Hayabusa-2 aborts close-in drop of visual marker on Ryugu
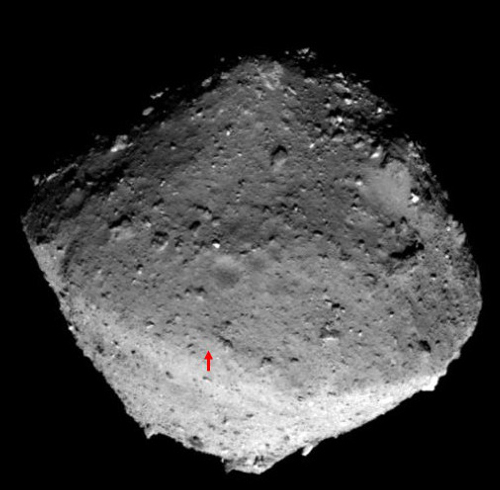
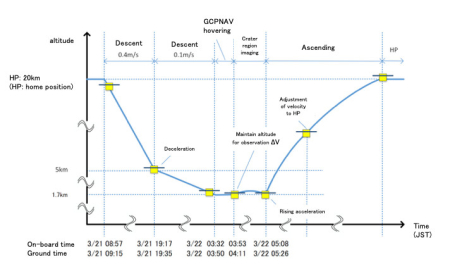
Japan’s asteroid probe Hayabusa-2 automatically aborted a planned drop of a visual markee on the asteroid Ryugu at the site where the probe created a crater in April.
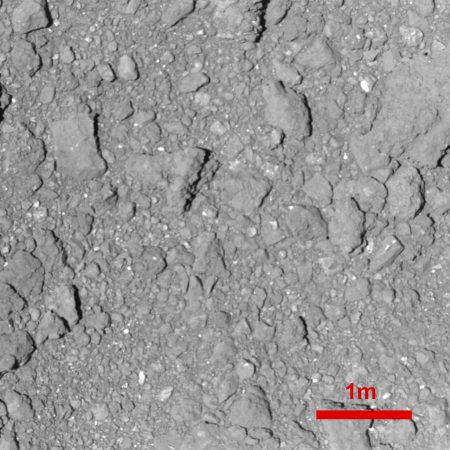
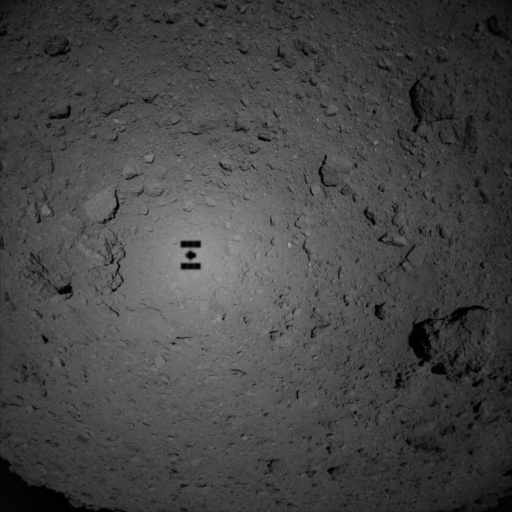
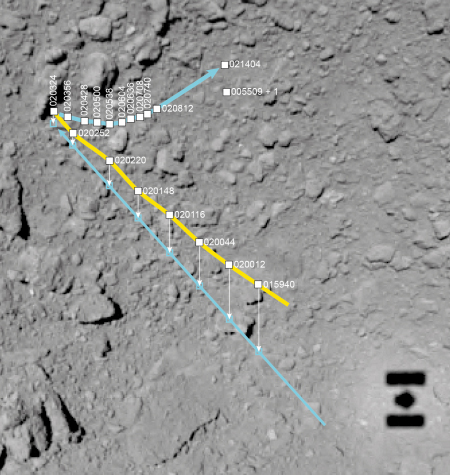
Thursday’s mission was to observe the targeted area in detail and drop a marker from an altitude of 10 meters. But officials say the probe automatically suspended the operation after it descended to about 50 meters above the surface. It then headed toward its standby position of 20 kilometers above Ryugu. Hayabusa2 is designed to automatically abort its landing if it detected any irregularity. The agency is looking into the cause of the arrested descent.
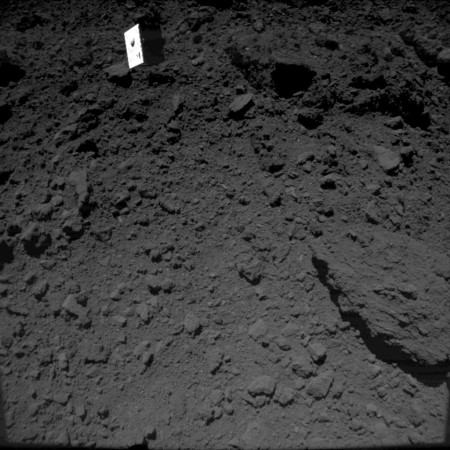
Once the marker is eventually in place, they will use it for guidance during a a second touchdown to grab further samples, this time hopefully of material churned up by the explosion that created the crater.
Japan’s asteroid probe Hayabusa-2 automatically aborted a planned drop of a visual markee on the asteroid Ryugu at the site where the probe created a crater in April.
Thursday’s mission was to observe the targeted area in detail and drop a marker from an altitude of 10 meters. But officials say the probe automatically suspended the operation after it descended to about 50 meters above the surface. It then headed toward its standby position of 20 kilometers above Ryugu. Hayabusa2 is designed to automatically abort its landing if it detected any irregularity. The agency is looking into the cause of the arrested descent.
Once the marker is eventually in place, they will use it for guidance during a a second touchdown to grab further samples, this time hopefully of material churned up by the explosion that created the crater.