An inactive volcanic vent on Mars
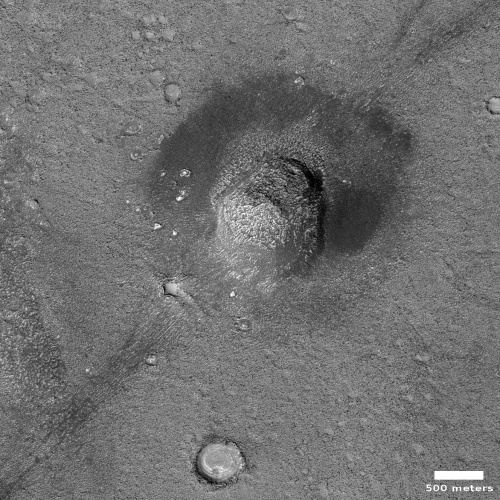
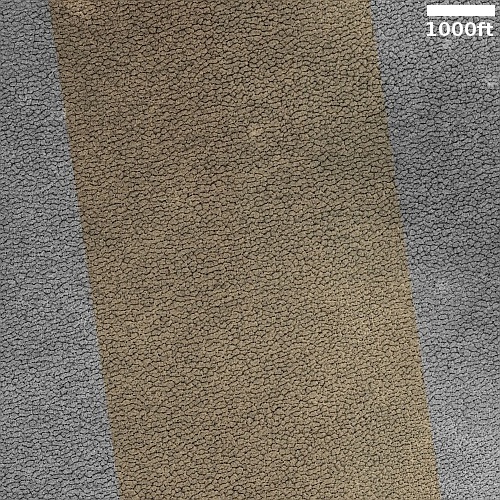
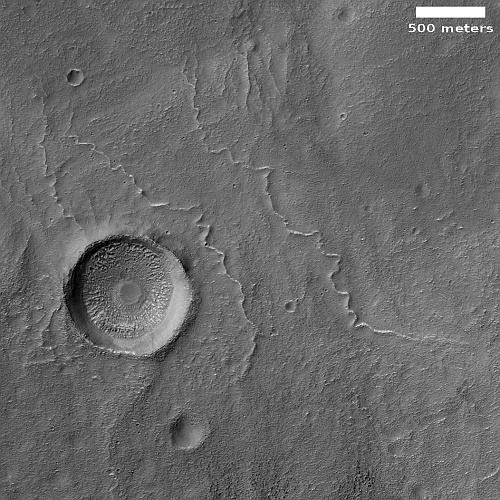
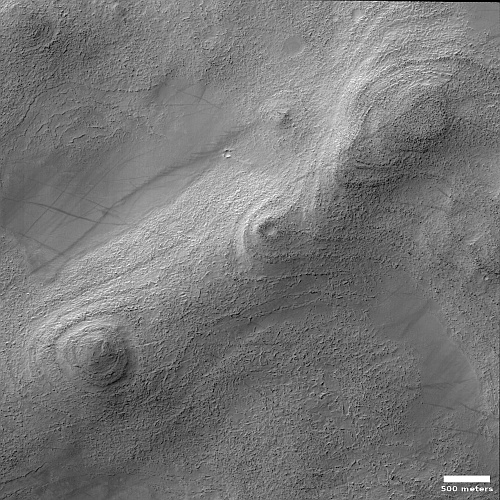
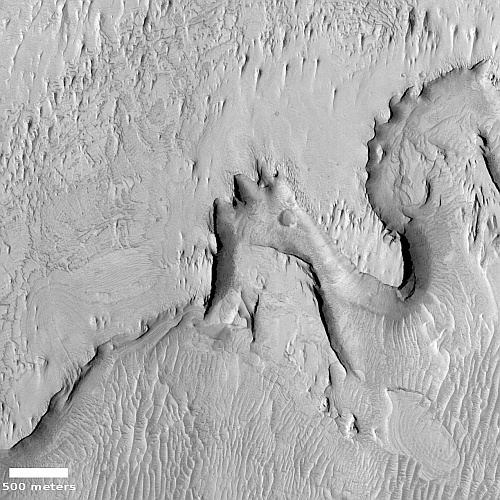
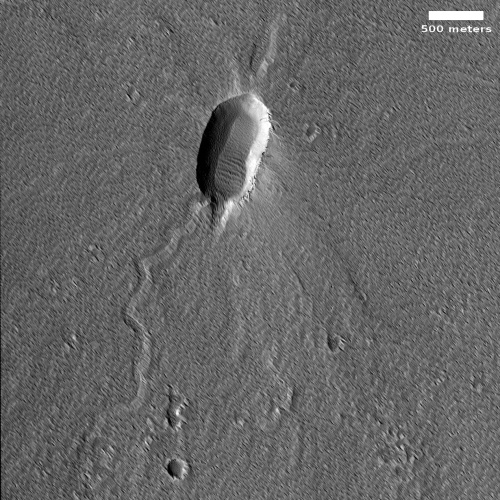
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken on October 5, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Labeled by the science team as “Vents and Lava Flows on Flank of Pavonis Mons,” the section to the right shows the picture’s largest vent. The downhill grade is to the south.
In the full photo you can see that this vent sits on top of a flat mound of hardened lava, all of which flowed from the vent in the distant past. The main flow of course went to the south, out the channel and down the flanks of Pavonis Mons, the middle volcano in the line of three just to the west of Mars’ giant Valles Marineris canyon. The caldera peak of Pavonis Mons is about 35 miles away, and sits at a height of 47,000 feet elevation, far higher than Mount Everest but still only the fourth highest Martian volcano.
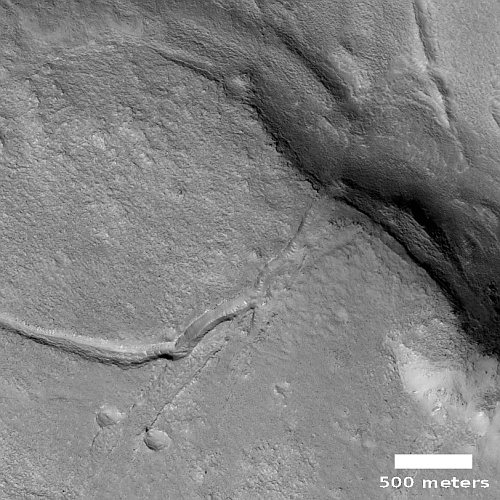
In the full picture, the entire surface also generally flows south, except for a crack that goes from northeast to southwest, possibly caused when the mountain flank sagged to the south.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken on October 5, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Labeled by the science team as “Vents and Lava Flows on Flank of Pavonis Mons,” the section to the right shows the picture’s largest vent. The downhill grade is to the south.
In the full photo you can see that this vent sits on top of a flat mound of hardened lava, all of which flowed from the vent in the distant past. The main flow of course went to the south, out the channel and down the flanks of Pavonis Mons, the middle volcano in the line of three just to the west of Mars’ giant Valles Marineris canyon. The caldera peak of Pavonis Mons is about 35 miles away, and sits at a height of 47,000 feet elevation, far higher than Mount Everest but still only the fourth highest Martian volcano.
In the full picture, the entire surface also generally flows south, except for a crack that goes from northeast to southwest, possibly caused when the mountain flank sagged to the south.
» Read more