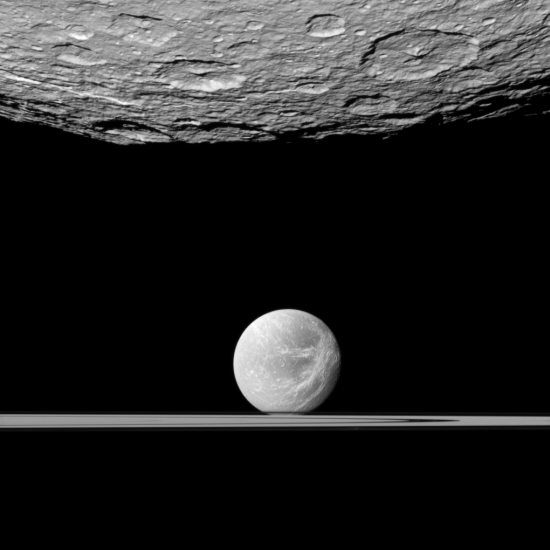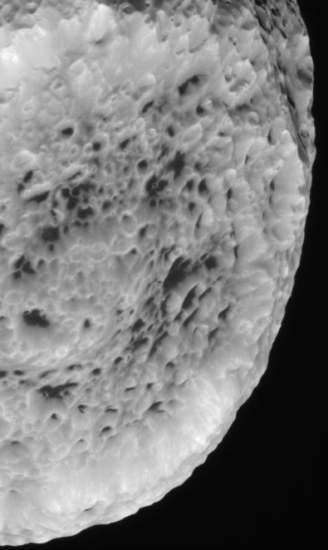
On August 25 Cassini did a close fly-by of the small Saturn moon Hyperion, getting as close as 15,500 miles. The mission has just released images from that fly-by.
Looks like a sponge, doesn’t it? This moon is small, only 168 miles across, which makes it about half the size of the asteroid Vesta that Dawn is presently orbiting. Why it is so peppered with craters is of course the big science question. I would guess this has something to do with the environment around Saturn, with its rings and the innumerable particles that come from it. Yet, other moons of Saturn are not as crater-filled, so there is obviously more to this than meets the eye.
This fly-by was the second closest of Hyperion that Cassini has done, the first passing over the the moon’s surface by only 310 miles. Because the irregularly-shaped moon’s rotation is more like a chaotic tumble, scientists could not predict what part of the surface they would see. To their luck the new images captured new territory.
Another fly-by is scheduled in only three weeks, on September 16, 2011. This time, however, the spacecraft won’t get as close, passing at a distance of about 36,000 miles.



