Worldview balloon completes 16-day flight
Capitalism in space: Worldview has successfully completed a sixteen day flight of its Stratollite high altitude balloon.
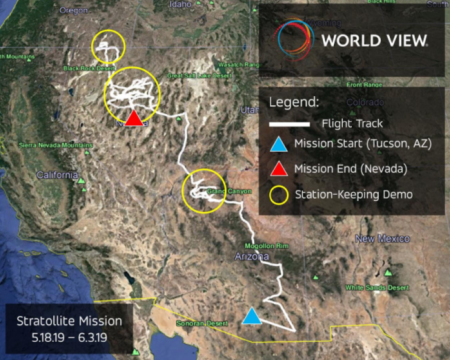
The map on the right is from their press release [pdf]. From the first link above:
During the 16-day flight, World View was able to spend up to eight days total in an area about 75 miles wide. It also demonstrated more precise station-keeping, says Hartman, by spending 55 straight hours in a region 62 miles wide and also 6.5 hours in an area a little less than 6 miles wide.
Staying within such a small area is crucial for the Stratollite system, as that capability could be useful for a number of different applications for customers, according to Hartman. He notes that such a system above Earth could be used by the military to aid certain missions operations, or the Stratollite could help monitor natural disasters like tornadoes and hurricanes, and help with disaster relief. “There’s just all kinds of very important use cases when we can provide a station keeping capability in an area as small as a [6-mile] diameter area,” says Hartman.
Throughout this flight, the Stratollite covered a distance of 3,000 miles, making its way to the Grand Canyon, Nevada, Oregon, and Utah. Once the World View team decided to bring the Stratollite back down to Earth, the company was able to land it within 400 feet of a targeted area in the Nevada desert where the vehicle was then recovered. World View even hopes to fly some of the components from this flight on an upcoming mission.
The company’s goal these days is not space tourism, but ground observations, and this flight is certainly a solid proof that they are getting close to achieving that goal.

Capitalism in space: Worldview has successfully completed a sixteen day flight of its Stratollite high altitude balloon.
The map on the right is from their press release [pdf]. From the first link above:
During the 16-day flight, World View was able to spend up to eight days total in an area about 75 miles wide. It also demonstrated more precise station-keeping, says Hartman, by spending 55 straight hours in a region 62 miles wide and also 6.5 hours in an area a little less than 6 miles wide.
Staying within such a small area is crucial for the Stratollite system, as that capability could be useful for a number of different applications for customers, according to Hartman. He notes that such a system above Earth could be used by the military to aid certain missions operations, or the Stratollite could help monitor natural disasters like tornadoes and hurricanes, and help with disaster relief. “There’s just all kinds of very important use cases when we can provide a station keeping capability in an area as small as a [6-mile] diameter area,” says Hartman.
Throughout this flight, the Stratollite covered a distance of 3,000 miles, making its way to the Grand Canyon, Nevada, Oregon, and Utah. Once the World View team decided to bring the Stratollite back down to Earth, the company was able to land it within 400 feet of a targeted area in the Nevada desert where the vehicle was then recovered. World View even hopes to fly some of the components from this flight on an upcoming mission.
The company’s goal these days is not space tourism, but ground observations, and this flight is certainly a solid proof that they are getting close to achieving that goal.
