The Yardbirds – Shapes of Things
An evening pause: Performed on French television in 1966. I suspect they are lip-synching to the record album, but the editing makes this hard to confirm.
Hat tip Diane Zimmerman.
An evening pause: Performed on French television in 1966. I suspect they are lip-synching to the record album, but the editing makes this hard to confirm.
Hat tip Diane Zimmerman.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News

Increasingly irrelevant in the right places
My headline reflects the sense of utter irrelevance of the FAA in announcing its approval of the launch licence for the tenth test launch of Starship/Superheavy (now scheduled for August 24, 2025) as well as its “closing” of its “investigation” into the failure during test flight nine.
As per the FAA in its statement, “There are no reports of public injury or damage to public property. The FAA oversaw and accepted the findings of the SpaceX-led investigation. The final mishap report cites the probable root cause for the loss of the Starship vehicle as a failure of a fuel component. SpaceX identified corrective actions to prevent a reoccurrence of the event.”
The FAA did not “oversee” SpaceX’s investigation. No one at the FAA has the slightest qualifications for doing so. All its bureaucrats did is sit in and watch, and when SpaceX’s engineers completed their work and “identified corrective actions,” the FAA paper-pushers pushed some paper to rubber stamp those conclusions.
Moreover, unlike during the Biden administration, the FAA did not waste any time or money retyping the SpaceX investigation. They simply approved it as is, and issued the launch license. And they apparently instantly agreed to the schedule proposed by SpaceX. In fact, it appears almost as if SpaceX announced the date before the FAA announced the license approval.
Elections matter. And they would matter less if we had had the sense in the past century to not cede so much power to an unelected federal bureaucracy that is really unfit to do the work we gave them. The goal now should be to take that power away from them, and to do it as quickly as it is humanely possible.
It appears at least when it comes to FAA launch licenses, Trump has made some significant progress towards this goal.
SpaceX today successfully placed another 24 Starlink satellites into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vanenberg in California.
The first stage completed its ninth flight, landing on a drone ship in the Pacific.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
101 SpaceX
46 China
11 Rocket Lab
9 Russia
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 101 to 79.
Now available in hardback and paperback as well as ebook!
From the press release: In this ground-breaking new history of early America, historian Robert Zimmerman not only exposes the lie behind The New York Times 1619 Project that falsely claims slavery is central to the history of the United States, he also provides profound lessons about the nature of human societies, lessons important for Americans today as well as for all future settlers on Mars and elsewhere in space.
“Zimmerman’s ground-breaking history provides every future generation the basic framework for establishing new societies on other worlds. We would be wise to heed what he says.” —Robert Zubrin, founder of the Mars Society.
All editions are available at Amazon, Barnes & Noble, and all book vendors, with the ebook priced at $5.99 before discount. All editions can also be purchased direct from the ebook publisher, ebookit, in which case you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
Autographed printed copies are also available at discount directly from the author (hardback $29.95; paperback $14.95; Shipping cost for either: $6.00). Just send an email to zimmerman @ nasw dot org.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, reduced and sharpened to post here, was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope as part of a survey of nineteen nearby galaxies. The galaxy, NGC 2835 and 35 million light years away, has been imaged many times in the past, but the new image contacts new wavelength data designed to identify nebulae. From the caption:
This image differs from previously released images because it incorporates new data from Hubble that captures a specific wavelength of red light called H-alpha. The regions that are bright in H-alpha emission can be seen along NGC 2835’s spiral arms, where dozens of bright pink nebulae appear like flowers in bloom. Astronomers are interested in H-alpha light because it signals the presence of several different types of nebulae that arise during different stages of a star’s life. Newborn massive stars create nebulae called H II regions that are particularly brilliant sources of H-alpha light, while dying stars can leave behind supernova remnants or planetary nebulae that can also be identified by their H-alpha emission.
Compare this image with the 2020 photo. The spiral arms are now alive with red and blue features not seen previously.
This survey hopes to find 50,000 nebula in the galaxies being observed.
The Kazakhstan government is now hoping to convert portions of its Baikonur spaceport not leased by Russia so that international rocket startups, or maybe its own commercial rocket startup, could launch from there.
While much of the site is still under Russian lease, Kazakhstan acquired the 100 km² Zenit launch site and assembly centre in 2018, and earlier this year took over the former “Gagarin” launch pad, which is now a tourist attraction. This opens the door for Astana [Kazakhstan’s capital] to negotiate directly with foreign operators.
… To give itself an edge and capitalise on the site’s potential, Kazakhstan plans to set up a special economic zone for “national space projects and foreign start-ups.” Kazakhstan’s Prime Minister Olzhas Bektenov has already confirmed talks with India’s Skyroot, China’s Deep Blue Aerospace, and several European firms. “We briefly discussed options for launch pads or joint grant applications,” confirmed Christian Schiemer, CEO of Germany’s HyImpulse. Other interested parties include Germany’s OHB and Rocket Factory Augsburg, as well as Airbus Defence & Space and Luxembourg’s SES.
China has also held talks about using Baikonur.
All of this however is very speculative, with sources expressing skepticism.
Kazakhstan however increasingly needs to do something to save Baikonur. At the moment the Russians have only one active launchpad, for its Soyuz-2 rocket. Two other launchpads for its Proton rocket are listed as active, but that rocket is largely retired. A fourth launchpad for Russia’s proposed new Soyuz-5 rocket remains unfinished, its future uncertain. With Russia increasingly shifting launches to its new Vostochny spaceport in the far east, it is very possible that it will eventually abandon Baikonur.
Kazakhstan has other reasons to make deals with foreign startups. Such deals will make it more independent from its untrustworthy neighbor to the north.
Leaving Earth: Space Stations, Rival Superpowers, and the Quest for Interplanetary Travel, can be purchased as an ebook everywhere for only $3.99 (before discount) at amazon, Barnes & Noble, all ebook vendors, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit.
If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big oppressive tech companies and I get a bigger cut much sooner.
"Leaving Earth is one of the best and certainly the most comprehensive summary of our drive into space that I have ever read. It will be invaluable to future scholars because it will tell them how the next chapter of human history opened." -- Arthur C. Clarke
The Japanese rocket startup Interstellar, which is being backed largely by Toyota, has announced that it has gotten five customer payloads for the first orbital launch of its Zero rocket.
This milestone mission will include cubesats from four organizations, Ocullospace, Wolfpack, Osaka Metropolitan University and Tokyo City University, and a fifth participant, DALRO Aerospace, that will supply the separation system for the universities’ cubesats. These 5 customers have already signed each a Launch Service Agreement with Interstellar. This launch highlights Interstellar’s growing global partnerships and commitment to expanding access to orbit.
These payloads are typical for a first launch. Three of these payloads are for educational institutions, while the remaining two are smallsat startups that have not launched yet, with one supported by the South Korean government. None have much money, so are willing to take the risk of a first launch.
As for when that first launch will take place, this is unclear. The company had previously targeted a launch in 2025, but based on the present status, this seems highly unlikely. The company itself was largely inactive from 2018 (when it did some suborbital test launches) until this year (when both Toyota and the Japanese government stepped in to provide financing). Expect it therefore to take time to get back into operation.
China today completed two launches using two different rockets from two different spaceports.
First, its Long March 4C rocket lifted off from its Xichang spaceport in southwest China, placing what its state-run press described as a satellite designed to do “space environment exploration and related technology tests,” No other information was released.
Next, its Long March 6A rocket lifted off from its Taiyuan spaceport in north China, placing the ninth set of Guowang satellites into orbit for a planned 13,000 constellation designed to compete with Starlink and Kuiper. This launch placed five satellites into orbit, bringing the total launched so far to 72.
In both cases, no word was released on where the rockets’ lower stages crashed inside China. This is especially significant for the Long March 4C rocket, which uses very toxic hypergolic fuels and lifted off from a spaceport much more inland than the Long March 6A.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
100 SpaceX
46 China
11 Rocket Lab
9 Russia
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 100 to 79.

Protest announcement. Click for original.
A Mexico activist group now plans to launch a fleet of boats that plan to violate the range and prevent the next Starship/Superheavy test launch.
A translated version of the protest announcement can be seen to the right. From the first link above:
A Mexican environmental group, Comité Global A.C., said it plans to protest the launch by sending boats into the Gulf of Mexico near Starbase. If they enter designated safety areas during the planned launch period, they could delay the mission.
The group’s leader said the Matamoros Port Authority gave permission for the protest dubbed “Operación Golfo de México.” It will also include protesters on Playa Bagdad, a Mexican beach just south of the Rio Grande where people often gather for Starship launches.
I have not yet gotten confirmation that the local port authority has approved this protest as the organization claims, but it also appears that this activist group intends to show up in boats regardless. If so, this protest could easily cause the next test launch, now scheduled for August 24, 2025, to be delayed endlessly.
It seems this is a matter for Trump and the Coast Guard. Someone must move in and remove these boats, arresting and fining the occupants for violating launch range restrictions that apply to all international waters.
Hat tip to reader Richard M.
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on July 4, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows the lower right quadrant of a five-mile-wide unnamed crater in the high northern mid-latitudes of Mars.
The science team in its label for this picture focuses on the gullies visible on the crater’s interior wall. To my Earth-bound eye, these gullies look like recent erosion caused by underground ice sublimating into gas, causing the surface to collapse downward into the crater. This however is a purely uneducated guess.
The floor of the crater however shows features that resemble glacial fill, seen in numerous high latitude craters on Mars. This is not surprising, as the crater is located at 59 degrees north latitude, close enough to the pole for there to be a lot of near surface ice to be present.
» Read more
The Space Force yesterday released a short press release, outlining its preparations and plans for the next X-37B mission, scheduled to launch on August 21, 2025.
The eighth mission of the X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle will launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, designated USSF-36, with a wide range of test and experimentation objectives. These will include demonstrations of high-bandwidth inter-satellite laser communications technologies and enhanced space navigation using the highest performing quantum inertial sensor in space.
Unfortunately, the military is no longer telling us which of its two X-37B’s is being launched. In fact, it is not clear whether both spacecraft are still operational. According to Wikipedia, this upcoming mission will be flown by the first of these vehicles, OTV-1, on its fourth flight. The other X-37B, OTV-2, has flown four times already, including the last mission of 434 days. I can find no confirmation of Wikipedia’s conclusions however.
Nonetheless, this spacecraft is one of the few projects built by Boeing in recent years that has done exactly what it was intended to do. If only Boeing’s other projects, such as Starliner, would run as smoothly.

Wants to be a dictator
As expected, the California Coastal Commission yesterday again rejected the proposed doubling of launches by SpaceX at the Vandenberg Space Force Base, from 50 to 100 launches per year, claiming this time it would destroy the environment.
“The sonic booms and their impacts on California’s people, wildlife and property are extremely concerning,” Commissioner Linda Escalante said at a hearing Thursday in Calabasas. “The negative impacts on public access, natural resources and environmental health warrant our scrutiny under California as a standard of review.”
The commissioners and its staff also argued that the launches were not related to national security or military purposes, but instead acted “to expand SpaceX’s commercial telecommunications network rather than serve federal agencies.” See the staff report [pdf] issued prior to the meeting.
The simple fact remains that it is a privately owned company engaged in activities primarily for its own commercial business. It is not a public federal agency or conducting its launches on
behalf of the federal government. It should therefore be regulated accordingly. [emphasis mine]
How dare SpaceX try to make a profit as a private company in America? And how dare the Space Force act as a servant of the people to provide this private company service? What have we come to?! Is communism and top-down authoritarian rule no longer America’s fundamental purpose?
Nor are the claims of the commission about the environment valid. » Read more
According to China’s state-run press, the Chinese pseudo-company Landspace experienced a failure yesterday during the launch of its Zhuque-2E rocket from the Jiuquan spaceport in northwest China.
A later update by the pseudo-company said the failure involved the rocket’s second stage, though little other information was provided.
In 2023 the Zhuque-2 rocket was the first to reach orbit using methane fuel, during the rocket’s second launch attempt. Overall it has launched six times, with two failures, on its first launch and yesterday.
Landspace hopes to launch its Zhuque-3 upgrade next year, designed to eventually land the first stage and reuse it. This failure could very well delay that plan.

Jared Isaacman has now proven he was
the wrong man for NASA administrator
In an op-ed posted today by Jared Isaacman and Newt Gingrich, the two men pushed the idea that NASA should lead a new “mini-Manhattan Project” to develop “nuclear-electric-powered spaceships” in order to conquer the heavens.
The President’s budget calls for an eventual pivot away from NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS)—leaving the heavy-lift rocket business to a capable commercial industry. That pivot should be toward something no other agency, organization, or company is capable of accomplishing: building a fleet of nuclear-electric-powered spaceships and extending America’s reach in the ultimate high ground of space.
The NASA centers, workforce, and contractors that manage, assemble, and test SLS are suited to take on this inspiring and necessary challenge. NASA Center at Michoud, for example, built landing craft during WWII, the Saturn V during the space race, the Space Shuttle, and the SLS. It is now waiting for the next logical evolution to ensure the competitiveness of our national space capabilities.
Oy. What piffle. » Read more
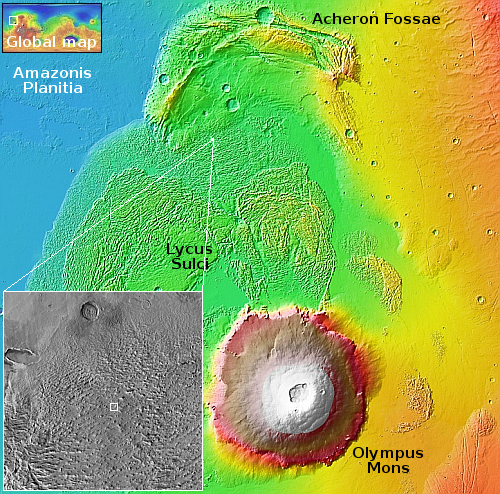
Today’s cool image revisits Lycus Sulci, the largest mountain range on Mars, about 1,400 mile wide and 1,800 miles long. The overview map to the right gives a sense of the roughness and chaotic nature of this region, extending north from Mars’ largest volcano, Olympus Mons.
At present scientists are unsure of the geology that formed Lycus Sulci, and how it is linked with Olympus Mons. The wide view to the right suggests it is the remains of a very ancient lava flow descending from the volcano that over time has become eroded to produce this wildly knobby terrain. That hypothesis remains unproven however. There is also evidence that the material here might instead be volcanic ash, deposited in many layers and eroded away with time.
The location of the cool image below is marked by the white dot, with the inset providing us a wider view of the surrounding terrain. Note the two craters to the north and west. Both appear to have been partly filled by flows coming from the south and east, respectively, adding weight to the theory that this region formed from lava flow.
» Read more
Even as leftist politicians and anti-Musk haters rage incoherently against SpaceX’s growing facility at Boca Chica, the company this week donated $4.4 million to upgrade the beach access and facilities at South Padre Island, near Starbase at Boca Chica.
Beachgoers visiting South Padre Island will soon be able to enjoy a surfside park with a smorgasbord of family-friendly amenities paid for by a $4.4 million contribution from Elon Musk’s SpaceX. Previously, MySA reported that the project was expected to cost $4.5 million, according to Texas Department of Licensing and Regulation records.
Cameron County Beach Access #3, a currently undeveloped pedestrian beach access located just outside the South Padre Island city limits, will soon begin construction on the latest phase of a multimillion-dollar improvement project that will transform it into a destination beach access. To that end, Cameron County leaders celebrated with a groundbreaking ceremony on Monday, August 11, at the access, located at 28495 State Park Road 100-North, on South Padre Island.
In other words, SpaceX is paying almost the entire bill for this work. It might now have the power to close these beaches when necessary, but it is also acting like a good citizen, improving those beaches for everyone when they are open.
It is expected this work will be completed by next year.
Scientists using the Webb Space Telescope have concluded that an Earth-sized exoplanet, orbiting the red dwarf star Trappist-1 in the habitable zone, does not appear to have an atmosphere, or if it does have one it is not like Earth’s.
The TRAPPIST-1 system is located 40 light-years away and was revealed as the record-holder for most Earth-sized rocky planets around a single star in 2017, thanks to data from NASA’s retired Spitzer Space Telescope and other observatories. Due to that star being a dim, relatively cold red dwarf, the “habitable zone” or “Goldilocks zone” – where the planet’s temperature may be just right, such that liquid surface water is possible – lies much closer to the star than in our solar system. TRAPPIST-1 d, the third planet from the red dwarf star, lies on the cusp of that temperate zone, yet its distance to its star is only 2 percent of Earth’s distance from the Sun. TRAPPIST-1 d completes an entire orbit around its star, its year, in only four Earth days.
Webb’s NIRSpec (Near-Infrared Spectrograph) instrument did not detect molecules from TRAPPIST-1 d that are common in Earth’s atmosphere, like water, methane, or carbon dioxide.
You can read the paper here [pdf].
The likelihood of life on this exoplanet has always been slim, simply because it orbits so close to the red dwarf, where it is vulnerable to the high energy flares the star periodically releases.
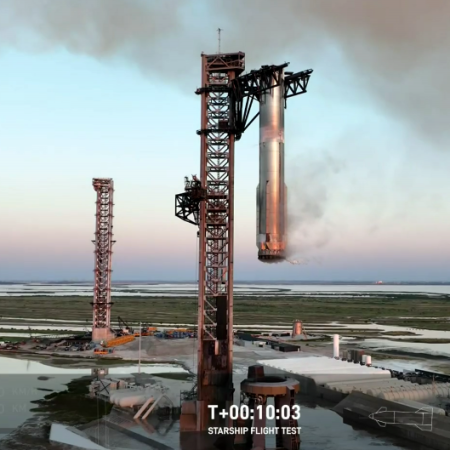

Superheavy after the October 2024 flight,
safely captured during the very first attempt
Link here.
SpaceX now appears to have completed the prelaunch testing of Starship prototype #37, having tested the ship again after swapping out an engine after the first static fire test. It is now moving to put Superheavy on the launchpad for its own static fire tests.
The bottom line is that SpaceX appears moving successfully towards a launch of the next test flight of Superheavy/Starship, its tenth, for sometime between August 22nd and August 28th.
The report also describes the company’s work to preserve Superheavy prototype #12, the first to be captured and recovered during the fifth orbital test flight in October 2024.
The picture to the right shows that Superheavy booster, hanging from the chopsticks just after it was captured.

Trump’s war with the swamp continues
Fight! Fight! Fight! In a new executive order issued yesterday, President Trump tasked NASA and the Transportation, Commerce, and Defense departments to work together to review and streamline the present regulations that have been hindering the American space industry for the past four years.
A summary of the order can be found here.
The order specifically tasks Transportation secretary Sean Duffy to review and streamline the regulations related to launches and re-entry, as well as the environmental requirements that were imposed during the Biden administration requiring numerous environment impact statements for practically any new project and even when an established project gets revised slightly. It has been these new rules that squashed the efforts of almost all the new American rocket companies during the Biden administration.
The order also demands that Commerce, Transportation, Defense, and NASA review the laws relating to coastal management that have allowed the states to block “spaceport infrastructure development.” All these agencies are also required to review their licensing rules to eliminate duplication while also eliminating rules that impede “novel space activities (missions not clearly or straightforwardly governed by existing regulatory frameworks).”
Finally, the order establishes a new position at the FAA but reporting directly to the Transportation secretary who will be expressly focused in following through on these regulatory reforms, with the primary goal to aid the commercial space industry.
While this order changes no specific regulations, it now forces the bureaucracy toward change, with deadlines set for action ranging from two to six months. Expect whole swathes of regulations and licensing requirements to disappear in the coming months. We might even see new rocket companies finally resume launches, something that ceased during the Biden years.
Having successfully completed two Starlink launches last night, putting a total of 52 satellites into orbit, SpaceX has now accomplished 100 successful orbital launches in 2025.
First, in the early evening last night the company launched 24 satellites from Vandenberg in California, its Falcon 9 rocket first stage completing its fifth flight, landing on a drone ship in the Pacific.
Seven hours later it placed another 28 Starlink satellites into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida. The first stage on this flight completed its tenth flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
100 SpaceX
44 China
11 Rocket Lab
9 Russia
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 100 to 77.
SpaceX’s launch rate has become so routine that it is important to note the truly amazing nature of its achievement. Until 2018, the entire world had trouble completing 100 launches in a year. In fact, prior to SpaceX’s arrival it only happened because the Soviet Union in the ’70s and ’80s launched many short term small reconnaissance satellites that only stayed in orbit for a few months. When the Soviet Union fell the launch rate fell below 100 and did not recover until SpaceX began increasing its launch rate.
In other words, this one American private company has fueled a renaissance in space exploration. And it has done so by being efficient, innovative, and most important of all, profitable. And it all happened under the banner of freedom.
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
An evening pause: From Peer Gynt, and performed by the Iceland Symphony Orchestra in 2019.
Hat tip Judd Clark.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.

The attitude of our modern press about science
A new study looking at 630 articles in popular press about the study of astrobiology (the possibility of life on other worlds) found that the press frequently exaggerated the findings, often taking relatively minor results that only vaguely and with great uncertainty suggested the presence of biology to speculate wildly that life had been found.
The research also found that university public relations departments tended to encourage this behavior with their own speculations in press releases. From the paper’s abstract:
Findings reveal that speculations and promises/expectations are more frequent in news articles and press releases compared to academic papers. Speculations about conditions for life and the existence of life beyond Earth are common, particularly in news articles covering exoplanet research, while promises of life detection are rare. Press releases tend to emphasize the significance of research findings and the progress of the field. Speculations and promises/expectations in news articles often occur without attribution to scientists and in quotes of authors of the studies, and slightly less so in quotes of outside experts. [emphasis mine]
The study looked at articles from the New York Times in the U.S., the Guardian in the United Kingdom, Folha and Estadão in Brazil, Público in Portugal, and El País in Spain. It consistently found these news sources consistently exaggerated the discoveries, often speculating with little evidence that the research had found evidence of life.
This paper merely confirms what I have reported repeatedly in the past few years. When scientists report that they may have detected a molecule in Venus’s atmosphere that on Earth is associated with life, the press immediately screams “Life found on Venus!” Or if scientists detect with great uncertainty similar life-related molecules in an exoplanet’s atmosphere and gently suggest it might mean life, the press screams “Exoplanet has life!”
In both these examples the research was very uncertain, and in both later research failed to confirm these conclusions.
Sadly this pattern now applies to almost every scientific result. Uncertain results based not even on observations but on theories are routinely touted these days by both press departments and news outlets as big discoveries, even if they are only describing uncertain theories that may prove true.
In fact, words like “may”, “might,” or “could” in headlines are always a give-away. They tell you that the story is not about an actual discovery, but a speculation that remains unproven. Such stories rarely get linked to here at Behind the Black, and if I do link to them, I spend a lot of time noting the uncertainties and weakness of the research.
If only all news outlets did the same.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on April 24, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), and was posted yesterday by the science team to illustrate the vast lava flows that cover much of Mars. From the caption:
This image captures the edge of a lava flow that partially buries older terrain in the Martian Southern Highlands. Where the edge of the lava flow made contact with the higher-standing topography, it formed a rumpled and ridged surface.
This lava flow is one of many massive flows that extend southwest from Arsia Mons, one of the largest shield volcanoes on Mars.
The mountain to the south rises about 3,700 feet above that rumpled lava ocean at its base.
» Read more
Access to SpaceX’s Starlink internet constellation to customers worldwide continues to expand.
First. Kazakhstan announced that Starlink is now available in that country, beginning today.
Next, the Ukraine government announced it is beginning beta testing of SpaceX’s direct-to-phone Starlink capability, with the product to launch to its citizens later this year.
With Starlink’s Direct to Cell system, Ukrainians will be able to send SMS messages in remote or hard-to-reach areas—such as in the mountains, during severe weather, or blackouts—without the need for expensive satellite equipment. The only requirements: a standard 4G smartphone with a SIM or eSIM card, and a clear view of the sky.
These actions by both Kazakhstan and the Ukraine underlines the negative consequences of Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine. Its former Soviet provinces, now independent, have become much more willing to forge alliances and deals with western nations and companies, in order to better protect themselves from possible attack.
In Lebanon however things have not gone so well. SpaceX’s request to offer Starlink has met with opposition in that nation’s parliament.
Lebanon’s parliamentary Media and Communications Committee raised serious legal and procedural concerns over a proposed license for SpaceX’s Starlink satellite internet service. Committee chair MP Ibrahim Mousawi and rapporteur MP Yassine Yassine said discussions with the telecom minister and officials from regulatory and oversight bodies revealed “major constitutional and legal violations.” These include bypassing Parliament’s authority to grant natural resource concessions, ignoring public procurement laws, sidelining the Telecommunications Regulatory Authority, and failing to ensure data sovereignty.
The committee recommended against Starlink, demanding a new and expanded review of the proposal. I suspect these ministers are either upset because they didn’t get their own kickbacks in the deal, or are worried that giving Lebanese citizens Starlink — thus bypassing all government censorship — might threaten their hold on power.