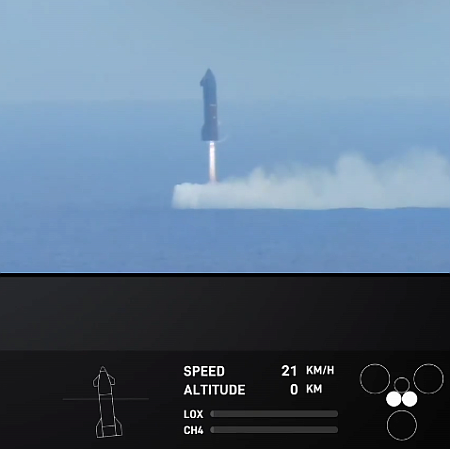
Musk: Starship will likely attempt a chopstick landing on the eighth test launch
UPDATE: The original post below is incorrect. I misread Musk’s tweet, not realizing he was refering exclusively to Starship when he wrote “ship.” He and his company now routinely use “ship” to refer to Starship and “booster” for Superheavy.
The real story behind this tweet is that SpaceX is working to attempt a chopstick catch of both Superheavy and Starship on the eighth test flight, after the as-yet unscheduled seventh flight. This means the eighth flight of Starship will be a full orbital flight, will use its Raptor engines to do a de-orbit burn to bring it back to Boca Chica, and that the company expects to have two launchpad towers ready to make the two catches.
Won’t that be an exciting event?
Original incorrect post:
———————————–
According to a tweet by Elon Musk on November 19, 2024, SpaceX will not attempt a chopstick landing of Superheavy on the seventh test orbital launch of Starship/Superheavy.
We will do one more ocean landing of the ship. If that goes well, then SpaceX will attempt to catch the ship with the tower.
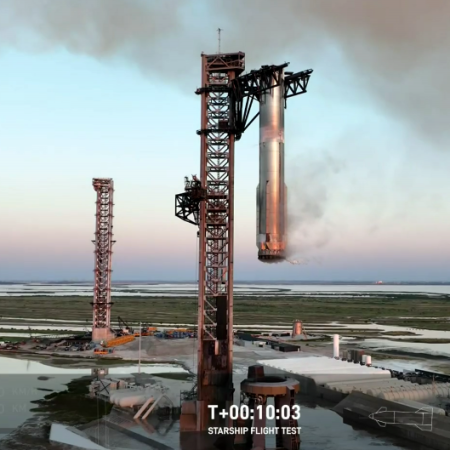
According to an update on the SpaceX website, the decision to abort the chopstick landing during this week’s sixth test flight was made because of issues at the launch tower:
Following a nominal ascent and stage separation, the booster successfully transitioned to its boostback burn to begin the return to launch site. During this phase, automated health checks of critical hardware on the launch and catch tower triggered an abort of the catch attempt. The booster then executed a pre-planned divert maneuver, performing a landing burn and soft splashdown in the Gulf of Mexico.
At this moment SpaceX has not provided any additional information on what those issues at the tower were, and might never do so since this is proprietary information. Nonetheless, it could be that more work is necessary to make sure the tower is healthy after launch, which is why they won’t attempt a chopstick landing next time.
As for when that seventh test flight will occur, we as yet have no word. The timing is going to depend on many factors, including the need for upgrades, the final flight plan decision, any changes then required to SpaceX’s FAA launch license, and finally the impact the new Trump administration will have on that red tape.
UPDATE: The original post below is incorrect. I misread Musk’s tweet, not realizing he was refering exclusively to Starship when he wrote “ship.” He and his company now routinely use “ship” to refer to Starship and “booster” for Superheavy.
The real story behind this tweet is that SpaceX is working to attempt a chopstick catch of both Superheavy and Starship on the eighth test flight, after the as-yet unscheduled seventh flight. This means the eighth flight of Starship will be a full orbital flight, will use its Raptor engines to do a de-orbit burn to bring it back to Boca Chica, and that the company expects to have two launchpad towers ready to make the two catches.
Won’t that be an exciting event?
Original incorrect post:
———————————–
According to a tweet by Elon Musk on November 19, 2024, SpaceX will not attempt a chopstick landing of Superheavy on the seventh test orbital launch of Starship/Superheavy.
We will do one more ocean landing of the ship. If that goes well, then SpaceX will attempt to catch the ship with the tower.
According to an update on the SpaceX website, the decision to abort the chopstick landing during this week’s sixth test flight was made because of issues at the launch tower:
Following a nominal ascent and stage separation, the booster successfully transitioned to its boostback burn to begin the return to launch site. During this phase, automated health checks of critical hardware on the launch and catch tower triggered an abort of the catch attempt. The booster then executed a pre-planned divert maneuver, performing a landing burn and soft splashdown in the Gulf of Mexico.
At this moment SpaceX has not provided any additional information on what those issues at the tower were, and might never do so since this is proprietary information. Nonetheless, it could be that more work is necessary to make sure the tower is healthy after launch, which is why they won’t attempt a chopstick landing next time.
As for when that seventh test flight will occur, we as yet have no word. The timing is going to depend on many factors, including the need for upgrades, the final flight plan decision, any changes then required to SpaceX’s FAA launch license, and finally the impact the new Trump administration will have on that red tape.