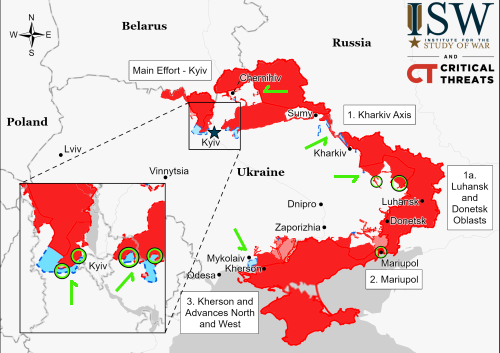
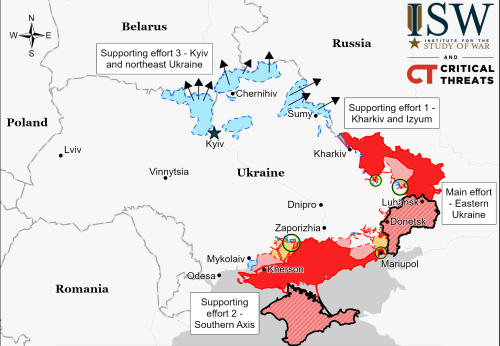
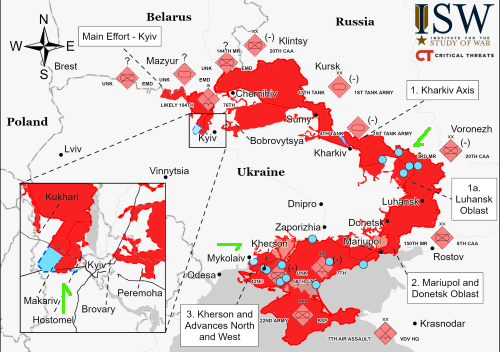
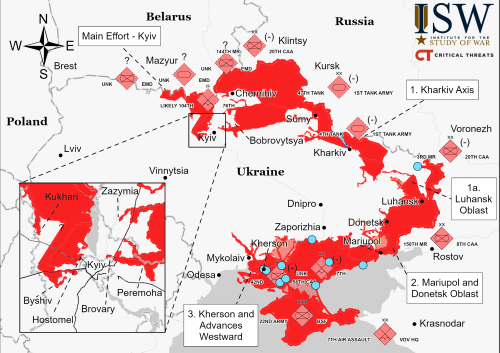
Europe removes its science instruments from future Russian lunar missions
The Europe Space Agency (ESA) yesterday announced that because of Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine it will no longer fly any science instruments on three upcoming Russian unmanned lunar probes.
ESA will discontinue cooperative activities with Russia on Luna-25, -26 and -27. As with ExoMars, the Russian aggression against Ukraine and the resulting sanctions put in place represent a fundamental change of circumstances and make it impossible for ESA to implement the planned lunar cooperation. However, ESA’s science and technology for these missions remains of vital importance. A second flight opportunity has already been secured on board a NASA-led Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) mission for the PROSPECT lunar drill and volatile analysis package (originally planned for Luna-27). An alternative flight opportunity to test the ESA navigation camera known as PILOT-D (originally planned for Luna-25) is already being procured from a commercial service provider.
In other words, Europe is switching to the many private American companies that are developing lunar landers for NASA science instruments. It has also signed onto a Japanese lunar mission. All have payload space, and all are willing to take the cash of a new customer.
Meanwhile, this is how Dmitry Rogozin responded to this decision:
“Good riddance! One less European dame off our backs, so Russia should go far with a lighter load,”
To sum this all up, when it comes to space, the Ukraine invasion has been Russia’s loss, and everyone else’s gain. Even if the invasion were to end today, it will take at least a decade to re-establish Russia’s business ties with the west.
Unfortunately, the invasion will cost the Ukraine as well. In making the above announcement ESA officials also said that it is looking for alternatives to the Ukrainian rocket engines used in its Vega-C upper stage.
At the news conference, ESA also discussed the future of its small Vega rocket, which relies on Ukraine-built engines in its upper stage. The engines are manufactured by the Ukrainian company Yuzhmash, which is based in the tech city of Dnipro. Although Dnipro has been under heavy bombardment, there have been no official reports so far about damage to Yuzhmash. It is, however, clear that ESA doesn’t expect to continue its partnership with the company in the future. “We now have sufficient engines for 2022 and 2023,” Aschbacher said. “We are working on options for 2024 and onwards based on different technologies.”
Daniel Neuenschwander, ESA’s director of space transportation, added: “We are working on engine opportunities within Europe and outside of Europe, which are either tested or, even better, already existing and fully qualified.”
Whether ESA completely breaks off its partnership with the Ukraine however is not certain. Should the war continue to favor the Ukraine, then it could be that partnership will continue. Only time will tell. Right now, it is simply prudent for ESA to look for more stable alternatives.
The Europe Space Agency (ESA) yesterday announced that because of Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine it will no longer fly any science instruments on three upcoming Russian unmanned lunar probes.
ESA will discontinue cooperative activities with Russia on Luna-25, -26 and -27. As with ExoMars, the Russian aggression against Ukraine and the resulting sanctions put in place represent a fundamental change of circumstances and make it impossible for ESA to implement the planned lunar cooperation. However, ESA’s science and technology for these missions remains of vital importance. A second flight opportunity has already been secured on board a NASA-led Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) mission for the PROSPECT lunar drill and volatile analysis package (originally planned for Luna-27). An alternative flight opportunity to test the ESA navigation camera known as PILOT-D (originally planned for Luna-25) is already being procured from a commercial service provider.
In other words, Europe is switching to the many private American companies that are developing lunar landers for NASA science instruments. It has also signed onto a Japanese lunar mission. All have payload space, and all are willing to take the cash of a new customer.
Meanwhile, this is how Dmitry Rogozin responded to this decision:
“Good riddance! One less European dame off our backs, so Russia should go far with a lighter load,”
To sum this all up, when it comes to space, the Ukraine invasion has been Russia’s loss, and everyone else’s gain. Even if the invasion were to end today, it will take at least a decade to re-establish Russia’s business ties with the west.
Unfortunately, the invasion will cost the Ukraine as well. In making the above announcement ESA officials also said that it is looking for alternatives to the Ukrainian rocket engines used in its Vega-C upper stage.
At the news conference, ESA also discussed the future of its small Vega rocket, which relies on Ukraine-built engines in its upper stage. The engines are manufactured by the Ukrainian company Yuzhmash, which is based in the tech city of Dnipro. Although Dnipro has been under heavy bombardment, there have been no official reports so far about damage to Yuzhmash. It is, however, clear that ESA doesn’t expect to continue its partnership with the company in the future. “We now have sufficient engines for 2022 and 2023,” Aschbacher said. “We are working on options for 2024 and onwards based on different technologies.”
Daniel Neuenschwander, ESA’s director of space transportation, added: “We are working on engine opportunities within Europe and outside of Europe, which are either tested or, even better, already existing and fully qualified.”
Whether ESA completely breaks off its partnership with the Ukraine however is not certain. Should the war continue to favor the Ukraine, then it could be that partnership will continue. Only time will tell. Right now, it is simply prudent for ESA to look for more stable alternatives.