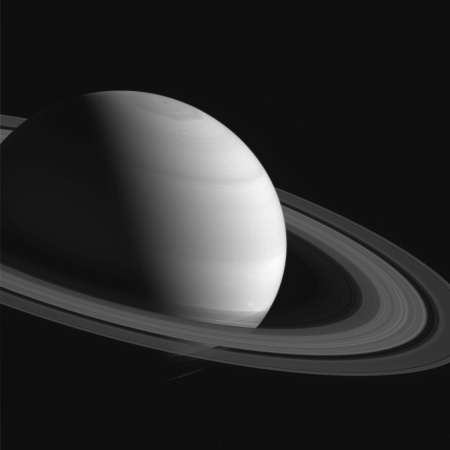
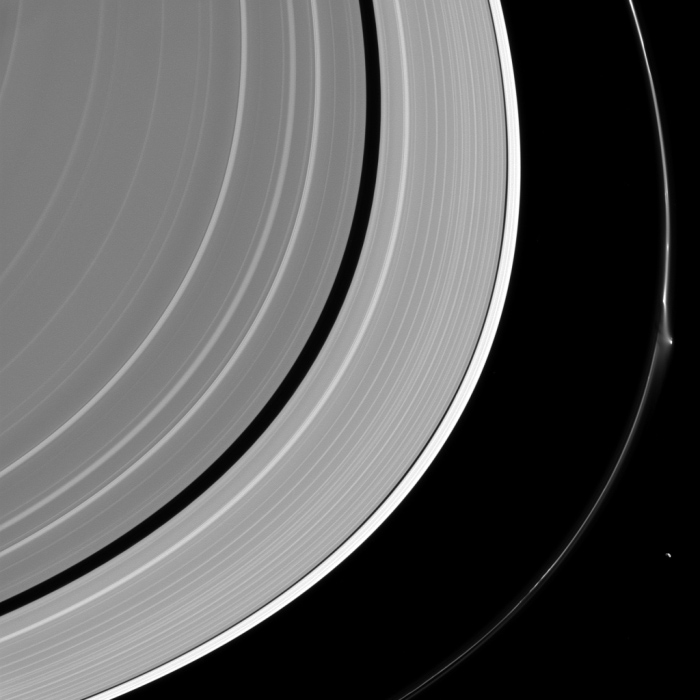
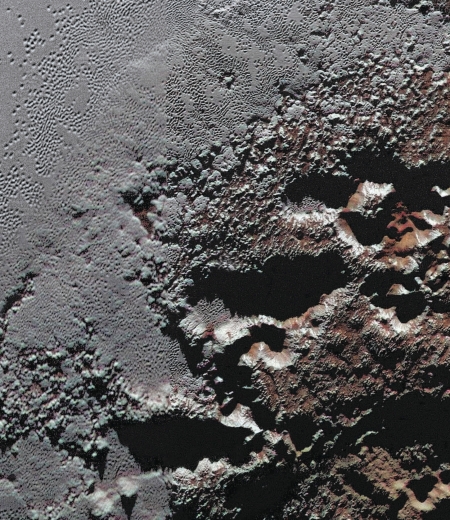
Ceres’s brightest spot

Cool image time: While I was in Washington the Dawn science team released a very nice close-up image of the bright spots inside Occator Crater on Ceres. On the right is a cropped version which focuses solely on the central brightest spot. The spot appears to overlie a central dome with a depression in the middle. Other data says the spot is the low area in the crater, and the linear cracks that radiate away as well as in concentric rings around the spot suggest that this central area has subsided, causing those cracks.
Make sure you look at the full image, as it includes the other smaller spots that are also inside Occator.

Cool image time: While I was in Washington the Dawn science team released a very nice close-up image of the bright spots inside Occator Crater on Ceres. On the right is a cropped version which focuses solely on the central brightest spot. The spot appears to overlie a central dome with a depression in the middle. Other data says the spot is the low area in the crater, and the linear cracks that radiate away as well as in concentric rings around the spot suggest that this central area has subsided, causing those cracks.
Make sure you look at the full image, as it includes the other smaller spots that are also inside Occator.