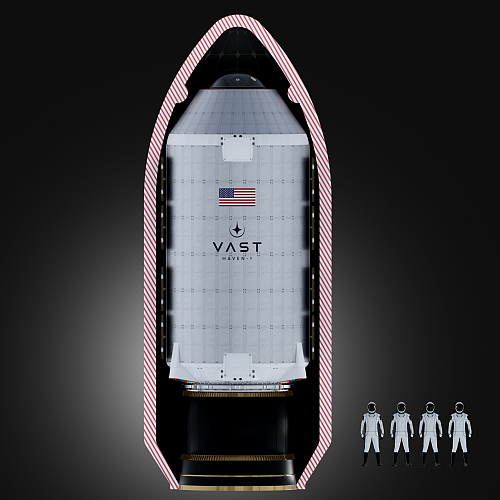
Another study suggests Saturn’s rings are young, much younger than the planet
Scientists using data from Cassini, which orbited Saturn from 2004 to 2017, have confirmed earlier research that said Saturn’s rings are much younger than the planet, only about 400 million years old.
From 2004 to 2017, the team used an instrument called the Cosmic Dust Analyzer aboard NASA’s late Cassini spacecraft to analyze specks of dust flying around Saturn. Over those 13 years, the researchers collected just 163 grains that had originated from beyond the planet’s close neighborhood. But it was enough. Based on their calculations, Saturn’s rings have likely been gathering dust for only a few hundred million years.
Though I cannot cite the earlier research, I distinctly remember a study from about a decade ago that posited the rings being young, only a few hundred million years old. This research confirms this conclusion, and likely firms up the theory considerably.
Scientists using data from Cassini, which orbited Saturn from 2004 to 2017, have confirmed earlier research that said Saturn’s rings are much younger than the planet, only about 400 million years old.
From 2004 to 2017, the team used an instrument called the Cosmic Dust Analyzer aboard NASA’s late Cassini spacecraft to analyze specks of dust flying around Saturn. Over those 13 years, the researchers collected just 163 grains that had originated from beyond the planet’s close neighborhood. But it was enough. Based on their calculations, Saturn’s rings have likely been gathering dust for only a few hundred million years.
Though I cannot cite the earlier research, I distinctly remember a study from about a decade ago that posited the rings being young, only a few hundred million years old. This research confirms this conclusion, and likely firms up the theory considerably.