New close-up images of Ceres

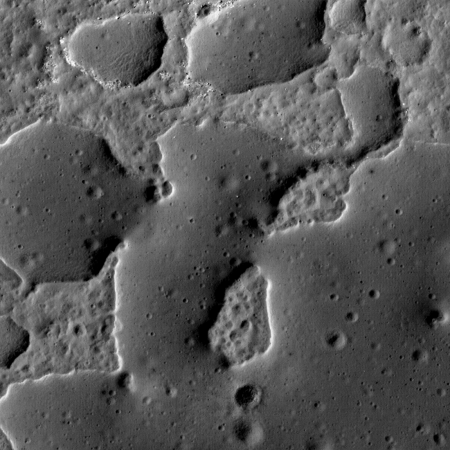
Cool image time! The image on the right, cropped and reduced in resolution to post here, is one of two images released today by the Dawn science team of the double bright spots found in Occator Crater, taken from the spacecraft’s tight final orbit above Ceres. This image shows what they have dubbed Cerealia Facula. The second image shows Vinalia Faculae.
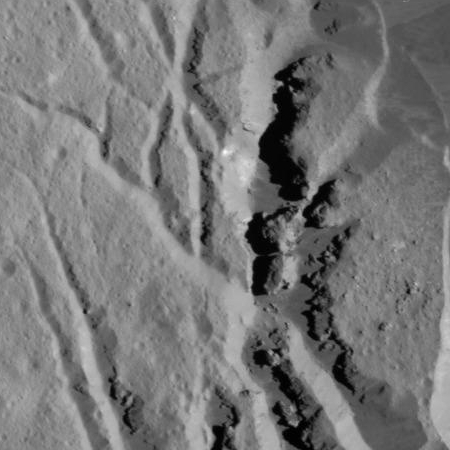
This mosaic of Cerealia Facula is based on images obtained by NASA’s Dawn spacecraft in its second extended mission, from an altitude as low as about 21 miles (34 kilometers). The contrast in resolution obtained by the two phases is visible here, reflected by a few gaps in the high-resolution coverage. This image is superposed to a similar scene acquired in the low-altitude mapping orbit of the mission from an altitude of about 240 miles (385 km).
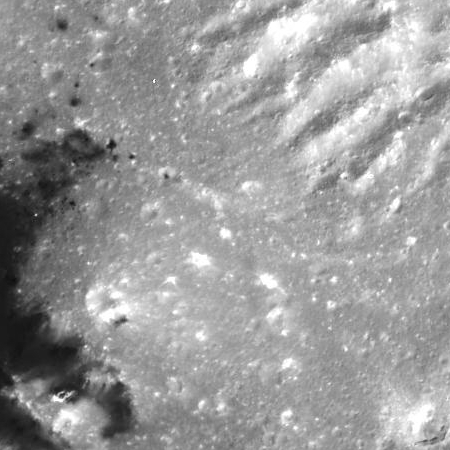

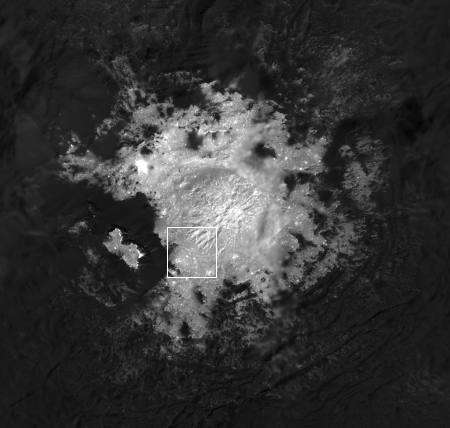
The second image on the left is a crop at full resolution of the area in the white box above. This gives you a taste of the many interesting things found in the full resolution image. For example, the bright spots scattered throughout this image suggest they are recent upwellings from below. The ridgelines in the upper right are either the remains of the water-ice volcano they think once stood here but subsequently slumped back down to form a depression, or pressure ridges being pushed up by later upwellings.
The full image has lots more. So does the image of Vinalia Faculae. Check them out.

Cool image time! The image on the right, cropped and reduced in resolution to post here, is one of two images released today by the Dawn science team of the double bright spots found in Occator Crater, taken from the spacecraft’s tight final orbit above Ceres. This image shows what they have dubbed Cerealia Facula. The second image shows Vinalia Faculae.
This mosaic of Cerealia Facula is based on images obtained by NASA’s Dawn spacecraft in its second extended mission, from an altitude as low as about 21 miles (34 kilometers). The contrast in resolution obtained by the two phases is visible here, reflected by a few gaps in the high-resolution coverage. This image is superposed to a similar scene acquired in the low-altitude mapping orbit of the mission from an altitude of about 240 miles (385 km).

The second image on the left is a crop at full resolution of the area in the white box above. This gives you a taste of the many interesting things found in the full resolution image. For example, the bright spots scattered throughout this image suggest they are recent upwellings from below. The ridgelines in the upper right are either the remains of the water-ice volcano they think once stood here but subsequently slumped back down to form a depression, or pressure ridges being pushed up by later upwellings.
The full image has lots more. So does the image of Vinalia Faculae. Check them out.