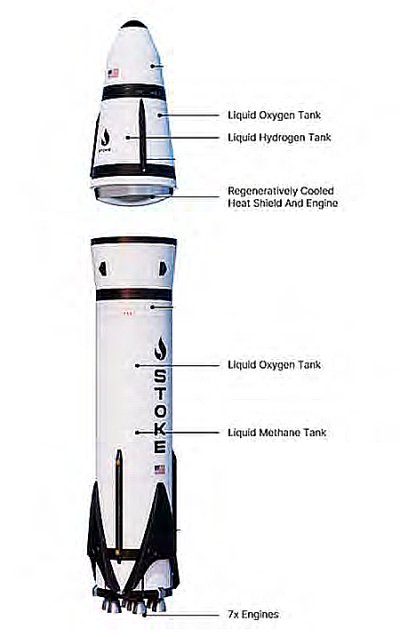
A sinuous Martian ridge of uncertain origin
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on July 21, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It was posted today by the camera team as a captioned image, with the caption as follows:
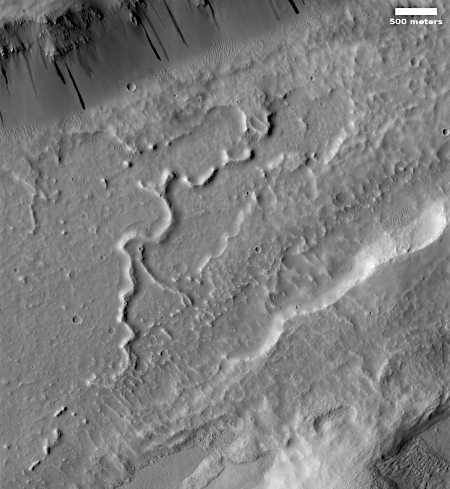
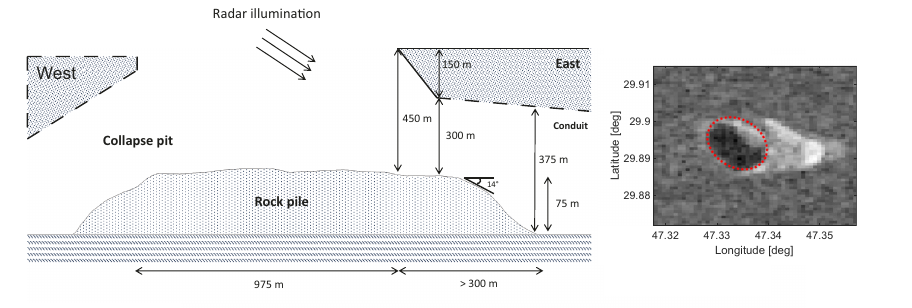
The sinuous ridge is approximately 10 meters wide and several kilometers long. The floor surrounding this ridge has been eroding laterally, forming pits and circular features suggestive of removal (sublimation) of subsurface ice. However, landforms such as channels or moraines that might suggest the presence of water or ice are lacking, so the ridge itself does not appear to have formed by fluvial or glacial processes.
Perhaps this curious feature is an exhumed dike formed from magma emanating from Alba Mons in subsurface fractures.
Alba Mons is a gigantic shield volcano to the west.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on July 21, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It was posted today by the camera team as a captioned image, with the caption as follows:
The sinuous ridge is approximately 10 meters wide and several kilometers long. The floor surrounding this ridge has been eroding laterally, forming pits and circular features suggestive of removal (sublimation) of subsurface ice. However, landforms such as channels or moraines that might suggest the presence of water or ice are lacking, so the ridge itself does not appear to have formed by fluvial or glacial processes.
Perhaps this curious feature is an exhumed dike formed from magma emanating from Alba Mons in subsurface fractures.
Alba Mons is a gigantic shield volcano to the west.
» Read more