One of Saturn’s many weird moons
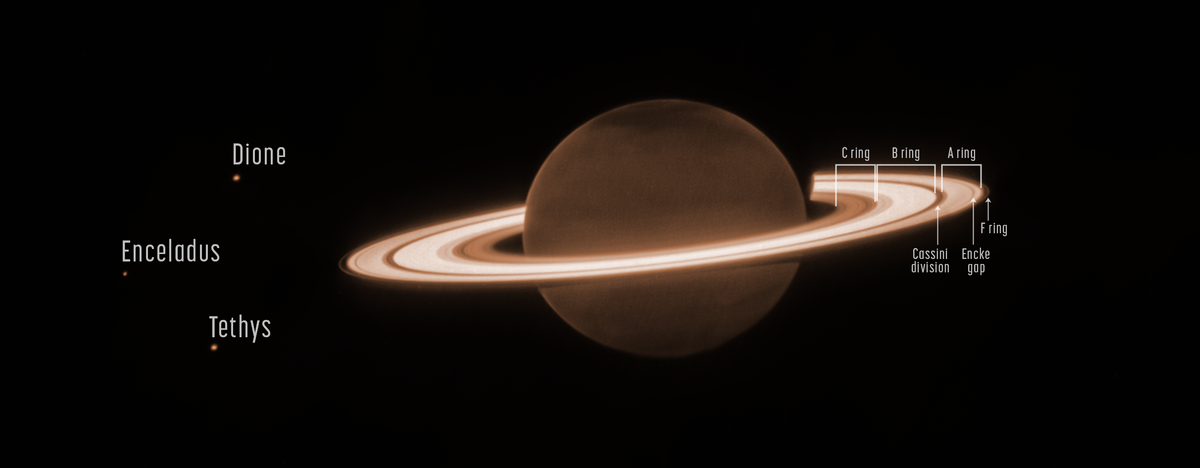
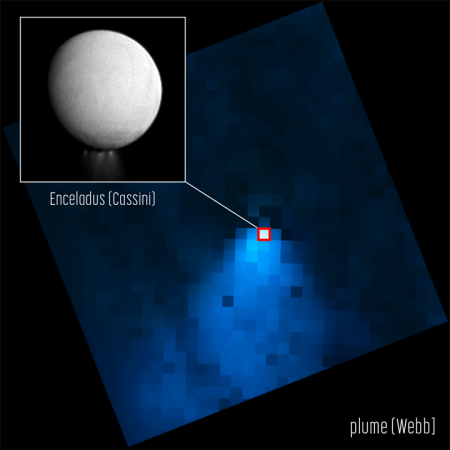
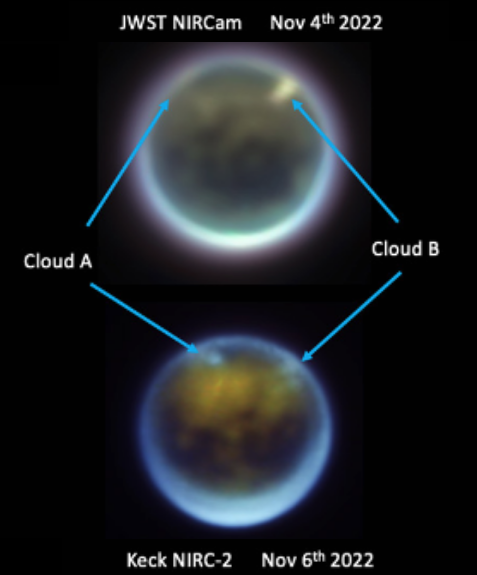
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on April 13, 2017 by the orbiter Cassini as it began it last close loops around Saturn before diving into its atmosphere to burn up.
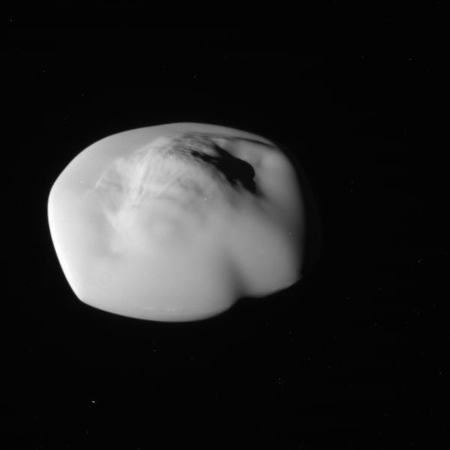
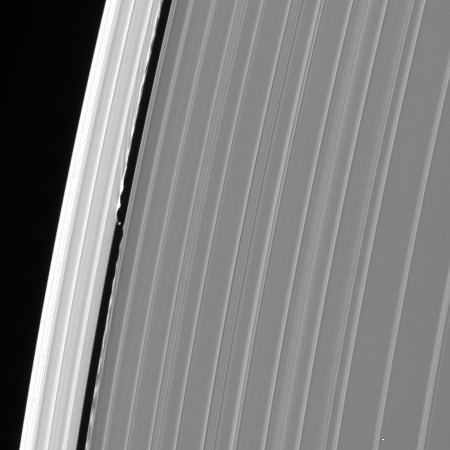
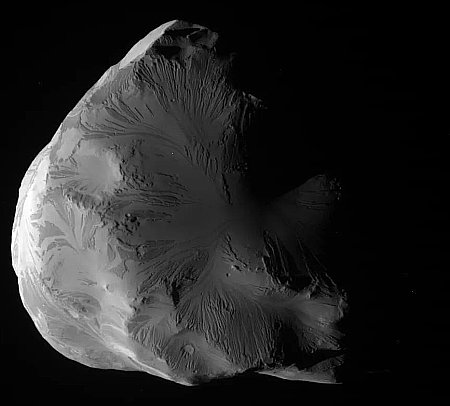
Those close loops allowed it to get good close-up images of a few of the tiny moons that orbit in or close to the gas giant’s rings. On the right is one of those pictures, of the moon Atlas, taken from a distance of about 10,000 miles.
The moon’s weird ravioli shape is thought to be caused by the accretion of dust and ice from the nearby rings along Atlas’s equator.
Scientists also found the moon surfaces to be highly porous, further confirming that they were formed in multiple stages as ring material settled onto denser cores that might be remnants of a larger object that broke apart. The porosity also helps explain their shape: Rather than being spherical, they are blobby and ravioli-like, with material stuck around their equators. “We found these moons are scooping up particles of ice and dust from the rings to form the little skirts around their equators,” Buratti said. “A denser body would be more ball-shaped because gravity would pull the material in.”
Atlas itself is about 25 miles wide and about 11.5 miles thick, at its thickest point. I suspect if you tried to walk on it you would sink into the accumulated dust and ice, as it is likely no more dense as newly fallen snow.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on April 13, 2017 by the orbiter Cassini as it began it last close loops around Saturn before diving into its atmosphere to burn up.
Those close loops allowed it to get good close-up images of a few of the tiny moons that orbit in or close to the gas giant’s rings. On the right is one of those pictures, of the moon Atlas, taken from a distance of about 10,000 miles.
The moon’s weird ravioli shape is thought to be caused by the accretion of dust and ice from the nearby rings along Atlas’s equator.
Scientists also found the moon surfaces to be highly porous, further confirming that they were formed in multiple stages as ring material settled onto denser cores that might be remnants of a larger object that broke apart. The porosity also helps explain their shape: Rather than being spherical, they are blobby and ravioli-like, with material stuck around their equators. “We found these moons are scooping up particles of ice and dust from the rings to form the little skirts around their equators,” Buratti said. “A denser body would be more ball-shaped because gravity would pull the material in.”
Atlas itself is about 25 miles wide and about 11.5 miles thick, at its thickest point. I suspect if you tried to walk on it you would sink into the accumulated dust and ice, as it is likely no more dense as newly fallen snow.