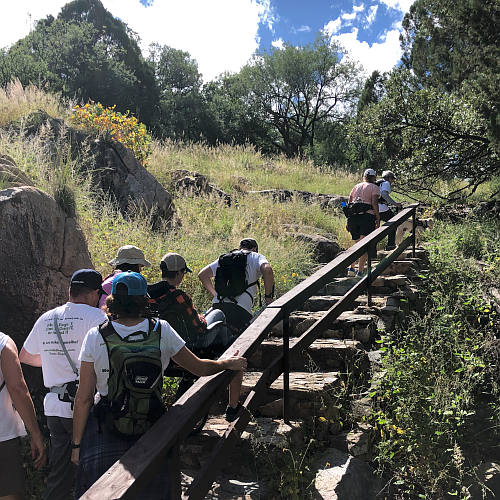
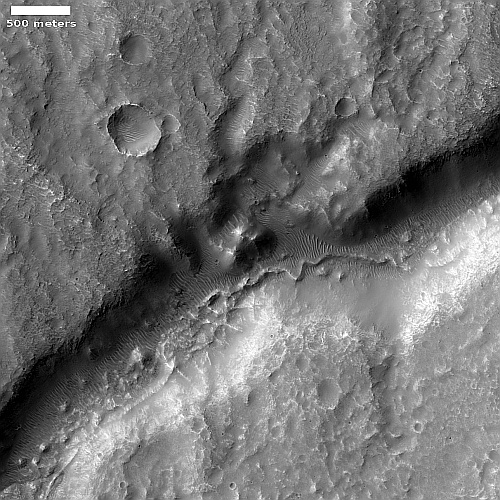
The Tucson crew for Luke 5 Adventures takes a hiker uphill
Since I was blacklisted by the caving community in 2021, I have been searching for a new outdoor hobby that would satisfy my interests and provide me a new social community.
This search has landed me in a very unusual place (a circumstance that for me has actually been very typical in my life). During a loop hike in October last year, Diane and I met a couple who were doing the loop in the opposite direction. The first time we met we chatted for a few minutes, and then moved on in opposite directions. When we met the second time, however, we talked longer and exchanged contact information. It appears that Angelo and Bonnie Piro also love hiking, recently moved to Tucson from New Jersey (which meant I had a lot in common with them), and were looking for people they could hike with.
Since then we have hiked together numerous times. One day in late November Angelo mentioned that they had the day before participated in a short hike whereby they helped transport a 9-year-old boy who could not walk on his own in a one-wheel chair — dubbed Rosie — over a trail, as part of a volunteer organization called Luke5Adventures. From its national webpage:
For those who aren’t physically able to hike it, forge it, climb it, cross it, or ascend it, we
we can make it possible.
As the founder of this organization, Kevin Schwieger, explains on the webpage,
I knew we needed to give this venture a name. My thoughts went to the Gospel of Luke, Chapter 5, and the account of the group of friends who took their paralytic friend to go see Jesus. The house where Jesus was speaking was so crowded that they could not get in. That didn’t stop them. They were determined to enable their friend to see something amazing. They carried him to the roof, cut the thatch away, and lowered him down through the hole in the roof to see Jesus! I pictured in my mind’s eye, groups of friends by the hundreds, using Rosies to take their new friends to see places and things that heretofore have been impossible. Not figuratively impossible, but, literally impossible.
It seemed to me that volunteering for this organization would give me an opportunity to do some fun outdoor stuff in a way that was new and interesting while doing good as well. It would also likely introduce me to some decent and righteous people with whom I could make some friends. That they were Christians and I was a secular Jew made no different to me, and I was quite confident it would make no difference to them either.
Not surprisingly, I was right.
» Read more