Los Cenzontles y Razilla Chiquilla – La Mula y El Arriero
An evening pause: The title in English: “The Mule and the Mule Driver.” The English subtitles make it all most decidedly clear.
Hat tip Jim Mallamace.
An evening pause: The title in English: “The Mule and the Mule Driver.” The English subtitles make it all most decidedly clear.
Hat tip Jim Mallamace.
The new colonial movement: The head of Syria’s ministry of communications and technology said during a visit to that country’s satellite remote sensing facility that their nation should organize a space program, beginning with the construction of an entirely home-built satellite.
I’m not sure how much of this will be possible considering how badly ripped apart Syria presently is because of its civil war. To me, it looks more like a some somewhat ignorant brasshat, while visiting a space facility, sounding off with what he would like done.
The astronomy community is mourning the passing of Riccardo Giacconi, a pioneer in space X-ray astronomy as well as the first director of the Space Telescope Science Institute, which operates Hubble.
What made him an especially interesting man is that he initially strongly opposed Hubble, preferring the money be spent on X-ray space telescopes. When, during the writing of The Universe in a Mirror, I asked him what prompted his change of opinion that made him head of Hubble, he explained that he felt he “wasn’t being used.” The money for X-ray astronomy just wasn’t there, and rather than chase rainbows he decided to hitch his wagon to something that was certain to produce new science.
The irony is that it was Hubble’s success that probably helped generate the funding for later X-ray space telescopes, such as Chandra.,
Giacconi was a unique and brilliant man. His early X-ray instruments were built by a private commercial company he ran, not a university or NASA. In a sense he was following the classic and older American model here that was abandoned in the 1970s, and is only now beginning to see a resurgence.
Link here. Lots of nice information, including the fact that Chang’e-3 seems to still be functioning in a limited manner, and that Chang’e-4 is depending not on solar panels but a radioactive thermal electric system, similar I think to the RPGs that NASA uses on its deep space missions. (I am uncertain however about this, based on looking at the video at the link, which seems to show solar panels on Chang’e-4. They could be instead panels to protect the spacecraft from the sun’s heat.)
They enter lunar orbit on December 12, and will likely land in the first week of January.
Two Russian astronauts yesterday successfully completed a difficult spacewalk aimed at inspecting the drill hole that had been found on the Soyuz capsule on ISS.
Around midnight in Moscow (4 p.m. EST), the cosmonauts began cleaning the work place to prepare tackling the micro-meteoroid shielding, which turned out to be easier than work with soft insulation. In around 10 minutes, they cut and peeled off a segment of the shielding, but it took them a few minutes to actually see the hole at the edge of the exposed area and they had to cut a second smaller piece of meteoroid shielding.
They improvised an attempt to pick black material extruding from the hole with forceps, but it was very difficult to do in bulky spacesuit and due to the brittle nature of the material. Around six hours into the spacewalk, they finally proceeded with a pre-planned sampling operation.
The spacewalk was so hard because they were working on the outside of the Soyuz capsule in an area where no spacewalk was ever planned. No handholds. They had to bring them with them, and attach them.
No word yet on any conclusions about the drill hole.
Posted from Buffalo, NY. I am finally back from Israel, only to end up in a very cold and snowy place, not my favorite environments. No matter. There is a lecture for me to give tonight.
An evening pause: Clara Bow doesn’t sing this, but the song was written about her for her hit 1927 silent movie, It, from which these clips were assembled.
Hat tip Edward Thelen.
One of OSIRIS-REx’s instruments has now found evidence of water on the rubble-pile asteroid Bennu.
Recently analyzed data from NASA’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) mission has revealed water locked inside the clays that make up its scientific target, the asteroid Bennu.
During the mission’s approach phase, between mid-August and early December, the spacecraft traveled 1.4 million miles (2.2 million km) on its journey from Earth to arrive at a location 12 miles (19 km) from Bennu on Dec. 3. During this time, the science team on Earth aimed three of the spacecraft’s instruments towards Bennu and began making the mission’s first scientific observations of the asteroid. OSIRIS-REx is NASA’s first asteroid sample return mission.
Data obtained from the spacecraft’s two spectrometers, the OSIRIS-REx Visible and Infrared Spectrometer (OVIRS) and the OSIRIS-REx Thermal Emission Spectrometer (OTES), reveal the presence of molecules that contain oxygen and hydrogen atoms bonded together, known as “hydroxyls.” The team suspects that these hydroxyl groups exist globally across the asteroid in water-bearing clay minerals, meaning that at some point, Bennu’s rocky material interacted with water. While Bennu itself is too small to have ever hosted liquid water, the finding does indicate that liquid water was present at some time on Bennu’s parent body, a much larger asteroid.
The image on the right, reduced to show here, was created from 12 images taken on December 2, 2018 from about 15 miles. If you click on the image you can see the full resolution photograph, which is quite incredible. While the asteroid’s shape is approximately what was expected from ground-based observations and computer modeling, the giant boulder on the limb on the bottom right is about four times bigger than expected.
The Voyager 2 spacecraft, launched in 1977, has entered interstellar space, becoming the second human spacecraft to achieve this.
Comparing data from different instruments aboard the trailblazing spacecraft, mission scientists determined the probe crossed the outer edge of the heliosphere on Nov. 5. This boundary, called the heliopause, is where the tenuous, hot solar wind meets the cold, dense interstellar medium. Its twin, Voyager 1, crossed this boundary in 2012, but Voyager 2 carries a working instrument that will provide first-of-its-kind observations of the nature of this gateway into interstellar space.
Voyager 2 now is slightly more than 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) from Earth. Mission operators still can communicate with Voyager 2 as it enters this new phase of its journey, but information – moving at the speed of light – takes about 16.5 hours to travel from the spacecraft to Earth. By comparison, light traveling from the Sun takes about eight minutes to reach Earth.
When I first wrote about these spacecraft in the 1990s, it was thought that Voyager 2 would probably not exit the solar system until the 2020s, meaning that its nuclear power source might die before that happened. That it has happened now, so much earlier, helps map the size of the heliosphere as well as the pressure that might be placed upon it by the interstellar medium
They’re coming for you next: The New York City government, in an effort to protect the used and iconic bookstore “The Strand,” is considering giving it landmark status, a designation the owner, wife of a liberal Senator Ron Wyden (D-Oregon), has begged them not to do.
The city’s Landmarks Preservation Commission is considering whether or not to designate the Strand a city landmark, protecting the store from financial marauders who want to scoop up its valuable real estate. But, in a bit of Shakespearean irony, the iconic bookstore is threatened by those charged with its preservation.
Strand’s current owner, Nancy Bass Wyden, wife of Oregon senator Ron Wyden, is not letting her liberalism balance the books. “By landmarking the Strand, you can also destroy a piece of New York history. We’re operating on very thin margins here, and this would just cost us a lot more, with this landmarking, and be a lot more hassle,” Wyden told the Commission during a public hearing.
Wyden also took a shot at Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos, owner of the great scourge of brick-and-mortar bookstores everywhere. “The richest man in America, who’s a direct competitor, has just been handed $3 billion in subsidies. I’m not asking for money or a tax rebate,” she explained, appealing not to the Commission’s egalitarian instincts, but to the principle of privacy. “Just leave me alone,” Wyden beseeched her would-be viceroys.
It doesn’t matter if you are Republican or Democrat, conservative or liberal, big government bureaucracies always end up abusing their power under the lie that they “are here to help you.” The sad thing is that Senator Wyden and his wife are not going to learn any lessons from this tale. I am certain that the Senator will continue to support the Democratic Party’s modern effort to socialize American society under the banner of an all-powerful federal bureaucracy, so that an even bigger government bureaucracy will have the ability to abuse its power over even more people, under the lie that they “are here to help you.”.
In order to avoid a conflict at ISS with the Dragon cargo freighter that just docked there, SpaceX has now delayed the unmanned test launch of its first Dragon manned capsule by ten days, to no earlier than January 17, 2019.
The article at the link is mostly focused on describing the experiments and cargo that the cargo freighter just brought to ISS, but it includes these scheduling details involving the unmanned test flight:
The cargo Dragon is the only vehicle currently capable of returning experiments from the International Space Station and is in relatively high demand. Thus, the worms will either return aboard this CRS-16 Dragon or wait until spring when the CRS-17 Dragon departs the orbital outpost. Regardless, once the newly delivered science experiments and cargo are removed from Dragon, the International Space Station crew will pack the craft full of return cargo before closing Dragon’s hatch and releasing it from the Station in mid-January 2019 for return to Earth.
Presently, CRS-16’s unberth and landing date is set for 13 January 2019, which at the time of the mission’s launch set up a potential overlap between CRS-16 and SpaceX’s Demonstration Mission -1 (DM-1) for the Commercial Crew Program.
At the time of CRS-16’s launch, the uncrewed DM-1 test flight had been targeting a No Earlier Than (NET) launch date of 7 January 2019 from LC-39A at the Kennedy Space Center, with a docking to the International Space Station to follow on 10 January. That NET 7 January launch date officially slipped on Friday to NET 17 January.
I once again want to emphasize that the only thing that I see that might delay this launch is NASA’s effort to slow it down.
A ULA Delta Heavy aborted its launch of a secret National Security Administration surveillance satellite last night at T-7.5 seconds.
It was not immediately clear whether any of the rocket’s three Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-68A main engines started their ignition sequences, but a statement later released by ULA said the computer-controlled countdown sequencer ordered an abort at T-minus 7.5 seconds.
In the statement, ULA said the abort was “due to an unexpected condition during terminal count at approximately 7.5 seconds before liftoff. “The team is currently reviewing all data and will determine the path forward. A new launch date will be provided when available,” ULA said.
Obviously, there is no word yet on a new launch date.
Boeing has canceled its sale of a communications satellite to a company that appears largely funded in secret by Chinese sources.
Boeing says it has canceled a controversial satellite order from a U.S.-based startup, which had received the bulk of its funding from a Chinese-government owned financial company. The deal, which critics warned could give China access to sensitive technology, comes amid a period of especially acrimonious relations between Washington and Beijing over a host of issues, including industrial espionage and intellectual property theft.
The Chicago-headquartered aerospace company announced its decision, which it said was only because of non-payment on the part of the customer, to nix the deal, worth more than $200 million, on Dec. 6, 2018. Two days earlier, the Wall Street Journal had published an expose detailing the links between the official buyer, Global IP, and a string of Chinese government operated entities and individuals with significant connections to China’s Communist Party and military establishment.
If carried out, the satellite sale would have provided the Chinese detailed information about the satellite’s technical design.
This story highlights the Chinese way of developing new technology: They generally steal it. Though their engineering upgrades are often brilliant, they have shown little innovation or originality in their work. Their entire manned program is an upgrade of the Russians Soviet-era space station program. Their decisions recently to build smallsat rockets as well as vertically landing reusable first stages only occurred after private commercial companies in the U.S. proved that both will work and can make money.
Boeing almost certainly backed out when it realized that the Chinese involvment was substantial, and exposed it to criminal penalties.
Hat tip Kirk Hilliard.
On December 2 New Horizons successfully completed another engine burn to refine its course for its January 1, 2019 flyby of the Kuiper Belt object Ultima Thule.
The maneuver was designed to keep New Horizons on track toward its ideal arrival time and closest distance to Ultima, just 2,200 miles (3,500 kilometers) at 12:33 a.m. EST on Jan. 1. At the time of the burn New Horizons was 4.03 billon miles (6.48 billion kilometers) from Earth and just 40 million miles (64 million kilometers) from Ultima – less than half the distance between Earth and the Sun. From that far away, the radio signals carrying data from the spacecraft needed six hours, at light speed, to reach home.
The team is analyzing whether to conduct up to three other course-correction maneuvers to home in on Ultima Thule.
The distance to Ultima Thule is still too much to produce detailed images. New Horizons however is going very fast, so in the coming three weeks this will change drastically, and for the better.
Using its Long March 3B rocket, China on December 7 successfully launched its Chang’e-4 rover/lander, aimed at being the first probe to land on the Moon’s far side.
It will take the probe five days to reach the Moon and land.
The same day China also launched two Earth observation satellites for Saudi Arabia, using its Long March 2D rocket.
The leaders in the 2018 launch standings:
35 China
20 SpaceX
13 Russia
10 Europe (Arianespace)
China has widened its lead over the U.S. 35 to 32 in the national rankings. China also looks like it is going to come close to meeting its prediction of 40 launches for 2018.
An evening pause: On this day, the anniversary of Pearl Harbor, we must remember all those who died to keep us free. Or as one of the memorials shown in the video says, “We mark the price of freedom.”
Hat tip Danae.
In order to better constrain Bennu’s future fly-bys of the Earth, including the possibility that it could impact the planet, scientists will be using the data sent from OSIRIS-REx to better understand its orbit, its composition, its surface make-up, and its thermal properties, all factors that can influence its future path in space.
This is really important, as Bennu has a good chance of hitting the Earth in the future.
About a third of a mile, or half a kilometer, wide, Bennu is large enough to reach Earth’s surface; many smaller space objects, in contrast, burn up in our atmosphere. If it impacted Earth, Bennu would cause widespread damage. Asteroid experts at the Center for Near-Earth Object Studies (CNEOS) at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, project that Bennu will come close enough to Earth over the next century to pose a 1 in 2,700 chance of impacting it between 2175 and 2196. Put another way, those odds mean there is a 99.963 percent chance the asteroid will miss the Earth. Even so, astronomers want to know exactly where Bennu is located at all times.
The article provides a good overview of the difficulty of properly calculating Bennu’s orbit into the future, and how the data from OSIRIS-REx will help make those calculations more precise.
InSight has unfolded its robot arm and is beginning to use it to photograph the surrounding area to figure out where to place the spacecraft’s ground-sensing instruments.
With a reach of nearly 6 feet (2 meters), the arm will be used to pick up science instruments from the lander’s deck, gently setting them on the Martian surface at Elysium Planitia, the lava plain where InSight touched down on Nov. 26.
But first, the arm will use its Instrument Deployment Camera, located on its elbow, to take photos of the terrain in front of the lander. These images will help mission team members determine where to set InSight’s seismometer and heat flow probe – the only instruments ever to be robotically placed on the surface of another planet.
They are proceeding carefully, so actually deployment might not occur for several months, just make everything goes well.
An evening pause: From 1967. If this doesn’t scream “The Sixties” I don’t know what does.
Hat tip Diane Zimmerman.
NOAA’s monthly update of the solar cycle, covering sunspot activity for November 2018, was released yesterday. As I have done every month since this website began in July 2011, I am posting it below, annotated to give it some context.
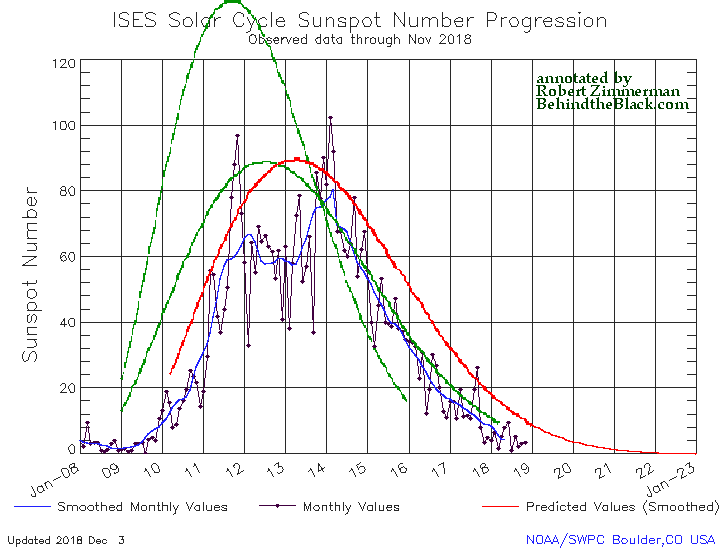
The graph above has been modified to show the predictions of the solar science community. The green curves show the community’s two original predictions from April 2007, with half the scientists predicting a very strong maximum and half predicting a weak one. The red curve is their revised May 2009 prediction.
As I have been expecting now for the last three months, NOAA has finally revised this graph to extend it past the end of 2018. The graph below is the graph from October, which follows the layout and design used since 2007. You can see the differences by comparing the two graphs. In extending the new graph to the end of 2022, they fortunately did not change the design significantly. However, because the new graph has a slightly different scale, I have stretched the green and red curves to make them fit properly. While I suspect the poor quality of the 2007 and 2009 predictions is one reason they do not include them on their graph, I think it essential to add them to better understand the limitations of the science.
» Read more
The joint European/Japanese mission BepiColombo has begun testing its ion engine thrusters for the first time in space as it heads to Mercury.
Testing took place during a unique window, in which BepiColombo remained in continuous view of ground-based antennas and communications between the spacecraft and those controlling it could be constantly maintained. This was the only chance to check in detail the functioning of this fundamental part of the spacecraft, as when routine firing begins in mid-December, the position of the spacecraft will mean its antennas will not be pointing at Earth, making it less visible to operators at mission control.
They have so far successfully tested two of the four engines.
Capitalism in space: SpaceX officials expect the first stage landing failure during yesterday’s launch to have little impact on the schedule of upcoming launches.
They also indicated that the cause of the landing failure had something to do with a malfunction in the stage’s grid fins. More important however was this tidbit about the second stage:
Koenigsmann also revealed at the briefing that the rocket’s upper stage, which successfully placed the Dragon cargo spacecraft in orbit, used redesigned composite-overwrapped pressure vessels (COPVs) used to store helium to pressurize the stage’s propellant tanks. SpaceX redesigned those COPVs after a September 2016 pad explosion in order to meet NASA safety requirements for future commercial crew missions.
NASA requires SpaceX to perform at least seven launches with the redesigned COPVs before the agency will allow its astronauts to fly on the vehicle. Koenigsmann said he believed this was the second launch to use the redesigned COPVs, after the launch of the Es’hail-2 communications satellite Nov. 15.
SpaceX appears very unconcerned about getting those remaining five flights, which illustrates their expectation that 2019 will have a substantial number of launches in the first half of the year, prior to the tentative June launch date for the first manned Dragon mission.
The uncertainty of science: Using new computer models, two solar scientists are now predicting that the next solar cycle will begin in about a year and will see an increase in sunspot activity, compared to the weak cycle just ending.
Their ensemble forecast surprisingly suggests it could even be stronger than the cycle which is just ending. They expect the next cycle to start rising in about a year following the end of the current sunspot cycle minimum and peak in 2024. Bhowmik and Nandi predict space environmental conditions over the next decade would be similar or slightly harsher compared to the last decade. They find no evidence of an impending disappearance of sunspot cycles and thus conclude that speculations of an imminent Sun-induced cooling of global climate is very unlikely.
Their conclusion is different than other predictions that are claiming a weak next cycle, or even the beginning of a grand minimum, with no suspots at all. Since an real understanding of the sunspot cycle remains elusive, and all these predictions rely on computer models, it is hard to say which will be right. The advantage this particular prediction has is that their model appears able to match what has happened for the past 100 years.
Stay tuned.
An evening pause: May they both rest in peace.
Make sure you watch the guitarist in the background near the end, shaking his head in disbelief at what he is hearing.
Hat tip Mike Nelson.
Cool image time! This week the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) science team made available its monthly release of new images taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The image above is just a small cropped section from one of those new images, released under the name “Rocky Highlands.” The image on the right is a cropped and reduced section of the full photograph, with the white box indicating the small section above. If you click on either you can see the full resolution uncropped photograph and explore its complex and rough terrain.
What should immediately strike you looking at the small inset section above is the difficulty anyone is going to have traversing this country. There are no flat areas. Every inch seems to be a broken and shattered collection of ridges, pits, craters, or rippled dunes. And the inset above is only a tiny representation of the entire image, all of which shows the same kind of badlands.
This forbidding place is located in the southern highlands of Mars, north of Hellas Basin and south of the transition zone that drops down to the northern lowland plains. The white cross on the map below indicates the image location, with green representing the transition zone, blue the northern plains, and red/orange the southern highlands..
» Read more
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket today successfully launched a Dragon cargo capsule to ISS.
Unfortunately, a problem with the first stage had it fail to land on its target landing pad, instead landing in the ocean. This failure is the first in quite some time for a SpaceX first stage. It was the first failure however of their Block 5 first stages, which might impact the manned Dragon launch schedule set for this coming year.
The leaders in the 2018 launch race:
33 China
20 SpaceX
13 Russia
10 Europe (Arianespace)
8 ULA
This SpaceX launch was the 100th successful rocket launch for 2018, the first time the global rocket industry has reached the century figure since 1991, before the fall of the Soviet Union. As SpaceX’s 20th launch this year it sets a new record for launches by a private company. In fact, this total exceeds the average number of launches for the entire U.S. from 2001 to 2016, and clearly demonstrates how SpaceX has not only become the world’s dominate launch company, its effort to foster competition into the launch industry has served to energize it, for everyone.
In the national rankings, China continues to lead the U.S. 33 to 32.
Arianespace yesterday successfully placed a South Korean weather satellite and an Indian communications satellite into orbit using its Ariane 5 rocket.
The Indian satellite was initially supposed to launch in the spring, but ISRO pulled it back to India just after its arrival in French Guiana to do more checks on it because of the failure of another satellite using similar components.
The leaders in the 2018 launch race:
33 China
19 SpaceX
13 Russia
10 Europe (Arianespace)
8 ULA
Arianespace had predicted it would do 14 launches this year. As this launch is described as its last 2018 launch, it appears they have fallen short of that prediction.
These standings will be updated later today, assuming SpaceX’s Dragon launch to ISS goes off as scheduled.
The Senate Judiciary Committee has demanded the FBI answer some questions about its raid of a whistleblower’s home in November.
This is nice, but the reality is that, as far as I can tell, the FBI is now a rogue agency, working for the Democratic Party in defiance of the law, the Trump administration, and Congress. Consider for example the article’s closing paragraphs:
The raid on Cain’s house was permitted by a court order issued by federal magistrate Stephanie A. Gallagher in the U.S. District Court of Maryland for Baltimore. The court order and all the documents justifying the raid are sealed and not available for public viewing.
On Nov. 30, The Daily Caller News Foundation (DCNF) requested that Gallagher unseal the affidavit and any other documents that served to justify the raid. The court has not yet responded to the DCNF. The FBI did not respond to a request for comment. The IG declined to comment.
The weak response by the Trump administration to their behavior these last two years has taught them they can act with arrogance without fear. For example, why has Trump done nothing about this? He is by law (which in this case is the Constitution, the highest law in the land) entirely in charge of the FBI and what it does.
Link here. It is the 25th anniversary this week of the space shuttle mission that installed the two cameras that fixed the mirror issue on the Hubble Space Telescope, and the press release at the link provides a nice short overview of that mission, and what was involved to make it happen.
Of course, for a much more detailed look at this story, you could also buy and read A Universe in a Mirror. There are a lot of very fascinating stories that no single press release can possibly mention that I described with glee in writing this book.
Capitalism in space: In its launch on December 3, SpaceX was unable to catch either half of the Falcon 9’s fairings as they floated down by parachute. However, both halves were recovered, and the company plans to try to dry them out and reuse them.
The recovery ship, Mr. Steven, failed to catch either in its giant net. Since both fairings however landed gently in the ocean, and were quickly recovered, the article notes that SpaceX is now considering a change in its method of recover. The method of landing appears to have the fairing halves almost act like small boats, thus protecting the delicate equipment on their interiors. It appears they have increased their waterproofing, and may now only need to get them out of the water quickly to make then reusable.
Posted from the West Bank city of Modi’in Ilit.