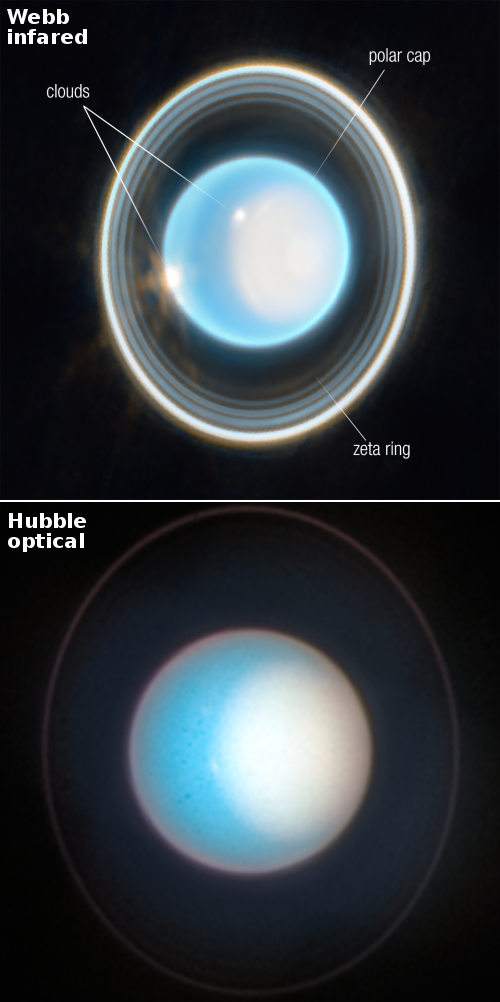
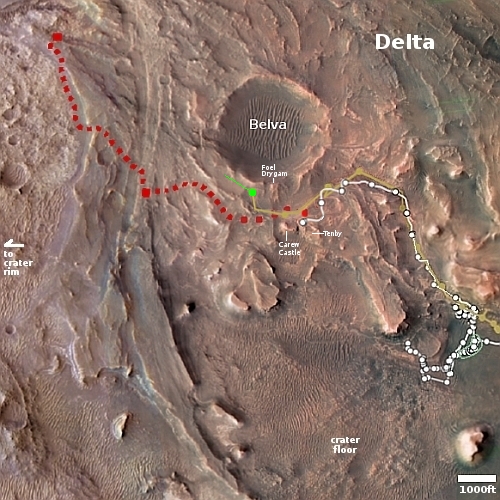
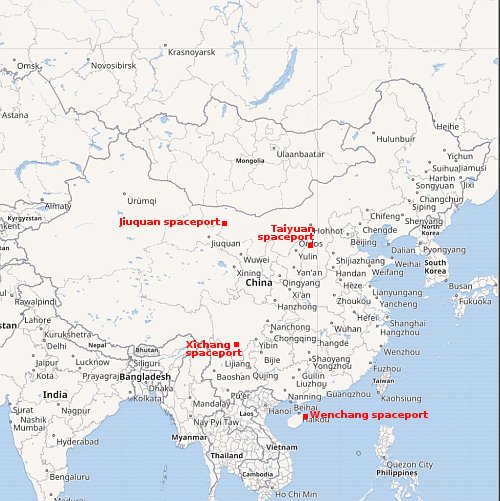
University of Arizona opens major facility for building and launching satellites
ARB’s anechoic chamber
Yesterday I attended the grand opening of the University of Arizona’s (UA) new Applied Research Building (ARB), designed to provide satellite builders as well as its students an almost completely comprehensive facility for the assembly, testing, and launching of satellites. From this event announcement:
To keep the university at the forefront of space science and exploration, ARB will serve as a world-class test and integration center for satellites, probes, and spacecraft, including:
- A 40-foot tall high-bay payload assembly area used for constructing high-altitude stratospheric balloons and nanosatellites also known as “CubeSats.”
- A thermal vacuum chamber that simulates environmental conditions in space to test balloon and satellite performance that is the largest of its kind at any university in the world.
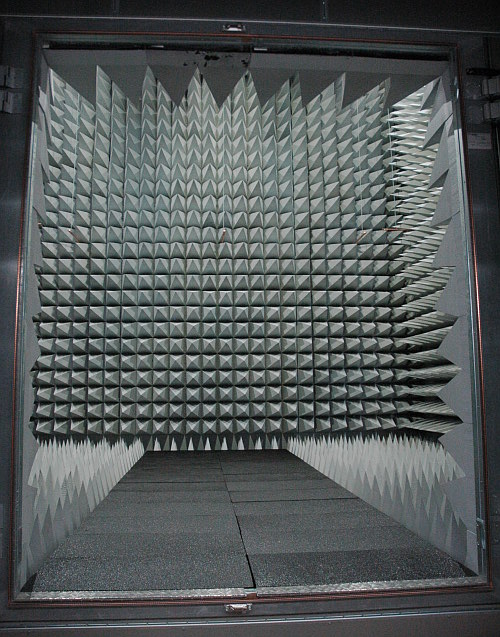
- A non-reflective, echo-free room called an anechoic chamber to test antennae for command, control, and data relay purposes.
- A large lab for testing the performance of a range of objects, from airplane wings to sensors.
The anechoic chamber is pictured above. For scale, if a person was standing in the middle of the chamber their height would reach about six rows up. The carbon-infused styrofoam pyramids are designed to dampen reflections of radio signals in order to simulate the space environment while testing the antennas on a satellite. This is apparently is of the largest such chambers in the United States.
» Read more

ARB’s anechoic chamber
Yesterday I attended the grand opening of the University of Arizona’s (UA) new Applied Research Building (ARB), designed to provide satellite builders as well as its students an almost completely comprehensive facility for the assembly, testing, and launching of satellites. From this event announcement:
To keep the university at the forefront of space science and exploration, ARB will serve as a world-class test and integration center for satellites, probes, and spacecraft, including:
- A 40-foot tall high-bay payload assembly area used for constructing high-altitude stratospheric balloons and nanosatellites also known as “CubeSats.”
- A thermal vacuum chamber that simulates environmental conditions in space to test balloon and satellite performance that is the largest of its kind at any university in the world.
- A non-reflective, echo-free room called an anechoic chamber to test antennae for command, control, and data relay purposes.
- A large lab for testing the performance of a range of objects, from airplane wings to sensors.
The anechoic chamber is pictured above. For scale, if a person was standing in the middle of the chamber their height would reach about six rows up. The carbon-infused styrofoam pyramids are designed to dampen reflections of radio signals in order to simulate the space environment while testing the antennas on a satellite. This is apparently is of the largest such chambers in the United States.
» Read more