Canadian rocket startup Nordspace signs deal for its mission control center

Proposed Canadian spaceports
The Canadian rocket startup Nordspace, which earlier this week signed a deal for another company to establish ground stations for its proposed Atlantic Spaceport, today signed an agreement with the company Kongsberg Geospatial to provide software for running its mission control center.
According to the news release TerraLens “will ingest data from multiple sensors to deliver real-time three-dimensional (3D) visualization of launch operations, range safety, decision support, and vehicle tracking. This will help streamline launch operations and enable deployment of critical space missions to orbit in under 48 hours.” Kongsberg said TerraLens builds on their “experience supporting range safety and mission-critical visualization for the Andøya Space and Defence project in Norway.”
Andøya is Norway’s new commercial spaceport that has been launching suborbital government rockets for decades.
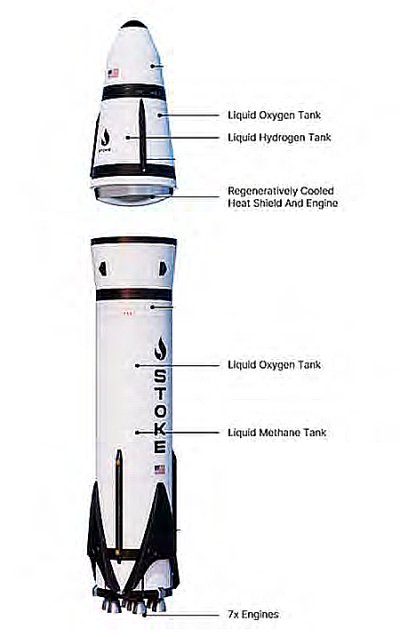
Nordspace continues to move forward quickly, having been established only three years ago. It is putting the pieces together for its spaceport, and is testing both a small suborbital rocket and the engines for its proposed orbital Tundra rocket. Though the race is certainly not over, it does appear Nordspace will get to orbit ahead of the Nova Scotia spaceport that was first proposed in 2016.

Proposed Canadian spaceports
The Canadian rocket startup Nordspace, which earlier this week signed a deal for another company to establish ground stations for its proposed Atlantic Spaceport, today signed an agreement with the company Kongsberg Geospatial to provide software for running its mission control center.
According to the news release TerraLens “will ingest data from multiple sensors to deliver real-time three-dimensional (3D) visualization of launch operations, range safety, decision support, and vehicle tracking. This will help streamline launch operations and enable deployment of critical space missions to orbit in under 48 hours.” Kongsberg said TerraLens builds on their “experience supporting range safety and mission-critical visualization for the Andøya Space and Defence project in Norway.”
Andøya is Norway’s new commercial spaceport that has been launching suborbital government rockets for decades.
Nordspace continues to move forward quickly, having been established only three years ago. It is putting the pieces together for its spaceport, and is testing both a small suborbital rocket and the engines for its proposed orbital Tundra rocket. Though the race is certainly not over, it does appear Nordspace will get to orbit ahead of the Nova Scotia spaceport that was first proposed in 2016.