New spaceport proposed in India independent of its space agency ISRO
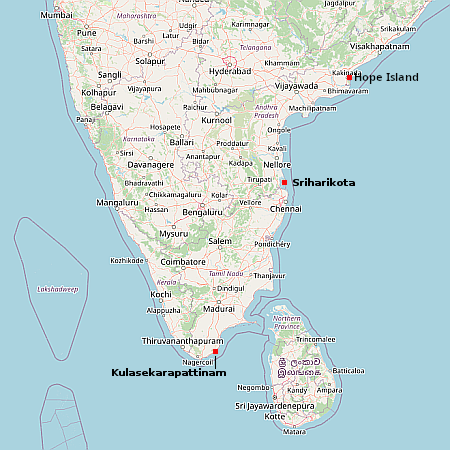
The existing and proposed spaceports in India
According to the chief minister of the Andhra Pradesh province of India, his government is presently in discussions with the private Indian energy company Greenko Group about establishing a partnership to build a commercial spaceport at Hope Island off the coast near the city of Kakinada.
Addressing the gathering of foreign investors in renewable energies and officials of the State government after performing ‘bhumi puja’ [ground-breaking] for the Green Hydrogen and Green Ammonia Production Complex in Kakinada, Mr. Naidu said, “Soon, we (Andhra Pradesh) will launch satellites from the Hope Island. It will come soon, and Kakinada will have a lot of advantages in the field of technology and innovation.”
“The Greenko Group is evincing interest in being a part of the State government’s Space City project that includes developing satellite launching facility. In a recent interaction, Greenko Founder and Group CEO Anil Kumar Chalamalsetty has shown interest in the Space City project on the Hope Island,” said Mr. Naidu.
The location has advantages over the Sriharikota spaceport, run by India’s space agency ISRO, which on polar orbital launches needs to use extra fuel to avoid flying over Sri Lanka to the south. This issue is one of the reasons ISRO is presently building that second spaceport to the south for its SSLV rocket.
If privately run, this new spaceport will have other advantages. It will possibly attract some of India’s new rocket startups, who will avoid some of the bureaucracy that accompanies any dealings with ISRO. ISRO launches always involve a gigantic number of government personnel, a cost these startups can’t afford. This new Hope Island spaceport might avoid these costs with low overhead and efficient operations.
Nothing is firm yet. From the statement above, it appears the negotiation is in a very preliminary stage, and might never bear fruit.
Hat tip BtB’s stringer Jay.

The existing and proposed spaceports in India
According to the chief minister of the Andhra Pradesh province of India, his government is presently in discussions with the private Indian energy company Greenko Group about establishing a partnership to build a commercial spaceport at Hope Island off the coast near the city of Kakinada.
Addressing the gathering of foreign investors in renewable energies and officials of the State government after performing ‘bhumi puja’ [ground-breaking] for the Green Hydrogen and Green Ammonia Production Complex in Kakinada, Mr. Naidu said, “Soon, we (Andhra Pradesh) will launch satellites from the Hope Island. It will come soon, and Kakinada will have a lot of advantages in the field of technology and innovation.”
“The Greenko Group is evincing interest in being a part of the State government’s Space City project that includes developing satellite launching facility. In a recent interaction, Greenko Founder and Group CEO Anil Kumar Chalamalsetty has shown interest in the Space City project on the Hope Island,” said Mr. Naidu.
The location has advantages over the Sriharikota spaceport, run by India’s space agency ISRO, which on polar orbital launches needs to use extra fuel to avoid flying over Sri Lanka to the south. This issue is one of the reasons ISRO is presently building that second spaceport to the south for its SSLV rocket.
If privately run, this new spaceport will have other advantages. It will possibly attract some of India’s new rocket startups, who will avoid some of the bureaucracy that accompanies any dealings with ISRO. ISRO launches always involve a gigantic number of government personnel, a cost these startups can’t afford. This new Hope Island spaceport might avoid these costs with low overhead and efficient operations.
Nothing is firm yet. From the statement above, it appears the negotiation is in a very preliminary stage, and might never bear fruit.
Hat tip BtB’s stringer Jay.