Contact re-established with dead solar satellite
Good news! After almost two years since contact was lost, NASA has re-established communications with Stereo-B, one of two solar research satellites designed to study the hemisphere of the Sun that does not face the Earth.
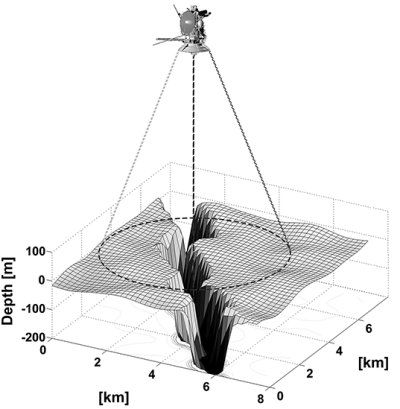
NASA re-established contact with a wayward sun-watching science satellite Sunday nearly two years after the spacecraft suddenly dropped off line during a test, the agency said in a statement Monday. NASA’s Deep Space Network, or DSN, “established a lock on the STEREO-B (spacecraft’s) downlink carrier at 6:27 p.m. EDT,” NASA said in a statement. “The downlink signal was monitored by the Mission Operations team over several hours to characterize the attitude of the spacecraft and then transmitter high voltage was powered down to save battery power. “The STEREO Missions Operations team plans further recovery processes to assess observatory health, re-establish attitude control and evaluate all subsystems and instruments.”
This is a big deal. Not only is it a testament to the spacecraft’s good design, it demonstrates the skill of the engineers at NASA who have regained contact.
Good news! After almost two years since contact was lost, NASA has re-established communications with Stereo-B, one of two solar research satellites designed to study the hemisphere of the Sun that does not face the Earth.
NASA re-established contact with a wayward sun-watching science satellite Sunday nearly two years after the spacecraft suddenly dropped off line during a test, the agency said in a statement Monday. NASA’s Deep Space Network, or DSN, “established a lock on the STEREO-B (spacecraft’s) downlink carrier at 6:27 p.m. EDT,” NASA said in a statement. “The downlink signal was monitored by the Mission Operations team over several hours to characterize the attitude of the spacecraft and then transmitter high voltage was powered down to save battery power. “The STEREO Missions Operations team plans further recovery processes to assess observatory health, re-establish attitude control and evaluate all subsystems and instruments.”
This is a big deal. Not only is it a testament to the spacecraft’s good design, it demonstrates the skill of the engineers at NASA who have regained contact.