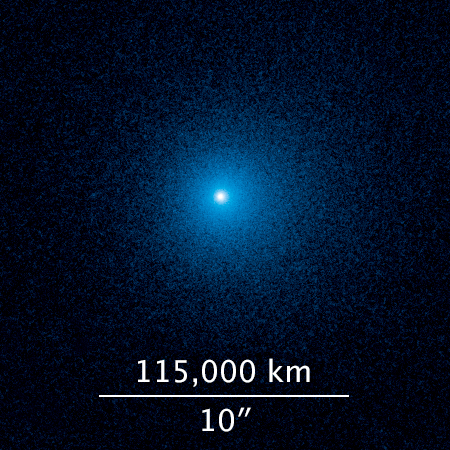
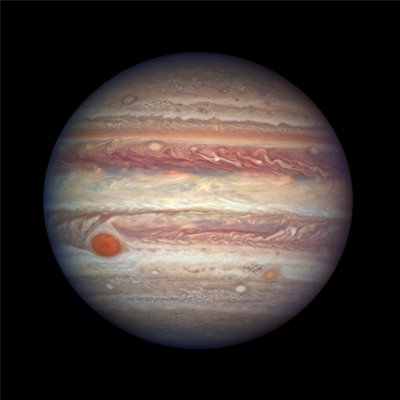
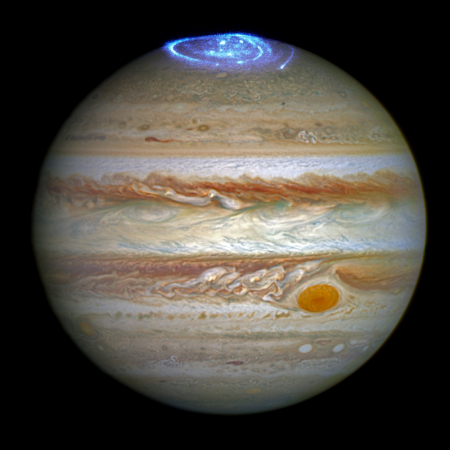
Hubble’s main camera in safe mode
The coming dark age: The Wide Field Camera on the Hubble Space Telescope has experienced “an anomaly” that has forced its shut down.
The announcement is a mere one paragraph long, and provides no further information.
This camera was installed on the space telescope during the last shuttle mission in 2009. It is now almost a decade since that mission, which was expected to extend Hubble’s life for at least five years. It is therefore not surprising that things are beginning to fail. In October they had a serious gyroscope problem when a gyroscope failed and they had problems getting their last back-up gyroscope to work. They got it working, but this has left us with a telescope with no gyroscope backups. With the next failure they will have to shift to one gyroscope mode, meaning sharp images will no longer be possible. Now the main camera has shut down.
Unfortunately, it appears that we are reaching the end of Hubble’s life span. The sad thing is that this shouldn’t be necessary. It can be repaired, but this would require a robot mission, something that would have been very difficult a decade ago but is quite doable at a reasonable cost today. No such mission is being considered however.
Even worse, the bad planning that is routine for our modern intellectual class has left us with no replacement, for the foreseeable future. In the late 1990s the astronomy community chose this path, deciding to replace Hubble with an infrared space telescope, the James Webb Space Telescope. They and NASA also decided to push the limits of engineering with Webb, resulting in a project that is about a decade behind schedule with a budget that has ballooned from $1 billion to $9 billion. Meanwhile, there has been no money for any other major space telescopes. And the one the astronomy community proposed in 2011, WFIRST, is already over budget and behind schedule, in its design phase.
The astronomy community has also decided in the past two decades that it could replace Hubble with giant ground-based telescopes, a decision that has so far proven to be problematic. Though adaptive optics can eliminate some of the fuzziness caused by the atmosphere, it limits observations to very narrow fields of view, meaning it cannot obtain large mosaics of big objects, such as this Hubble release earlier this week of an image of the nearby Triangulum Galaxy. Moreover, almost all of the giant ground-based telescopes built so far have struggled with many engineering issues.
In terms of astronomy, we are thus about to go blind, returning to the days prior to the space age when our view of the heavens was fuzzy and out of focus.
The coming dark age: The Wide Field Camera on the Hubble Space Telescope has experienced “an anomaly” that has forced its shut down.
The announcement is a mere one paragraph long, and provides no further information.
This camera was installed on the space telescope during the last shuttle mission in 2009. It is now almost a decade since that mission, which was expected to extend Hubble’s life for at least five years. It is therefore not surprising that things are beginning to fail. In October they had a serious gyroscope problem when a gyroscope failed and they had problems getting their last back-up gyroscope to work. They got it working, but this has left us with a telescope with no gyroscope backups. With the next failure they will have to shift to one gyroscope mode, meaning sharp images will no longer be possible. Now the main camera has shut down.
Unfortunately, it appears that we are reaching the end of Hubble’s life span. The sad thing is that this shouldn’t be necessary. It can be repaired, but this would require a robot mission, something that would have been very difficult a decade ago but is quite doable at a reasonable cost today. No such mission is being considered however.
Even worse, the bad planning that is routine for our modern intellectual class has left us with no replacement, for the foreseeable future. In the late 1990s the astronomy community chose this path, deciding to replace Hubble with an infrared space telescope, the James Webb Space Telescope. They and NASA also decided to push the limits of engineering with Webb, resulting in a project that is about a decade behind schedule with a budget that has ballooned from $1 billion to $9 billion. Meanwhile, there has been no money for any other major space telescopes. And the one the astronomy community proposed in 2011, WFIRST, is already over budget and behind schedule, in its design phase.
The astronomy community has also decided in the past two decades that it could replace Hubble with giant ground-based telescopes, a decision that has so far proven to be problematic. Though adaptive optics can eliminate some of the fuzziness caused by the atmosphere, it limits observations to very narrow fields of view, meaning it cannot obtain large mosaics of big objects, such as this Hubble release earlier this week of an image of the nearby Triangulum Galaxy. Moreover, almost all of the giant ground-based telescopes built so far have struggled with many engineering issues.
In terms of astronomy, we are thus about to go blind, returning to the days prior to the space age when our view of the heavens was fuzzy and out of focus.