Russians successfully test replacement Soyuz capsule for leaks
The next Soyuz capsule to launch to ISS has now been passed its leak tests on the ground as it is being prepared for a February 20th launch.
“At the Baikonur cosmodrome, leak tests of the Soyuz MS-23 transport crewed spacecraft have been completed,” the [Roscosmos press release] said. In the coming days, checks of the propulsion system’s automation equipment, onboard digital computerized system and radio engineering systems will follow. Also, the thermal control system is to be filled with a coolant.
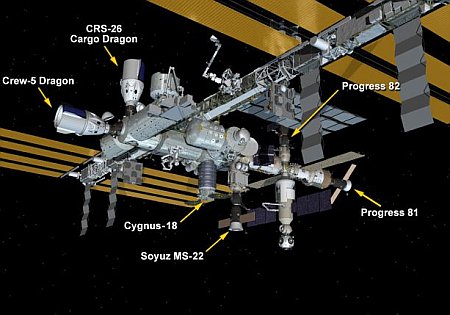
The launch has been moved up one month in order to speed the replacement of the leaking Soyuz presently on ISS.
The next Soyuz capsule to launch to ISS has now been passed its leak tests on the ground as it is being prepared for a February 20th launch.
“At the Baikonur cosmodrome, leak tests of the Soyuz MS-23 transport crewed spacecraft have been completed,” the [Roscosmos press release] said. In the coming days, checks of the propulsion system’s automation equipment, onboard digital computerized system and radio engineering systems will follow. Also, the thermal control system is to be filled with a coolant.
The launch has been moved up one month in order to speed the replacement of the leaking Soyuz presently on ISS.