Will Dawn head to another asteroid?
NASA is still reviewing the proposal by the Dawn science team that they send the spacecraft to another asteroid in its last years before its fuel runs out.
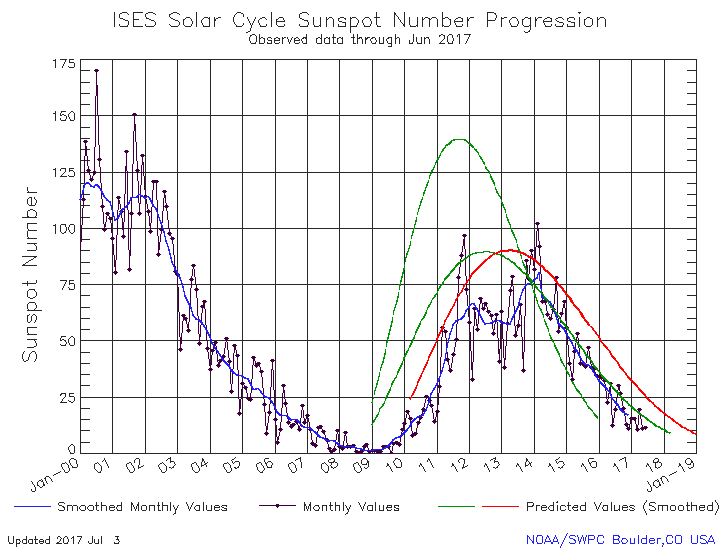
The spacecraft has continued operations despite problems with its reaction wheels, used for attitude control. After suffering the loss of two of its four reaction wheels earlier in the mission, a third wheel malfunctioned in April. The spacecraft went into safe mode briefly, but controllers resumed operations with hydrazine thrusters taking over for the failed wheel. That failure will eventually lead to the end of the mission when the spacecraft runs out of hydrazine. “It does reduce our lifetime because we have to use hydrazine at a faster rate,” Raymond said at the SBAG meeting in June.
That lifetime, she said, is dependent on the spacecraft’s orbital altitude. Dawn has spiraled out to a higher orbit during its extended mission, which reduces the amount of hydrazine needed for attitude control. “The lifetime is now highly dependent on orbital altitude because we need to use the jets to fight the gravity gradient torques,” she said. In its current high orbit, Raymond said that Dawn had sufficient hydrazine, as well as xenon propellant used for the ion engine, to operate at least through the end of 2018.
NASA is still reviewing the proposal by the Dawn science team that they send the spacecraft to another asteroid in its last years before its fuel runs out.
The spacecraft has continued operations despite problems with its reaction wheels, used for attitude control. After suffering the loss of two of its four reaction wheels earlier in the mission, a third wheel malfunctioned in April. The spacecraft went into safe mode briefly, but controllers resumed operations with hydrazine thrusters taking over for the failed wheel. That failure will eventually lead to the end of the mission when the spacecraft runs out of hydrazine. “It does reduce our lifetime because we have to use hydrazine at a faster rate,” Raymond said at the SBAG meeting in June.
That lifetime, she said, is dependent on the spacecraft’s orbital altitude. Dawn has spiraled out to a higher orbit during its extended mission, which reduces the amount of hydrazine needed for attitude control. “The lifetime is now highly dependent on orbital altitude because we need to use the jets to fight the gravity gradient torques,” she said. In its current high orbit, Raymond said that Dawn had sufficient hydrazine, as well as xenon propellant used for the ion engine, to operate at least through the end of 2018.