Glowworms in Motion – time lapse
An evening pause: What could be better? Glowworms, a cave, and beautiful music by Dexter Britain called Light Bridges.
Hat tip Danae.
An evening pause: What could be better? Glowworms, a cave, and beautiful music by Dexter Britain called Light Bridges.
Hat tip Danae.
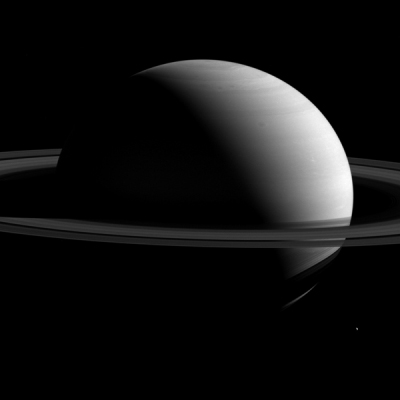

Cool image time! Be sure to click on this link to see the full resolution Cassini version of the image on the right. Its resolution is 10 miles per pixel, and even so the giant planet cannot be fit in the frame.
One moon, Tethys, is visible, though to make it so required its brightness to be increased by 2. Also, if you look close at the bands at the north pole you can see their strange still-not-understood pentagon shape.
The uncertainty of science: New data from the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) does not correspond to the Standard Model of physics, and suggest the possibility that one or two previously unpredicted particles might exist.
Then again, the explanation could be as simple as instrument error. We will have to wait and see.
In December four of seven zinnia plants in a greenhouse on ISS became sickly or died because they were receiving too much water and developed mold.
The story doesn’t really tell us much, but this paragraph reveals I think some fundamental management problems in the way NASA is running the station:
ISS commander and NASA astronaut Scott Kelly reported the mold to Mission Control Dec. 22 just as Veggie principal investigator Trent Smith was trying to manage the water problem. In pictures, Smith saw water on the plants a few days before. He told Discovery News he was trying to relay a command from NASA’s station operations team to increase fan speed in Veggie, but the mold developed before the command could be put through. One solution was, on Christmas Eve, to designate Kelly “commander” of Veggie. Kelly now has more autonomy to make changes to Veggie’s conditions if he feels the plants need it.
The scientist noticed a problem but was unable to cut through the communications bureaucracy to talk to the astronauts so that changes could be made quickly. Meanwhile, the astronauts on board ISS had not been given the freedom to make common sense changes themselves. The result is that some of the plants died.
The solution, to give an astronaut more “autonomy”, is one that the Russians learned a long time ago on their Mir space station. It was also a lesson NASA learned even longer ago on Skylab. Moreover, when astronauts are finally flying interplanetary spaceships to the planets with greenhouses just like this, they will have to have that autonomy, no matter what rules NASA establishes. It seems amazing to me that NASA is still learning this lesson now.
One more thought: It is not really a problem that the scientist had trouble reaching the astronauts quickly. In fact, it probably indicates an area of management that NASA is handling well. Communications from the ground up to ISS can be a major problem, as everyone wants to talk to the astronauts and if NASA didn’t control that communications the astronauts would never have time to do anything. Thus, placing limits on that communications makes sense, though once again it also requires that the astronauts be given a great deal of freedom to make their own decisions, as they might not be able to talk to the right experts whenever necessary.
The uncertainty of science: New data of the red giant star Betelgeuse says that the star simply doesn’t have the energy to eject the large amount of gas it routinely blows into space.
“[W]e now have a problem”, says Graham Harper, an astrophysicist at the University of Colorado Boulder. “If you’re going to eject matter you have to put energy in, and we’re not seeing that.” Harper and his colleagues used the US–German Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA), a 2.5-metre telescope that flies in a modified Boeing 747 aeroplane, to take Betelgeuse’s temperature. They found that the star’s upper atmosphere was much cooler than expected — so cool, in fact, that it doesn’t seem to have enough energy to kick gas out of its gravitational pull and into space.
“This challenges all our theoretical models,” Harper said on 7 January at a meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Kissimmee, Florida. [emphasis mine]
The data suggests the temperature of the ejected gas to be only about 512 degrees Fahrenheit. This is far too cool to fit any theory for explaining the vast amounts of gas that the star routinely puffs into space. It also suggests, not surprisingly, that scientists do not yet have a enough information to develop a clear understanding of stellar evolution. They have enough information to form rough theories, but there is still much too much they do not know.
With time running out as Comet 67P/C-G moves away from the Sun, the Rosetta engineering team is going to try one more time to contact the lander Philae.
The lander team are going to try another method to trigger a reponse from Philae: on 10 January they will send a command, via Rosetta, to attempt to make Philae’s momentum wheel switch on. “Time is running out, so we want to explore all possibilities,” says Stephan Ulamec, Philae lander manager at DLR. Philae’s momentum wheel ensured that it was stable during its descent from the orbiter on 12 November, 2014.
If the command is successfully received and executed, the hope is that it might shift the lander’s position.”At best, the spacecraft might shake dust from its solar panels and better align itself with the Sun,” explains Philae technical manager Koen Geurts at DLR’s lander control centre.
They also believe that one of the lander’s two transmitters and one of its two receivers are broken, which makes communications difficult at best.
NOAA’s monthly update of the solar cycle, showing the Sun’s sunspot activity in December, was posted earlier this week, and I am posting it here, as I do every month, with annotations to give it context.
The decline in sunspots continues, tracking closely the rate of decline predicted by the 2007 and 2009 predictions (the lower green curve and the red curve) but the overall solar maximum has been far shorter and less powerful than predicted.
» Read more
Two scientists summarize the challenge for finding alien life in the universe.
Look for high amounts of oxygen and mid-infrared energy, the second of which has already produced some candidates.
A recent large survey by the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) satellite did identify five red spiral galaxies whose combination of high MIR and low near-ultraviolet luminosities are inconsistent with simple expectations from high rates of star formation. A conventional explanation for these observations, such as the presence of large amounts of internal dust, has not been ruled out, however. Such peculiar objects deserve follow-up observations before we explore whether they might represent the signatures of galaxy-dominating species.
The article is very thoughtful, however, and outlines in detail the issues and problems the research faces. We might, in a few decades, have the capability to answer this question, but then, the aliens might be alien enough to still be undetectable. Or they might not exist at all.
Scientists have now officially added four new elements to the periodic table, completing the discovery of all elements through 118.
All of the elements were created in the lab, by smashing lighter atomic nuclei together. The unstable agglomerations of protons and neutrons last mere fractions of a second before they fall apart into smaller, more stable fragments.
The teams that have been given credit for the discoveries can now put forward proposals for the elements’ names and two-letter symbols. Elements can be named after one of their chemical or physical properties, a mythological concept, a mineral, a place or country, or a scientist. Priority for discovering element 113 went to researchers in Japan, who are particularly delighted because it will become the first artificial element to be named in East Asia. When the element was first sighted 12 years ago, ‘Japonium’ was suggested as a name.
While creating element 119 is believed possible, beyond that it is thought unlikely that anything heavier can be produced in the lab.
Update: It appears the story below is bogus. (Hat tip Pzatchok.) It appears to be a combination of two different stories, one in which gardeners from the Miami Nation in Indiana donated old seeds to a research group, and the second where that same research group attempted to grow seeds found in a Kentucky cave, with poor results.
Original post:
Students who discovered some ancient seeds in a clay pot at an archaeological site in Canada successfully planted them to grow a previously extinct species of squash.
Not all the seeds grew, but enough did. Moreover, the new squash produced new seeds. This once extinct squash is no longer extinct. And according to the article is also tastes delicious!
The uncertainty of peer review: A science journal has published a fake study that supposedly proved that kissing a child’s “boo-boo” has no medicinal value.
In their study, the authors claim to be members of the Study of Maternal and Child Kissing (SMACK) Working Group, which they say is a subsidiary of Procter and Johnson, Inc., the maker of “Bac-Be-Gone ointment and Steri-Aids self-adhesive bandages.” Procter and Johnson, which is not a real consumer goods company, is an obvious mash-up of Procter & Gamble and Johnson & Johnson, two consumer packaged goods companies which sell health care items like bandages and ointments. The only contact information for the study’s authors disclosed in the research paper is a Gmail address. Bac-Be-Gone ointment and Steri-Aids also do not appear to be actual products available for sale. Additionally, many of the academic research references listed at the end of the study–including one article entitled “So what the hell is going on here?”–also appear to be fake.
The journal, the Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice, claims on its website that all papers published by it are copy-edited and peer-reviewed. In this case I suppose the reviewers worked for Comedy Central .
The Cassini science team have released the first images from Cassini’s last fly-by of Saturn’s moon Enceladus.
More images are still being downloaded.
After a 30 year hiatus, the Department of Energy has produced the first plutonium-238 in the United States since the late 1980s.
Plutonium-238 is the fuel of choice for deep-space exploration. But for nearly 30 years, nobody in the United States was making it.
On Tuesday, that all changed. The Department of Energy announced that 50 grams of the stuff had been made by researchers at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Oak Ridge, Tenn. Fifty grams isn’t much, but this is the first time the substance has been made in the country since the Savannah River Plant in South Carolina stopped making it in the late 1980s.
What this does is provide NASA and the U.S. the ability to fly unmanned deep space missions for many more years. Without this plutonium-238, there would be no practical way to power spacecraft traveling out beyond Mars orbit.
And why did the U.S. stop making plutonium-238 in the late 1980s? The story is of course complicated, but one of the big factors is that at that time nuclear power had become politically incorrect after the Three Mile Island and Chernobyl nuclear power plant failures, and thus politicians fell over themselves to be the first to ban any such production, even if it was harmless and incredibly beneficial.
Because of a serious technical problem with its prime instrument, NASA has decided that its InSight Mars lander will not make its March 2016 launch window and has suspended the mission.
NASA said the decision to delay follows unsuccessful attempts to repair a leak affecting the device, which requires a vacuum seal around its three main sensors to withstand the harsh conditions of the Martian environment. A leak discovered earlier this year, that prevented it from retaining vacuum conditions, was successfully repaired, and the mission team “was hopeful the most recent fix also would be successful.”
However, the instrument once again failed to hold a vacuum during testing on Monday in extreme cold temperature.
It is even possible that the mission will be cancelled entirely because of the problem.
The Dawn science team has now released new high resolution images of Ceres taken from the spacecraft’s lowest orbit.
Dawn took these images of the southern hemisphere of Ceres on Dec. 10, at an approximate altitude of 240 miles (385 kilometers), which is its lowest-ever orbital altitude. Dawn will remain at this altitude for the rest of its mission, and indefinitely afterward. The resolution of the new images is about 120 feet (35 meters) per pixel.
Among the striking views is a chain of craters called Gerber Catena, located just west of the large crater Urvara. Troughs are common on larger planetary bodies, caused by contraction, impact stresses and the loading of the crust by large mountains — Olympus Mons on Mars is one example. The fracturing found all across Ceres’ surface indicates that similar processes may have occurred there, despite its smaller size (the average diameter of Ceres is 584 miles, or 940 kilometers). Many of the troughs and grooves on Ceres were likely formed as a result of impacts, but some appear to be tectonic, reflecting internal stresses that broke the crust.
Make sure to click on the link. The images show that Ceres is not the dull boring surface that the wider shots have suggested.
The uncertainty of science: New modeling suggests that the wet gullies seen on Mars can be produced by dry ice, not water.
The theory is not completely new, but Cedric Pilorget and François Forget, with the University of Paris-Sud, and Paris’ Pierre and Marie Curie University, respectively, flesh out the idea with some hard numbers. Their new computer model calculates seasonal changes and impacts of an underlying layer of regolith, a carbon dioxide ice layer and the carbon dioxide-dominated gas atmosphere above. The simulation can take into account a variety of latitudes, slopes and other parameters.
The scientists found that most of the gullies could be created in a process that does not require any liquid water.
The president of the National Association of Scholars has written a scathing letter to the National Academy of Sciences condemning the unopposed candidacy of Dr. Marcia K. McNutt, the present editor-in-chief of the journal Science, as president of the Academy.
Their complaint has to do with her policy at Science of censoring any dissenting opinions on a number of science subjects, including climate change.
Science [the journal] promotes the so-called consensus model of climate change and excludes any contrary views. This issue has become so polarized and polarizing that it is difficult to bring up, but at some point the scientific community will have to reckon with the dramatic discrepancies between current climate models and substantial parts of the empirical record. Recent evidence of Science bias on this issue is the June 26, 2015 article by Dr. Thomas R. Karl, “Possible artifacts of data biases in the recent global surface warming hiatus”; the July 3, 2015 McNutt editorial, “The beyond-two-degree inferno”; the November 13, 2015 McNutt editorial, “Climate warning, 50 years later”; and the November 25, 2015 AAAS News Release, “AAAS Leads Coalition to Protest Climate Science Inquiry.”
Dr. McNutt’s position is, of course, consistent with the official position of the AAAS. But the attempt to declare that the “pause” in global warming was an illusion has not been accepted by several respected and well-informed scientists. One would not know this, however, from reading Science, which has declined to publish any dissenting views. One can be a strong supporter of the consensus model and yet be disturbed by the role which Science has played in this controversy. Dr. McNutt and the journal have acted more like partisan activists than like responsible stewards of scientific standards confronted with contentious claims and ambiguous evidence. The relevant documents and commentary regarding the Karl paper and McNutt editorials can be examined at https://www.nas.org/images/documents/Climate_Change.pdf. [emphasis mine]
The letter outlines two other areas where McNutt has appeared to play favorites in areas of scientific controversy, and thus questions the wisdom of allowing her to run unopposed for presidency of the National Academy of Sciences.
What is important about this letter is that indicates that there is an increasing pushback from scientists against the demands of orthodoxy. Rather than going along with the powers-that-be, the National Association of Scholars is stating its increasing distrust of the scientific integrity of those powers.
Posted from Sedona, Arizona.
For the first time ever astronomers have been able to predict and photograph the appearance of a supernova, its light focused by the gravitational lensing caused by a galaxy and the dark matter that surrounds it.
The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has captured the image of the first-ever predicted supernova explosion. The reappearance of the Refsdal supernova was calculated from different models of the galaxy cluster whose immense gravity is warping the supernova’s light.
What makes this significant is that the prediction models were based on the theory of gravitational lensing and required the presence of dark matter to work. That they worked and were successful in predicting the appearance of this gravitationally bent light (bent by the dark matter it passed through) is a very strong confirmation of both concepts. Up until now I have been somewhat skeptical of gravitational lensing. This confirmation removes some of that skepticism.
In the past forty years the use by scientists of descriptive words to positively hype their results in their papers has increased steadily.
Researchers at the University Medical Center Utrecht in the Netherlands say that the frequency of positive-sounding words such as ‘novel’, ‘amazing’, ‘innovative’ and ‘unprecedented’ has increased almost nine-fold in the titles and abstracts of papers published between 1974 and 2014. There has also been a smaller — yet still statistically significant — rise in the frequency of negative words, such as ‘disappointing’ and ‘pessimistic’.
…The most obvious interpretation of the results is that they reflect an increase in hype and exaggeration, rather than a real improvement in the incidence or quality of discoveries, says Vinkers. The findings “fit our own observations that in order to get published, you need to emphasize what is special and unique about your study,” he says. Researchers may be tempted to make their findings stand out from thousands of others — a tendency that might also explain the more modest rise in usage of negative words.
The word ‘novel’ now appears in more than 7% of PubMed paper titles and abstracts, and the researchers jokingly extrapolate that, on the basis of its past rise, it is set to appear in every paper by the year 2123.
This study was focused on the medical field, so it is unclear if its results could be extrapolated to other science fields. I suspect it can.
Lots of cool images! The science team running Rosetta’s high resolution camera have finally made available to the public the camera’s large archive of images.
The images cover the period 20 June 2014 – 16 September 2014, corresponding to Rosetta’s approach to the comet, arrival, and insertion into orbit.
In exchange for creating and running the mission, the scientists had been given a 12 month period in which these hi-res images belonged entirely to them. This gave them the chance to use them to publish papers documenting their discoveries. While this is a reasonable arrangement — used by most planetary missions in some manner to reward the scientists who made the mission possible — with Rosetta the hi-res images were kept so close to the vest that practically none have been seen, until now. Moreover, this release is very late, anywhere from 15 to 18 months after the images were taken, not 12.
Most other planetary missions make sure that at least some images are released as the mission proceeds, since the images were paid for by the public. The European Space Agency should take a look at its future policies for publicly-funded missions to make sure the public gets better access in the future.
Engineers have determined that Hayabusa-2’s fly-by of Earth on December 3 successfully put the spacecraft on the right course to rendezvous with asteroid Ryugu in 2018.

Curiosity has arrived at the first Martian dune ever observed up close and has begun its investigation.
The image above is a cropped version of a close up image showing the sand ripples on the surface of the dune. The press release also includes an amazing very very very close-up image of the pock-marked grain-covered surface. [link fixed]
Cool movie time! The Dawn science team has released a movie compiled from images taken by the spacecraft, showing in false color the entire dwarf planet’s rotation as well as doing a fly-over of Occator Crater with its double bright spot.
I have posted the movie below the fold. The false colors illustrate the different materials so far detected on the surface, and help explain the nature and origin of the surface features.
» Read more
Based on an analysis of Dawn images scientists now believe that the bright spots on Ceres are salt deposits, not water ice.
Le Corre and colleagues, using images from Dawn’s framing camera, suggest that these salt-rich areas were left behind when water-ice sublimated in the past. Impacts from asteroids would have unearthed the mixture of ice and salt. “The location of some bright spots also coincide with places where water vapor was detected by other spacecraft,” said Reddy, a PSI Research Scientist. “This gives us confidence that the bright spots are likely salt deposits left over by sublimating salty water.”
While the bright spots themselves are not ice, they are what is left over after salty water evaporates.
The head of France’s space agency announced today that repairs to their instrument for NASA’s InSight Mars lander will be completed in time to ship the instrument to the U.S. in time for the scheduled March launch.
Briefing reporters here at the COP21 United Nations Climate Change Conference, Jean-Yves Le Gall said the leak, which compromised the required high-precision vacuum chamber carrying InSight sensors, was caused by a defective weld that is applied to close off the tank.
The leak’s cause has been identified and a new weld performed, Le Gall said. Tests to confirm the new weld’s integrity are underway and, assuming no problems, will be completed in time to ship the instrument to the United States in the first week of January. It will then be integrated into the InSight lander in preparation for the March launch.
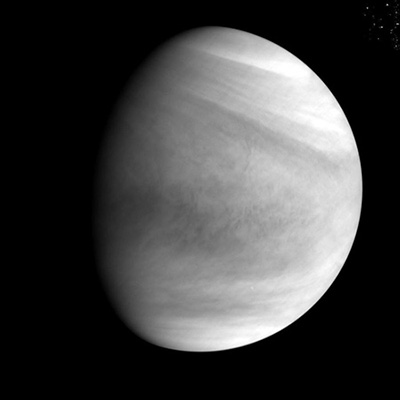
Japanese engineers have confirmed that Akatsuki has entered orbit around Venus and can now begin science observations.
The image on the right was taken by the spacecraft’s ultraviolet camera, and clearly shows the as-yet unidentified dark material in Venus’s upper atmosphere. These dark streaks have been seen since the first Venus fly-by in the 1960s, but no observations have been able to determine what the material is that shows up as dark in ultraviolet light.
This success is a triumph for the engineers that operate Akatsuki. Kudos to them!
New observations of the star KIC 8462852 to see if an alien civilization had produced laser signals has produced a null result, reinforcing the conclusion that the erratic dimming of the star is not caused by alien megastructures.
On six nights between October 29 and November 28, 2015, scientists searched for pulses as short as a billionth of a second at the Boquete Optical SETI Observatory in Panama, using a 0.5 m Newtonian telescope. The observatory’s relatively small telescope uses a unique detection method having enhanced sensitivity to pulsed signals. If any hypothetical extraterrestrials had beamed intentional laser pulses in the visible spectrum toward Earth, the Boquete observatory could have detected them so long as they exceeded the observatory’s minimum detectable limit.
KIC 8462852 has puzzled astronomers because it shows irregular dimming unlike anything seen for another star. The anomalous light curve was measured using NASA’s Kepler telescope, as part of its search for exoplanets. However, even though a planet the size of Jupiter would cause dimming of approximately 1%, the dimming observed for KIC 8462852 was far greater – up to 22%. Just as strange, the dimming didn’t follow the regular pattern of a planet orbiting a star, but instead was unpredictable. The best explanation to date is that the dimming may have been caused by cometary fragments in a highly elliptical orbit around KIC 8462852, intercepting starlight at the same time the Kepler mission was observing it.
On Sunday NOAA posted, as it does each month, its monthly update of the solar cycle, showing the Sun’s sunspot activity in November. And as I have done every month since 2010, I am posting it here, with annotations to give it context.
Though sunspot activity in November was just slightly higher than in October, the increase was so small that it is insignificant. Essentially, the overall decline in sunspot count continues, matching almost perfectly the ramp down predicted by the 2007 low prediction. Solar activity continues to be far weaker then anything seen in a century. Whether this suggests a coming Grand Minimum, however, is not known. Solar activity could continue to decline as we move into the next solar cycle, or it could recover. Our understanding of what causes the sunspot cycle remains somewhat fuzzy, which means our ability to predict what will happen next is as fuzzy..
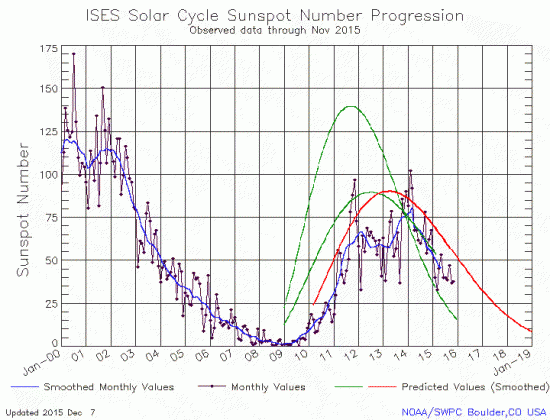
The graph above has been modified to show the predictions of the solar science community. The green curves show the community’s two original predictions from April 2007, with half the scientists predicting a very strong maximum and half predicting a weak one. The red curve is their revised May 2009 prediction.
In discovering a new solid state for carbon scientists have also discovered that it is a relatively inexpensive way to produce diamonds.
Professor Jay Narayan of North Carolina State University is the lead author of three papers describing the work that sees Q-carbon join the growing list of carbon solids, a list that includes graphite, graphene, fullerene, amorphous carbon and diamond. He has suggested that the only place Q-carbon might be found in the natural world is in the core of certain planets.
The researchers created Q-carbon by starting with a thin plate of sapphire (other substrates, such as glass or a plastic polymer, will also work). Using a high-power laser beam, they coated the sapphire with amorphous carbon, a carbon form with no defined crystalline structure. They then hit the carbon with the laser again, raising its temperature to about 4,000 Kelvin, and then rapidly cooled, or quenched, the melted carbon. This stage of quenching is where “Q” in Q-carbon comes from.
The researchers have found that, depending on the substrates, tiny diamonds will form within the Q-carbon, suggesting to me that they have actually discovered how diamonds are formed deep below the Earth. The hot high pressure environment there allows Q-carbon to naturally form, and in the process of its solidification diamonds are a byproduct.
Five years after the Japanese Venus probe Akatsuki’s main engines failed while trying to put it into orbit, the spacecraft today fired its attitude thrusters and was successfully inserted into orbit.
This is a singular achievement by the Japanese engineers running the mission. They improvised a plan using the thrusters, which were designed to adjust the spacecraft orientation, not its course, and were able to get Akatsuki in an solar orbit that brought it back to Venus.