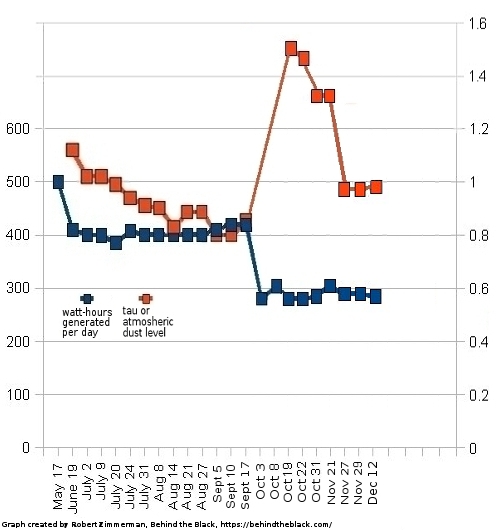
Russian official: Soyuz leak possibly caused by micrometeorite hit
According to Sergei Krikalev, who heads Roscosmos’ manned program, the leak of coolant from the Soyuz capsule docked at ISS could have been caused by a micrometeorite hit.
Sergei Krikalev, a veteran cosmonaut who serves as the director of crewed space flight programs at Roscosmos, said a meteorite striking one of external radiators of the Soyuz MS-22 capsule could have caused the coolant to escape.
The malfunction could affect the performance of the capsule’s coolant system and the temperature in the equipment section of the capsule but doesn’t endanger the crew, Krikalev said in a statement.
Krikalev said Russian flight controllers were assessing the situation and following temperature indicators on the Soyuz. “There have been no other changes in parameters on the Soyuz spacecraft and the station, so there is no threat for the crew,” he said.
The “equipment section of the capsule” is its service module, not its habitable orbital module or descent module.
Krikalev, the first Russian to fly on the space shuttle and occupy ISS, is a generally very reliable source. He is speculating, but not wildly but based on what is so far known. The upcoming inspection of the Soyuz using an ISS robot arm will soon tell us whether he is right or not. Krikalev also said that the inspection will tell them whether this capsule can be used to return its astronauts to Earth.
According to Sergei Krikalev, who heads Roscosmos’ manned program, the leak of coolant from the Soyuz capsule docked at ISS could have been caused by a micrometeorite hit.
Sergei Krikalev, a veteran cosmonaut who serves as the director of crewed space flight programs at Roscosmos, said a meteorite striking one of external radiators of the Soyuz MS-22 capsule could have caused the coolant to escape.
The malfunction could affect the performance of the capsule’s coolant system and the temperature in the equipment section of the capsule but doesn’t endanger the crew, Krikalev said in a statement.
Krikalev said Russian flight controllers were assessing the situation and following temperature indicators on the Soyuz. “There have been no other changes in parameters on the Soyuz spacecraft and the station, so there is no threat for the crew,” he said.
The “equipment section of the capsule” is its service module, not its habitable orbital module or descent module.
Krikalev, the first Russian to fly on the space shuttle and occupy ISS, is a generally very reliable source. He is speculating, but not wildly but based on what is so far known. The upcoming inspection of the Soyuz using an ISS robot arm will soon tell us whether he is right or not. Krikalev also said that the inspection will tell them whether this capsule can be used to return its astronauts to Earth.