Engineers have shut down the Gehrels-Swift space telescope in a last attempt to save it

Katalyst’s proposed Swift rescue mission.
Click for original image.
In order to delay the moment the orbit of the Gehrels-Swift Observatory decays — to increase the chance a rescue mission can get there in time — engineers have now stopped almost all scientific observations temporarily.
On Feb. 11, NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory temporarily suspended most science operations in an effort to reduce atmospheric drag and slow the spacecraft’s orbital decay. Halting these activities will enable controllers to keep the spacecraft in an orientation that minimizes drag effects, extending its time in orbit in anticipation of a reboost mission.
“Normally, Swift quickly turns to view its targets — especially the fleeting, almost daily explosions called gamma-ray bursts — with multiple telescopes,” said principal investigator S. Bradley Cenko at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “Swift’s Burst Alert Telescope will continue to detect gamma-ray bursts, but the spacecraft will no longer slew to observe targets with its other telescopes.”
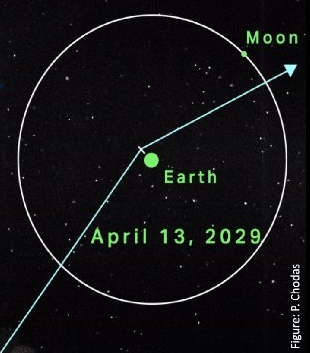
…To maximize the orbit boost’s chances of success, Swift’s average altitude needs to be above about 185 miles. As of early February, Swift’s average altitude had fallen below about 250 miles.
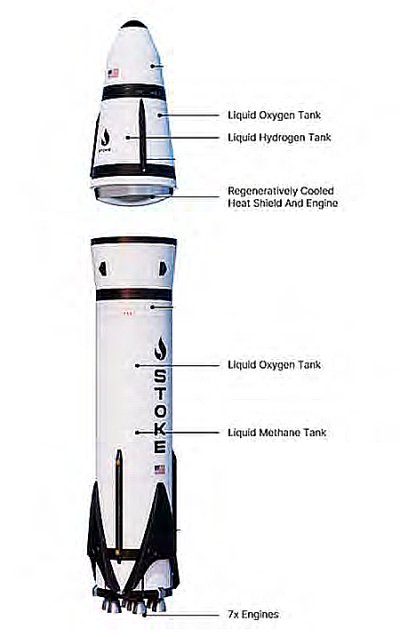
NASA has awarded the orbital repair startup Katalyst the contract to rescue Gehrels-Swift, but the company has a very challenging mission. It got the contract only a few months ago, in September 2025, and is refitting its planned satellite rescue demo mission to save the space telescope instead. The graphic to the right shows how its rescue robot will approach and grab Gehrels-Swift to raise its orbit, but it must be noted that the telescope has no planned grapple points, and Katalyst’s robot has never done this before.
Moreover, the robot will be launched using the last Pegasus rocket in Northrop Grumman’s warehouse, with a launch scheduled now for sometime this summer. That means Katalyst has had to go from contract award to launch in less than a year, a pace that up until now has been unheard of in the space business. If successful however Katalyst will once again demonstrate the benefits of the capitalism model, whereby NASA buys the product from the private sector rather than building it itself. Left to NASA, this rescue mission would never happen.
And even if Katalyst’s rescue fails, that the company could get it built and launched in such a short time still proves the value of the capitalism model. Freedom and capitalism and competition at least made the attempt possible.

Katalyst’s proposed Swift rescue mission.
Click for original image.
In order to delay the moment the orbit of the Gehrels-Swift Observatory decays — to increase the chance a rescue mission can get there in time — engineers have now stopped almost all scientific observations temporarily.
On Feb. 11, NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory temporarily suspended most science operations in an effort to reduce atmospheric drag and slow the spacecraft’s orbital decay. Halting these activities will enable controllers to keep the spacecraft in an orientation that minimizes drag effects, extending its time in orbit in anticipation of a reboost mission.
“Normally, Swift quickly turns to view its targets — especially the fleeting, almost daily explosions called gamma-ray bursts — with multiple telescopes,” said principal investigator S. Bradley Cenko at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “Swift’s Burst Alert Telescope will continue to detect gamma-ray bursts, but the spacecraft will no longer slew to observe targets with its other telescopes.”
…To maximize the orbit boost’s chances of success, Swift’s average altitude needs to be above about 185 miles. As of early February, Swift’s average altitude had fallen below about 250 miles.
NASA has awarded the orbital repair startup Katalyst the contract to rescue Gehrels-Swift, but the company has a very challenging mission. It got the contract only a few months ago, in September 2025, and is refitting its planned satellite rescue demo mission to save the space telescope instead. The graphic to the right shows how its rescue robot will approach and grab Gehrels-Swift to raise its orbit, but it must be noted that the telescope has no planned grapple points, and Katalyst’s robot has never done this before.
Moreover, the robot will be launched using the last Pegasus rocket in Northrop Grumman’s warehouse, with a launch scheduled now for sometime this summer. That means Katalyst has had to go from contract award to launch in less than a year, a pace that up until now has been unheard of in the space business. If successful however Katalyst will once again demonstrate the benefits of the capitalism model, whereby NASA buys the product from the private sector rather than building it itself. Left to NASA, this rescue mission would never happen.
And even if Katalyst’s rescue fails, that the company could get it built and launched in such a short time still proves the value of the capitalism model. Freedom and capitalism and competition at least made the attempt possible.