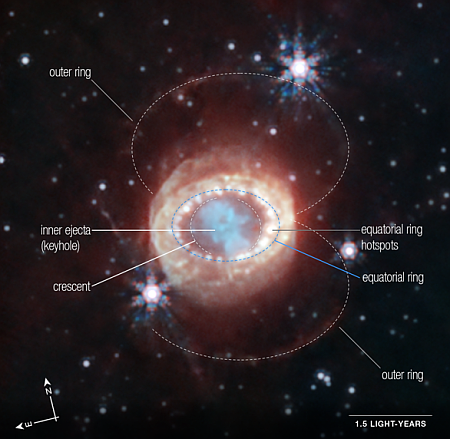
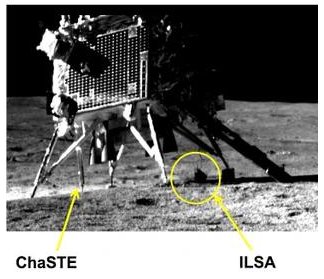
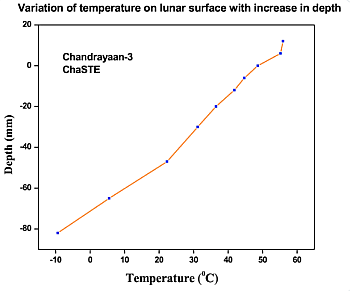
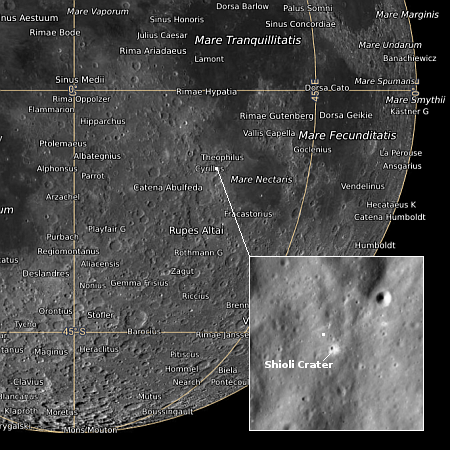
The splatter surrounding a mid-latitude Martian crater
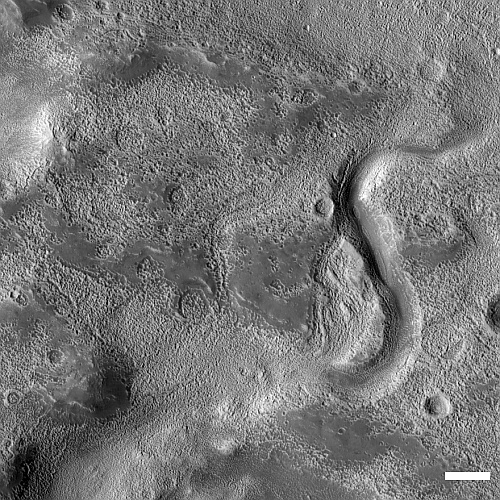
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on April 12, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what the scientists simply label as “Northern Mid-latitude Terrain”.
I have focused in on that meandering channel and the landscape around it. On Earth we would assume that channel marks the drainage of a river or stream, possibly also shaped by a glacier at some point because of its U-shaped profile. This guess is strengthened by the elevation data from MRO, which shows the channel descending to the southwest about 440 feet along its 2.2 mile length.
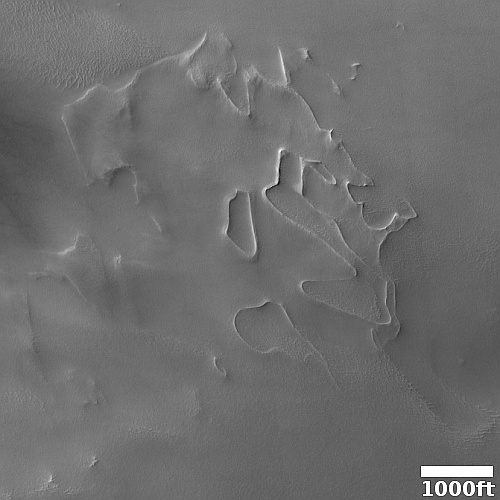
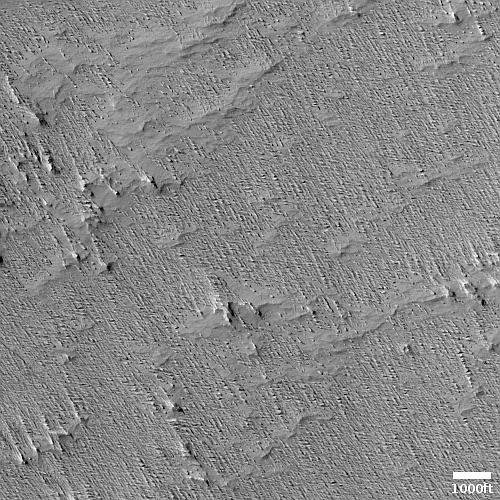
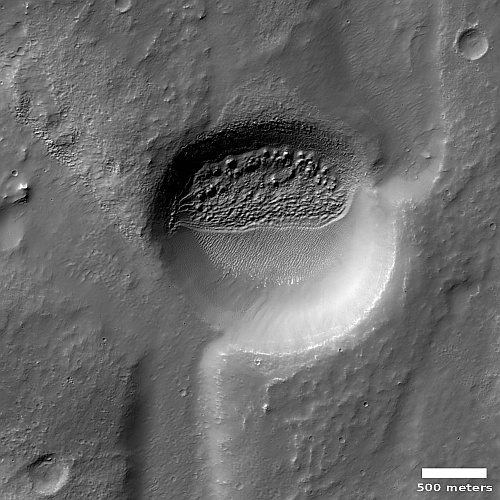
The channel and the eroded look of the surrounding terrain suggests strongly the presence of near-surface ice at this location, which is not unreasonable based on its 32 degree north latitude. The wider look below only adds further strength to this hypothesis, but also adds a lot more details explaining the genesis of this strange landscape.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on April 12, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what the scientists simply label as “Northern Mid-latitude Terrain”.
I have focused in on that meandering channel and the landscape around it. On Earth we would assume that channel marks the drainage of a river or stream, possibly also shaped by a glacier at some point because of its U-shaped profile. This guess is strengthened by the elevation data from MRO, which shows the channel descending to the southwest about 440 feet along its 2.2 mile length.
The channel and the eroded look of the surrounding terrain suggests strongly the presence of near-surface ice at this location, which is not unreasonable based on its 32 degree north latitude. The wider look below only adds further strength to this hypothesis, but also adds a lot more details explaining the genesis of this strange landscape.
» Read more