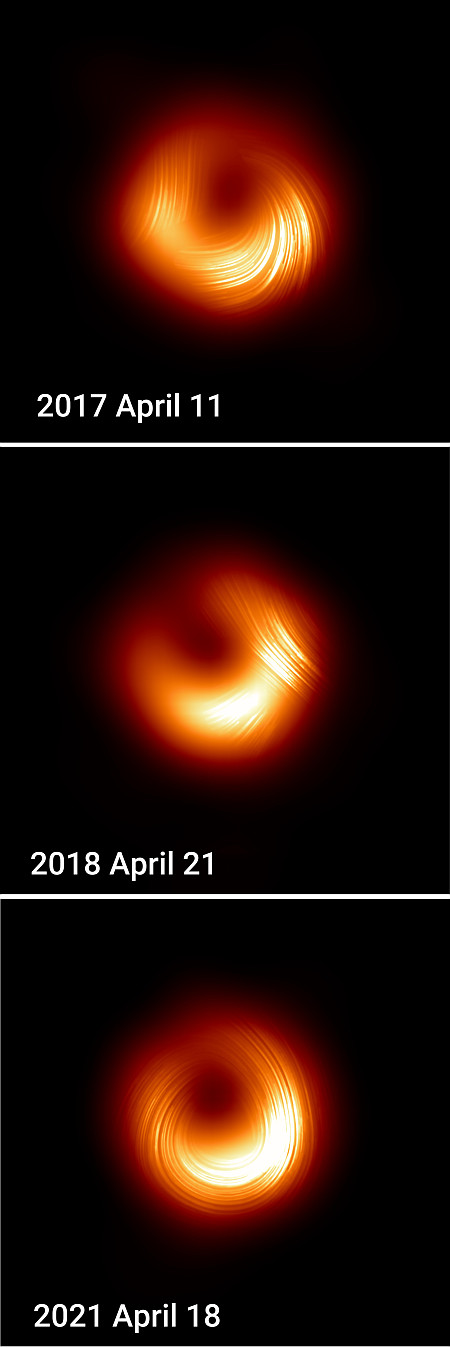
Avio wins U.S. launch contract for its Vega-C rocket
Capitalism in space: In what I think is a first, the Italian rocket company Avio has won a Vega-C launch contract without any participation from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) commercial division Arianespace.
The contract is also with an American company, SpaceLaunch, to put an “institutional Earth observation satellite” in orbit in 2027.
The significance of the deal is that Avio is now successfully marketing and selling its Vega-C rocket, without the middleman Arianespace taking a cut. As part of the shift of ESA and Europe to the capitalism model, whereby it no longer runs things but acts merely as a customer, it also freed Avio from the clutches of Arianespace. Previously, Avio built the rocket for that government agency, which then marketed and sold it to satellite companies. Avio had no control over profit or price. In fact, it didn’t really own its own rocket.
This absurd situation is now ending. There are still a handful of Vega-C launches that were contracted for under Arianespace, but after these Avio will be completely in charge. This deal, announced yesterday, is the beginning of that process.
Capitalism in space: In what I think is a first, the Italian rocket company Avio has won a Vega-C launch contract without any participation from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) commercial division Arianespace.
The contract is also with an American company, SpaceLaunch, to put an “institutional Earth observation satellite” in orbit in 2027.
The significance of the deal is that Avio is now successfully marketing and selling its Vega-C rocket, without the middleman Arianespace taking a cut. As part of the shift of ESA and Europe to the capitalism model, whereby it no longer runs things but acts merely as a customer, it also freed Avio from the clutches of Arianespace. Previously, Avio built the rocket for that government agency, which then marketed and sold it to satellite companies. Avio had no control over profit or price. In fact, it didn’t really own its own rocket.
This absurd situation is now ending. There are still a handful of Vega-C launches that were contracted for under Arianespace, but after these Avio will be completely in charge. This deal, announced yesterday, is the beginning of that process.